Thesis
Organizations across all industries have been ramping up their AI adoption, with 56% of global enterprises implementing AI for at least one business function in 2021. However, more than 80% of all machine learning (ML) and AI projects never make it to production and stall before deployment. Often, this is due to poor data quality and a lack of cohesive ML strategy.
DataRobot is a ‘pick and shovel’ AI platform that enables enterprises to build, deploy, monitor, and manage ML models. It enables data scientists as well as non-technical or novice business analysts to automate all the time-consuming model development tasks — from data cleaning to deployment — in a process known as automated machine learning (AutoML) that allows users to speed up the time it takes to build operational models.
DataRobot provides an AI platform that automates and accelerates the machine learning lifecycle, from data preparation and model training to deployment and monitoring. It is designed to make AI accessible to everyone regardless of their technical expertise. DataRobot’s turnkey, out-of-the-box ML solutions are designed to enable business decision-makers, data analysts, data scientists, and engineers to reduce underlying complexities and put models into production more quickly.
Founding Story
DataRobot was co-founded by Jeremy Achin (former CEO) and Tom DeGodoy (former CTO) in 2012. While working at Travelers Insurance, the pair became convinced that there was a supply-and-demand problem in data science. They believed that there were not enough skilled data scientists to meet the ever-increasing demand as organizations of all sizes tapped into their data to generate actionable insights. This insight led them to establish DataRobot as an AutoML tool that enables expert data scientists, ML engineers, and analysts who may or may not have prior ML knowledge to build predictive models at a faster pace.
In March 2021, Achin and DeGodoy both left their positions as the CEO and CTO, respectively, with Achin replaced as CEO by then-COO Dan Wright. However, Wright was forced to resign in July 2022 after he and four other top executives were accused of selling $32 million worth of stock after working in the company for only one and a half years or less. During the same time, longtime employees could not cash out their shares. Debanjan Saha, a former Google Cloud executive, was appointed as the permanent CEO in July 2022 after serving as the President and COO.
Product
