Thesis
Animal protein has long been a staple of the human diet. However, social and environmental issues regarding modern processes of raising and slaughtering livestock have become more pressing in the modern era. For example, the raising of livestock drives significant deforestation and makes up ~14% of all man-made emissions.
As consumers begin to recognize climate change as a major issue, they are becoming more aware of the role that beef production plays in climate change. A 2022 survey of 1K consumers found that over 80% were willing to replace beef purchases with lower carbon footprint meats and meat alternative. However, only 5% of consumers in the US and UK are willing to become vegetarians, signaling a widening demand for plant-based meat alternatives, which emit up to 90% less greenhouse gasses compared to meat.
As a result, funding has flooded into the plant-based meat market in recent years, and it has become a $7.5 billion market as of 2021. When compared to the $280 billion global meat market, it’s clear there’s considerable room to grow. However, in the face of deteriorating macroeconomic conditions, the faux meat market cooled down significantly starting in 2021, and saw a decrease in sales for 22 consecutive months leading up to November 2022.
Despite this, plant-based meat producer Impossible Foods has retained momentum even amidst a broader downturn, having grown sales to $137 million in 2022 which represented 70% year-over-year growth. To stay ahead of their competition, Impossible Foods will need to continue to create products that resonate with consumers, drive prices lower through economies of scale, and reach profitability.
Founding Story
Impossible Food’s founder is Patrick O. Brown. In 1982, Patrick received a medical degree from the University of Chicago before deciding shortly afterwards to dedicate himself to scientific research. Brown then spent his research career at various institutions including the Howard Hughes Institute, University of California, and Stanford. Some of his notable contributions include findings regarding how genomes of AIDS infect the gene of the host and creating DNA Microarrays, which have since become standardized in labs around the globe.

Source: Berkeley
In 2001, frustrated by the difficulty of accessing scientific journals and the cost associated with it, Brown helped launch the Public Library of Science which gave open and free access to journals to the scientific community.
Then, in 2009, Brown went on an 18 month sabbatical with the goal of identifying how he wanted to spend the later stages of his career. Brown came to the belief that climate change was the biggest issue facing the planet and felt he could make significant change in the meat production space, which was known to be one of the biggest contributors to climate change.
Originally, Brown felt that all he had to do was bring awareness to the problem through organizing an “A-list” workshop at the National Research Council in 2010. However, the workshop had minimal impact. At this point, Brown realized that the best way to disrupt the meat industry would not be through driving awareness, but rather through a consumer product.
In 2011, Brown officially launched Impossible Foods, initially focused on creating a ground beef product. The ground beef manufacturing process not only has the most significant negative impact on the environment within the meat industry, but also makes up 60% of total beef consumption.
Over the next decade, Brown led Impossible Foods to becoming one of the industry leaders and a $10 billion enterprise. In March 2022, Brown stepped down from the CEO position and moved into the position of Chief Visionary Officer to focus on longer-term strategic initiatives. Brown was replaced as CEO by Peter McGuinness , previously President and COO of the Chobani yogurt company.
Product
As of late 2022, Impossible Foods offers seven different plant-based meat products including beef, sausage, chicken, pork, meatballs, Impossible branded packaged meals, and third party packaged meals with Impossible Foods’ products.
Impossible Beef

Source: Impossible Foods
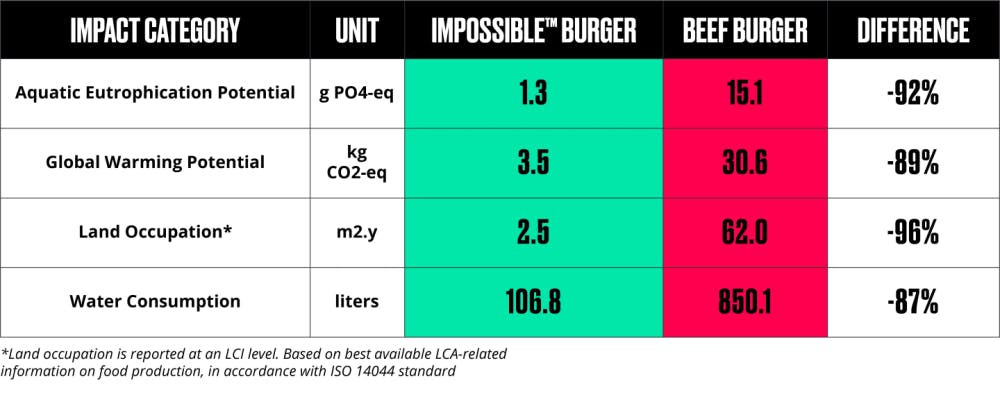
The company launched its first ground beef product in 2016. The key ingredients that made up this product include soy, heme, sunflower oil, coconut oil, and various binding agents. Impossible Foods beef products are sold both as ground meat and in meat patty form. Impossible Foods estimates that their beef has a significantly lower environmental footprint than animal meat, and claims that its products require 96% less land, 92% less water, and 91% less GHG emissions in order to produce.
Source: Impossible Foods
Impossible Pork