In a traditional ML project setting, a data science team consists of different personas such as data analysts, data engineers, and data scientists who are tasked with manually preparing data, and training predictive models before they are deployed. The whole process can take weeks to complete and requires expertise in programming languages and statistical and domain knowledge.
DataRobot’s product focuses on adding efficiency to that development process. Analysts with limited ML knowledge can upload data to DataRobot’s platform and select the target variables they want to forecast. DataRobot can train dozens of models, systematically compare them, and select the best model for the particular business need. Users can then deploy their models through a single line of API code and integrate the models into applications and business processes.
In March 2023, DataRobot announced its new AI Platform 9.0 — a lifecycle platform built for predictive and generative AI with broad ecosystem interoperability.
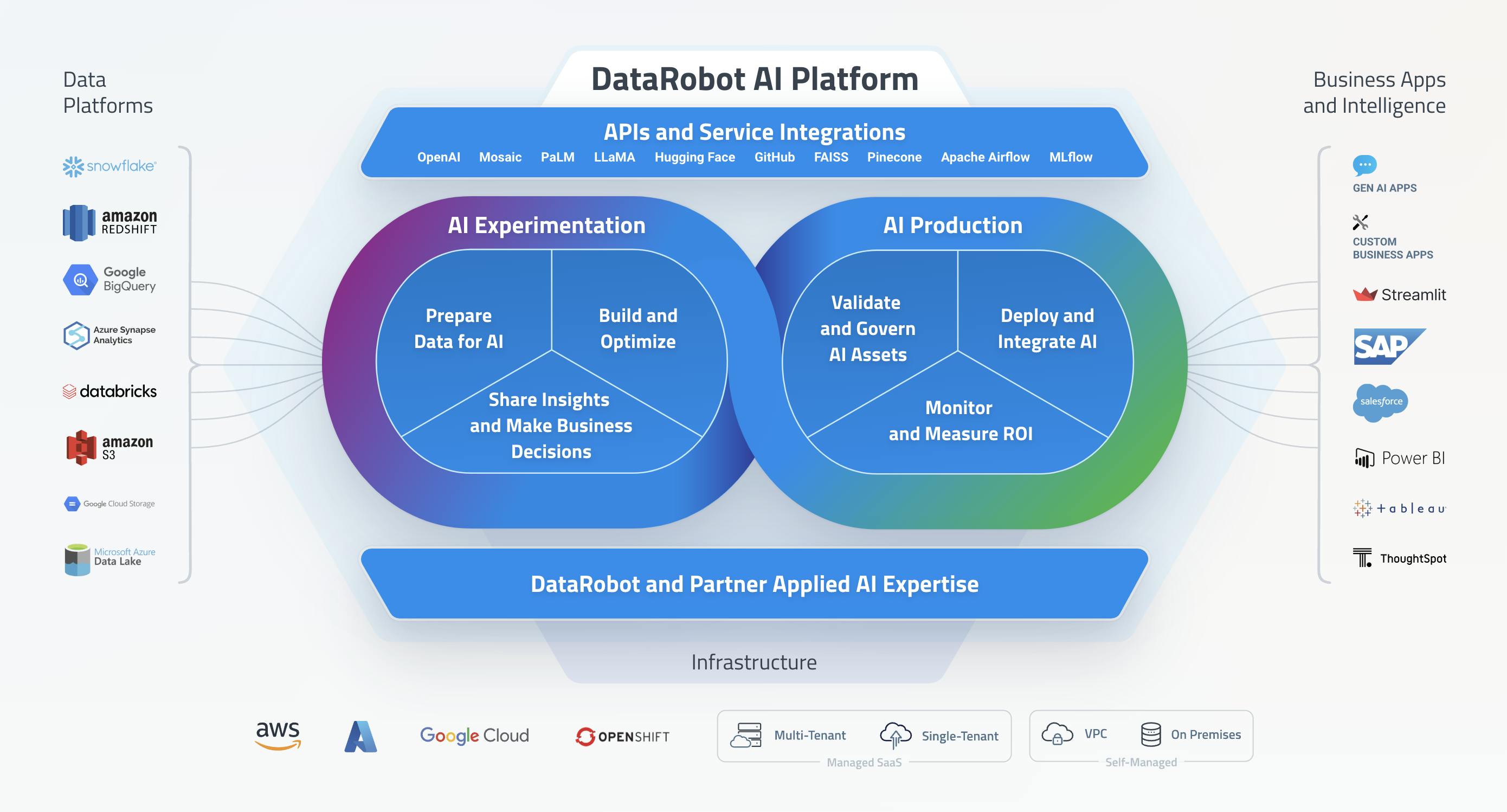
Source: DataRobot
The platform centers around several modules:
AI Experimentation: Experiment with multiple AI problem framings, identify key drivers, and build precise models that drive impact.
AI Production: Manage, scale, and govern generative and predictive AI assets, in a a centralized control and command center.
Platform Deployment: Integrations can unify data warehouses, APIs, workflow tooling, BI tools, and business apps with the DataRobot AI Platform with a flexible delivery model.
AI Experimentation
Data Preparation
DataRobot offers data preparation solutions that enable users to explore, profile, combine, clean, pre-process, and set up datasets for ML at an accelerated pace. Specifically, it allows users to analyze, and transform structured data directly from Snowflake with security, compliance, or financial controls. It also offers AI assistance that provides recommendations and guidance for standardizing categorical variables in datasets. Further, DataRobot Data Preparation provides users with data governance tools to securely manage and track data transparency.
Source: DataRobot
Build and Optimize
DataRobot AI Platform helps customers experiment with generative and predictive AI use cases. It provides out-of-the-box capabilities for a code-free or code-first approach and supports a wide range of data types including location, text, documents, and images. Data scientists can now collaborate with low-code users to build models for their business use cases.
Source: DataRobot
Share Insights and Make Decisions
DataRobot aims to help users improve communication and collaboration between business stakeholders and data scientists. It provides features and deep model insights to help users explain topics ranging from AI outcomes, and why a model made a decision, to producing activation maps, image embeddings, data slices, and cluster insights. Users can go beyond insights to make business decisions, simultaneously analyzing tradeoffs on what should be adjusted or improved.
Source: DataRobot
AI Production
Validate and Govern AI Assets
DataRobot allows customers to standardize and scale governance across its AI assets and ensure all are managed to the standard. Users can bring approval workflows and audit ability to their models across all cloud environments. DataRobot AI Production unifies policies providing the same roles, governance, and object structure to help customers manage its model inventory.
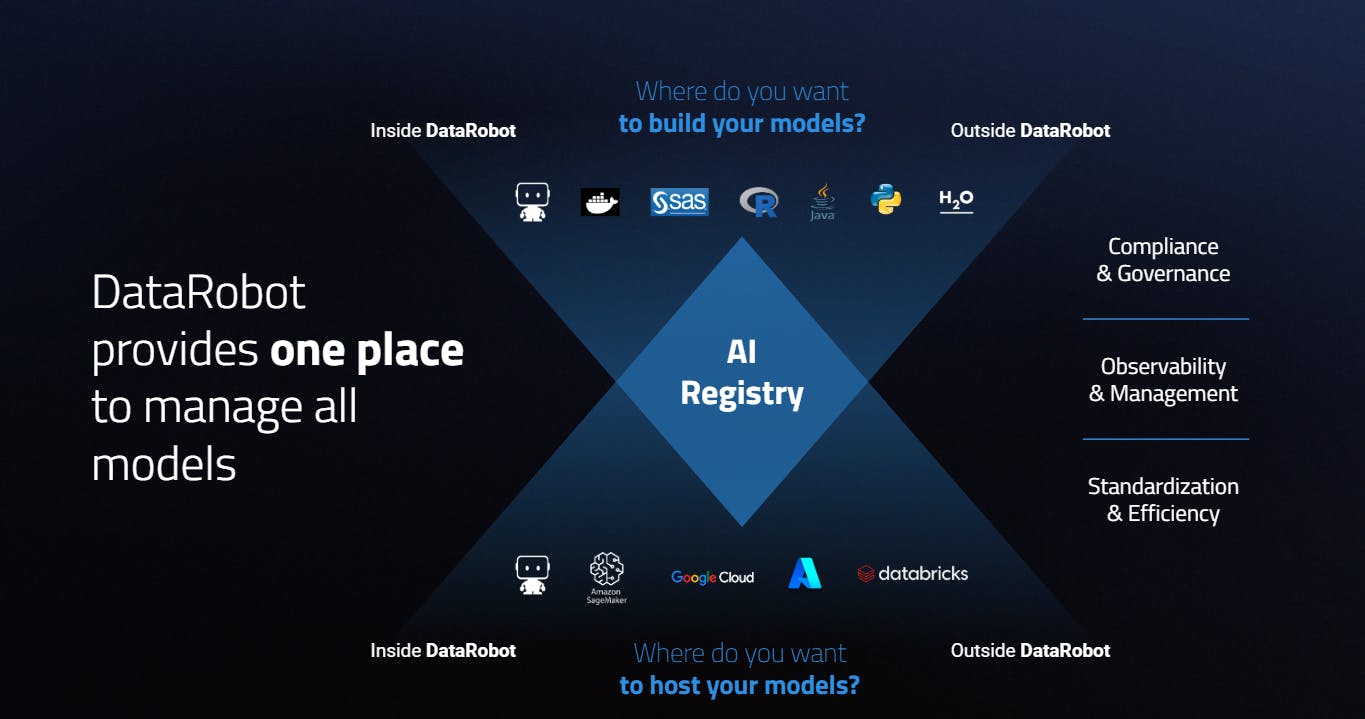
Source: Datarobot
Deploy and Integrate AI
DataRobot provides end-to-end capabilities to help customers deploy generative AI and predictive AI into custom applications at a faster pace. It also helps customers integrate AI into their business tools and processes and helps manage hundreds of models. The company’s integrations enable automatic deployment to cloud environments such as Microsoft Azure, Snowflake, AWS, GCP, on-premises, or edge devices.