Source: Impossible Foods
Impossible Foods then launched its pork product in 2021 with similar core ingredients to the original beef product. The pork product is sold in ground form. Impossible estimates that their plant based pork has a significantly lower environmental footprint including requiring 66% less land, 81% less water, and 77% less GHG emissions.
Impossible Chicken

Source: Impossible Foods
Impossible Foods chicken products also launched in 2021. The chicken products come in 3 forms including chicken tenders, chicken nuggets, and chicken patties. The plant-based chicken is made from a combination of soy, sunflower oil, a binding agent, starch, among other ingredients. Impossible Foods estimates that compared to animal based chicken, Impossible Chicken uses 49% less land, 44% less water, and 36% less GHG emissions.
Impossible Meatballs

Source: Impossible Foods
The company launched its meatballs product in 2021 with similar core ingredients to the original beef product. The meatballs product comes in two forms, including Homestyle and Italian. Impossible Meatballs are estimated by Impossible Foods to require 85% less water, 88% less land, and 87% less GHG emissions than animal equivalents.
Impossible Sausage

Source: Impossible Foods
The company launched its sausage products in 2022 with the similar core ingredients of the original beef product. The sausage products are sold in ground, patty, and links forms. There is one classic flavor for the ground product, two flavors of patties, Spicy and Savory, and three flavors of links, Bratwurst, Italian, and Spicy. Impossible Foods estimates that its sausage product has a significantly lower environmental footprint than animal-based sausage, requiring 41% less land, 79% less water, and 71% less GHG emissions.
Impossible Meals