Source: DataRobot
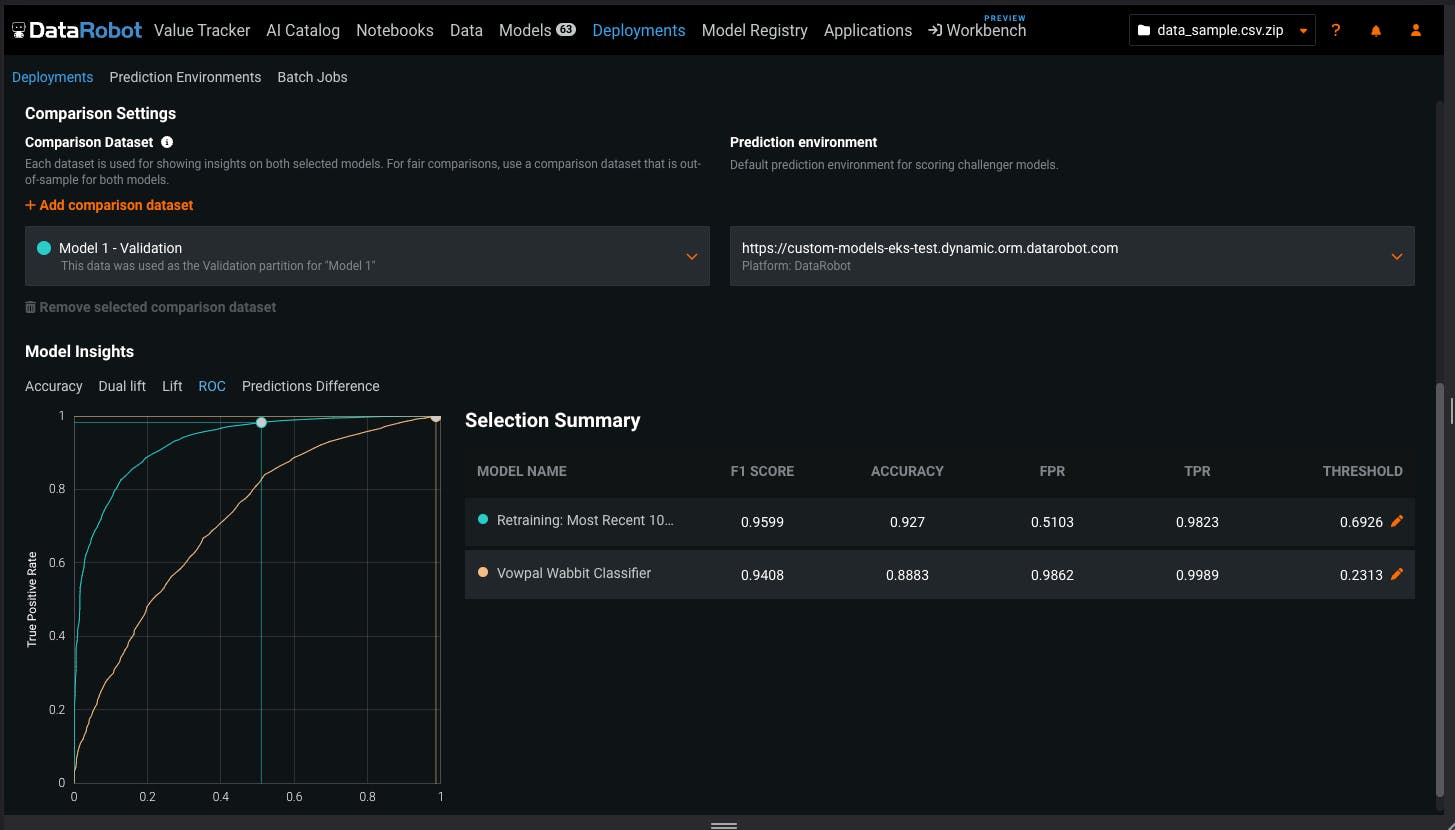
Monitor and Measure ROI
DataRobot helps enterprises monitor and manage generative AI and predictive AI models that are in production. The model management tool in DataRobot’s platform allows users to monitor changes to accuracy over time, as well as changes to speed and response time. The solutions also enable organizations to plug in models that are built in or outside of DataRobot’s ecosystem and generate API access. In addition, it offers lifecycle management and governance of ML models in production including the detection and rectification of poorly performing models.