Source: Impossible Foods
Impossible Foods also launched a line of single serve pre-made frozen meals in 2022. As of the end of 2022, Impossible Foods offers eight different meals ranging from teriyaki chicken, pasta bolognese, and burrito bowls, featuring Impossible Meat. Impossible Foods also licenses its meats to third-party food manufacturers to create its own meals featuring Impossible Foods products like Buitoni Impossible Ravioli and Home Chef Impossible Meatloaf.
Market
Customer
Impossible Food’s goal is to market themselves beyond just vegetarians and vegans in order to compete with the global meat industry. Therefore, the company views the market for global meat consumption as their TAM including people of all ages, genders, and socio-economic backgrounds. Around 41% of Americans have tried a plant-based meat product, a figure that is closer to 50% for people under 50, likely for environmental and social reasons. Additionally, 39% of men and 43% of women have eaten plant-based meat. Finally, 54% of Americans making over $100,000 a year have tried the product compared to 31% for people making under $40,000 annually. The discrepancy in the socio-economic consumption of the products can likely be attributed to the fact that plant-based meat is currently more expensive than animal meat.
Market Size
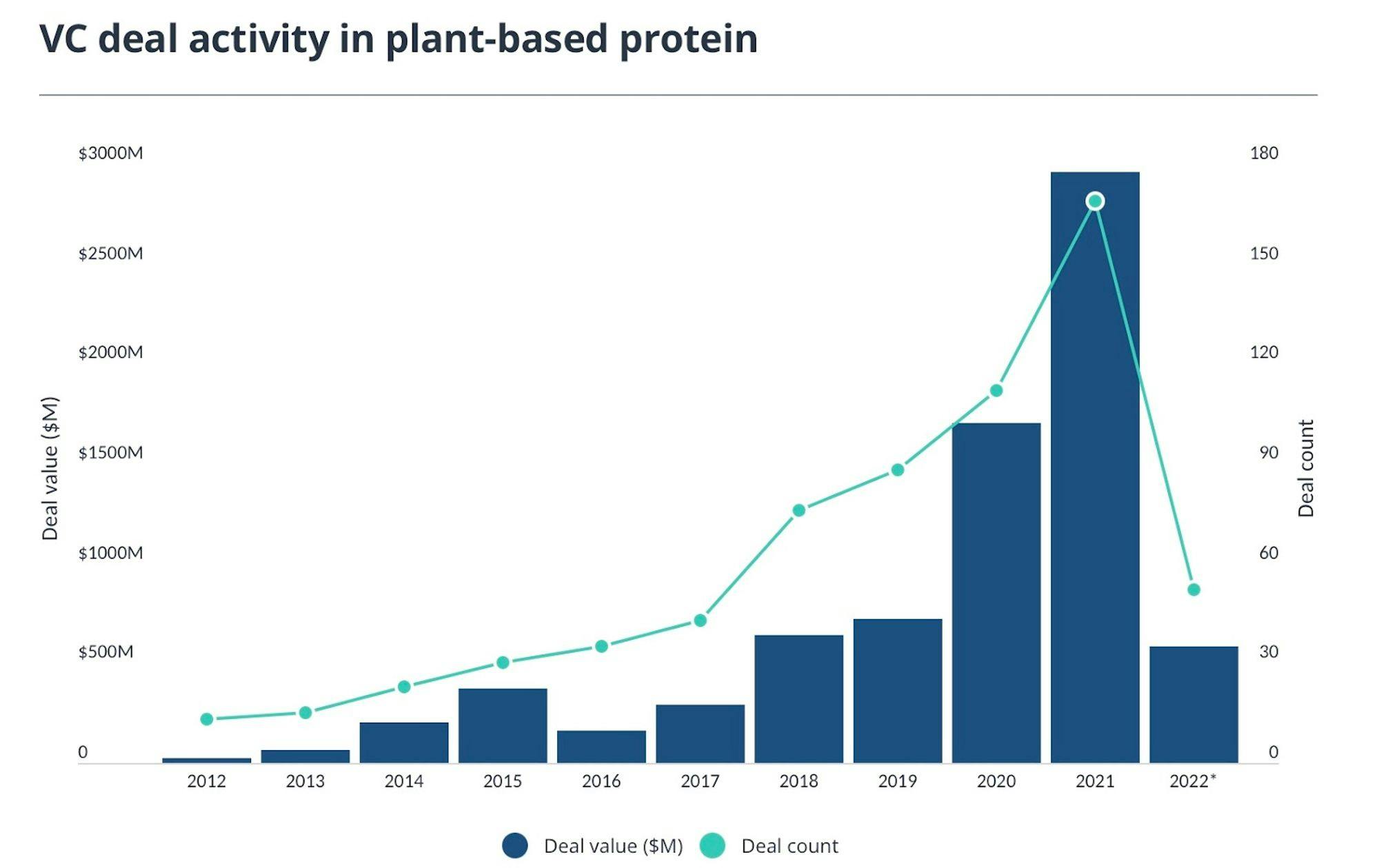
Impossible Food’s goal is to not only market itself towards vegetarians and vegans, but to disrupt the entire meat industry as a whole. The meat industry is a $270 billion market domestically and $1.4 trillion globally. By comparison, the plant-based meat market in the US was $7.5 billion in 2021 and is expected to grow to $15.8 billion by 2028, representing a CAGR of 15%. The plant-based meat market has also seen significant investment from venture capital investment over the past several years: in 2021 there was nearly $3 billion of capital invested in the space, representing a ~4x increase from 2019 and ~2x from 2020.
Source: Pitchbook
Traction
Impossible Foods has had several significant milestones over the years, helping them grow their footprint to over 7 products, 25K stores, 40K restaurants, and an international presence in several countries.
In 2017, Impossible Foods achieved a significant milestone by securing a distribution agreement with Dots Foods, America’s largest food re-distributor. This partnership gave Impossible Foods access to nine US distribution warehouses with distribution capabilities to all 50 states.
At the end of 2017, Impossible Food had a presence in over 400 restaurants nationwide. In 2018, Impossible Foods launched in its first international market, Asia. By the end of 2018, Impossible was in over 5K restaurants in all 50 states and announced that they had surpassed over 13 million in total Impossible Burger sales. The company also had over 100 restaurants in Asia and Macau.