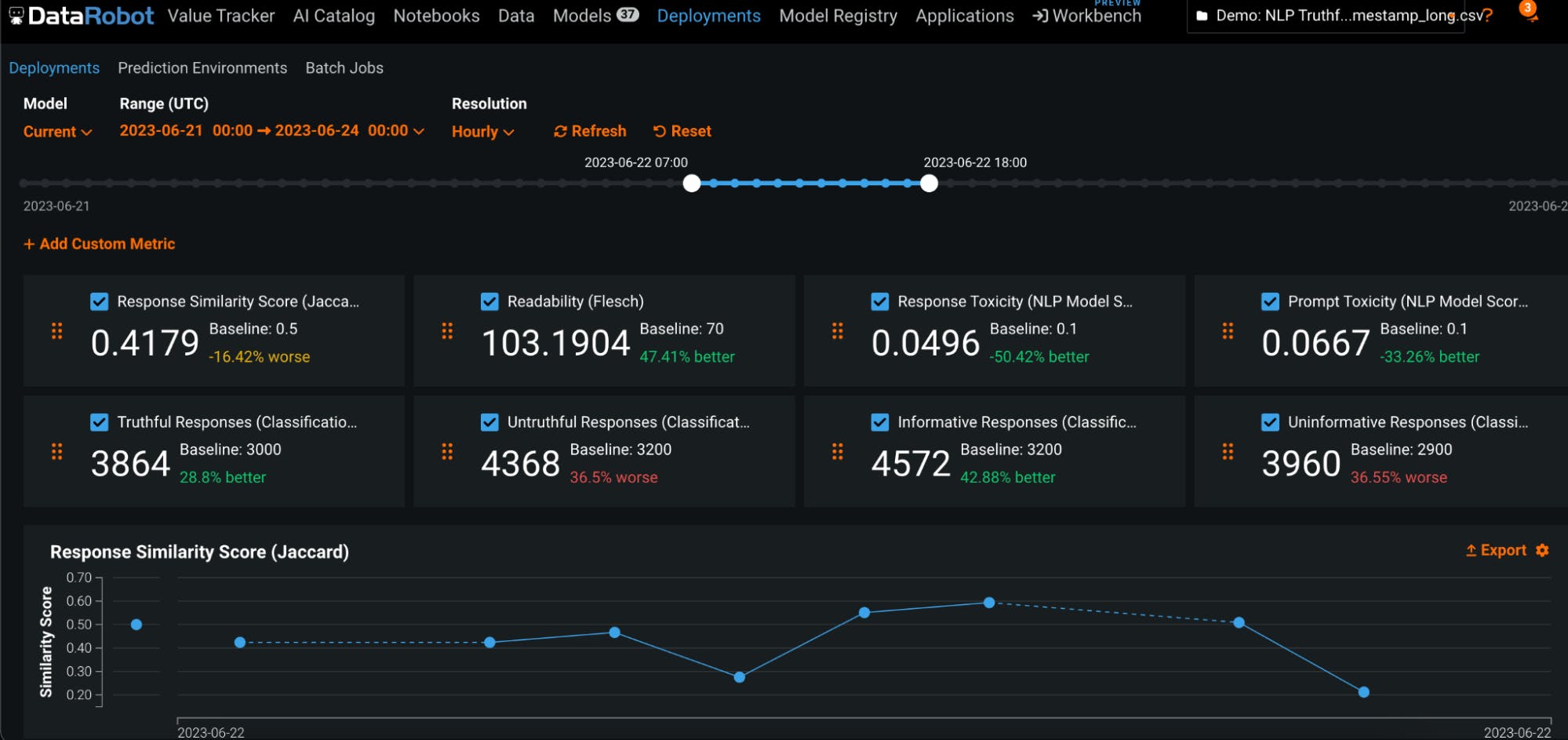
Source: DataRobot
Pathfinder
DataRobot offers a marketplace, Pathfinder, where users can discover hundreds of AI-powered applications, use cases, notebooks, and third-party integrations and connectors, such as Snowflake and Amazon S3.
Market
Customer
DataRobot’s primary users are data scientists practitioners who are tasked with developing and deploying ML models at a faster pace than they would normally do when building manually from scratch. The company largely targets the enterprise market and appeals to organizations that are all at different phases of their AI initiatives — from those just rolling out their AI strategies to those aiming to expand their AI efforts.
The company counted a third of the Fortune 50 firms as customers as of September 2022 and had clients across various sectors including healthcare, banking, retail, manufacturing, public sectors, oil and gas, healthcare and life sciences, manufacturing, retail, and financial services.
Market
The global AutoML market is projected to grow from $1 billion in 2023 to $6.4 billion in 2028 (representing a 45% CAGR from 2022 to 2028). The MLOps market is expected to grow from $1.1 billion in 2022 to $5.7 billion in 2027 (41% CAGR from 2023-2025) to $6.2 billion in 2028. Growth in both segments is largely driven by growing data volume and data complexity, shortage of skilled data scientists and ML experts, and increased AI business use cases across verticals including healthcare and financial services.
Competition
The AutoML and MLOps markets are highly fragmented, with Gartner counting as many as 300 players in the MLOps space alone. DataRobot’s strength lies in the automation of ML processes with capabilities like automated data preparation, model development, time series forecasting, and deployment.
Dataiku: Dataiku, founded in 2013, is a key direct competitor of DataRobot and offers similar suite products including Data Preparation, AutoML, AI applications, and MLOps solutions. The company has raised a total of $864.8 million in funding as of October 2023, with its last round being a $200 million Series F in December 2022 at a $3.7 billion valuation.
H20.ai: H20.ai is an AI cloud platform founded in 2012 that aims to “democratize generative AI” and offers a variety of AI, ML, MLOps, and cloud solutions. It has raised a total of $251.1 million in funding as of October 2023, with a $100 million Series E which valued the company at $1.6 billion in November 2021.
Palantir Foundry: Palantir is a public company that was founded in 2003 and has a market cap of $38.3 billion as of October 2023. Palantir’s Foundry product is a software platform that helps organizations integrate, analyze, and manage data. Its customers include government agencies as well as financial companies and other private businesses.
C3.ai: C3.ai, which was founded in 2009, brands itself as “enterprise AI software” and provides a suite of enterprise AI applications and a platform for developing and deploying AI applications. Its applications are designed to help businesses improve their operations in a variety of ways, such as predicting equipment failures, optimizing supply chains, and detecting fraud. It is a public company with a $3.2 billion market cap as of October 2023.
Determined AI: Determined AI, founded in 2017, is a deep learning training platform that simplifies distributed training, hyperparameter tuning, experiment tracking, and resource management. It is designed to help researchers and engineers train and deploy deep learning models faster and more efficiently. It was acquired by Hewlett Packard Enterprise in June 2021 for an undisclosed amount.
Business Model
The DataRobot AI Platform is priced as an annual subscription. Organizations can customize their solution to meet business goals. While the company does not disclose pricing plans on its website, it charges based on two types of customer needs for its 9.0 platform:
Essentials: Build and apply AI to deliver business value quickly. This covers most features in each module.
Business Critical: Scale to meet business demands with advanced experimentation and broad integrations. This covers all features in its features
Traction
DataRobot grew its annual recurring revenue (ARR) by 25% to $176 million in the fiscal year ending January 2022. Under Wright, management previously set a target of 80% growth to $255 million in the 12 months ending January 2022. However, the company missed that forecast, partly driven by the loss of a $29 million annual contract with the US Department of Health and Human Services. DataRobot’s ARR stood around $180 million in the quarter ending in April 2022.
The company has partnerships with other enterprise software providers such as Microsoft, Snowflake, SAP, Thoughtspot, Databricks, Google Cloud, Azure, AWS, and Tableau. In July 2022, Forrester named it a leader in the AI/ML Platforms category.
Valuation
As of October 2023, DataRobot has raised $1 billion in total funding from investors including NEA, Tiger Global Management, Sutter Hill Ventures, Altimeter, and Snowflake Ventures. Its last funding round was a $300 million Series G in June 2021, co-led by Altimeter and Tiger Global at a post-money valuation of $6.3 billion. That valuation represents ~35x multiple on an ARR of $176 million for the fiscal year ending January 2022.
Another comparable data science company is Databricks, which crossed $1 billion in ARR as of Q2 2022 and is estimated to have reached $1.3 billion in ARR at the end of 2022. In October 2022, Databricks cut its private valuation from $38 billion to $31 billion (~30x multiple to Q2 2022 ARR).
Key Opportunities
Product Expansion
While DataRobot brands itself as an end-to-end AI platform, there are some features that are missing from its toolkit or are not as robust as the competition. For instance, the company does not currently offer a data labeling product that could compete with Dataiku’s ML-assisted labeling service. DataRobot’s 8.0 platform also lags behind its main competitor Dataiku when it comes to data preparation solutions since the company primarily focuses on automated model development and training. DataRobot has the opportunity to invest more in these areas as it aspires to build a platform that covers the ML lifecycle as a whole.
AI Governance and Explainability
With the increasing importance of ethics and transparency in AI, DataRobot has an opportunity to lead in AI governance and explainability. Developing robust tools for model interpretability, bias mitigation, and compliance with regulatory standards can set DataRobot apart in the market. This will be particularly crucial as governments and industries establish stricter guidelines for AI deployment.
Key Risks
Competition and Consolidation
The AI and AutoML space is highly competitive, with established tech giants and startups entering the market. DataRobot needs to continually innovate to stay ahead. Furthermore, the industry is susceptible to consolidation, with larger companies acquiring smaller ones. DataRobot could face threats from mergers and acquisitions that could impact its market share.
Management Turmoil
In September 2022, DataRobot appointed its third CEO in as many years after Dan Wright stepped down in July 2022. The Chief Revenue Officer and the Chief Legal Officer also departed in early 2022 after being in the company for less than two years. The high executive turnover could create uncertainty and derail the progress of a company that has already missed revenue guidance and is facing a slowdown in growth.
Cash Burn
During Wright’s tenure, DataRobot burned $250 million in cash for operating activities in the 12 months ending April 2022, tripling its burn from Achin’s tenure at the helm. While DataRobot is purported to hold $400 million in cash as of April 2022, the high and increasing burn rate is concerning, particularly against the backdrop of decelerating revenue growth. Without additional funding and assuming the current course and speed, that suggests roughly three years in runway for the company.
Summary
DataRobot was one of the earliest pioneers in the AutoML field and has, over the years, expanded its product offerings to other ML domains such as data engineering and MLOps in an attempt to become an enterprise-grade end-to-end ML platform. Under Saha’s leadership, the company repositioned its solutions to better serve the generative and predictive AI market. That said, the company has faced multiple challenges including executive turnover, and low morale among employees. DataRobot had a cash runway of just over a year and a half as of April 2022 and it remains to be determined whether the new leadership and product direction can course correct the ship. A return to fundamentals is critical for the company to tap into the private capital market or consider an IPO under strenuous market conditions.