In 2019, Impossible Foods launched the Impossible Burger in grocery stores for the first time, signing significant distribution deals with mainstream grocers like Wegmans. In many locations, the Impossible Burger became the top selling product in stores. Specifically, in California, the Impossible Burger outsold the next top product by more than 6x. At the end of 2019, Impossible was in over 17K restaurants nationwide.
In 2020, Impossible Foods signed critical distribution agreements with US grocery stores like Albertsons, Safeway, Trader Joe’s, Walmart, Sprouts, taking the total number of grocery stores to over 10K in the US. Additionally, Impossible signed a deal with Burger King to sell the Impossible Sausage as part of the Impossible Croissan'wich to over 7.5K Burger Kings nationwide.
In 2021, Impossible Foods added four new international markets including Canada, UAE, Australia, and New Zealand. Additionally, the company was in over 22K grocery stores and 40K restaurants globally. Other notable accomplishments included increased distribution deals with Walmart, establishing distribution with Lidl, and cutting prices by 20%. In 2022, Impossible had several more international launches of individual products. For example, Impossible Beef arrived in Australia and New Zealand and Impossible Foods launched several chicken products in the UK, Canada, and Hong Kong.
Business Model
Impossible Foods generates revenue from the sales of their plant-based meat products. The company has three main sources of revenue: grocery stores, restaurants, and online. Impossible is in over 25K grocery stores including Walmart, Trader Joe’s and Costco. Impossible Foods also has distribution deals with 40K restaurants in three different continents to sell Impossible products.
Additionally, Impossible Foods has entered into the private labeling business represented by their partnership with Krogers. The company also offers the sale of its products via the internet, but it is not a classic direct-to-consumer model. Consumers can buy the products via the Impossible Foods website and receive delivery via Instacart. The company also does sell products on Amazon. The price of the products vary based on the location and distribution methods. Specifically, for grocery stores, Impossible Foods cut prices on multiple occasions, in 2020 and 2021, taking the minimum price of sale to $6.80. This still represents a premium to classic ground meat, but over time, the company expects to become cheaper than classic beef.
Competition
Impossible Foods operates in a competitive space with a variety of different players including pure plant-based food companies like Beyond Meat, large food conglomerates with plant based divisions like Kelloggs' Morningstar Farms, as well as large scale venture backed companies like UPSIDE Foods.
Beyond Meat
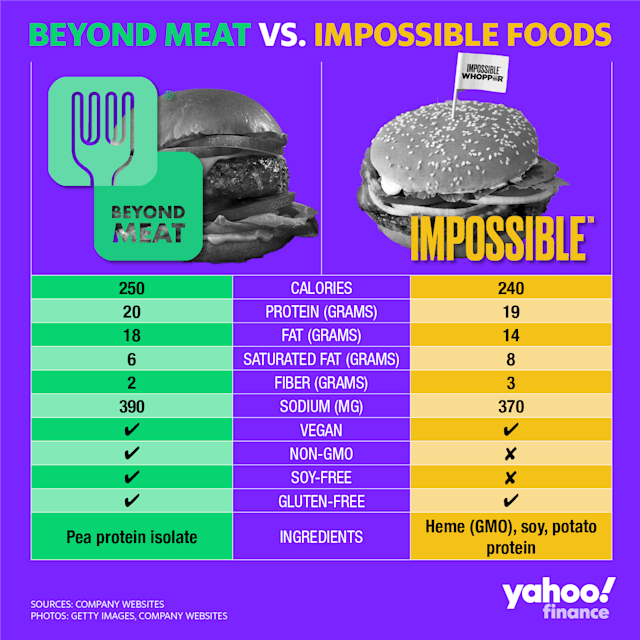
Beyond Meat is Impossible Foods’ largest direct competitor. Beyond Meat was founded by Ethan Brown in 2009, two years before Impossible Food. Beyond Meat’s first product was plant-based chicken which it launched in 2012. Beyond Meat later launched its first meat product in 2014, as well as pork products in 2020. Beyond Meat had raised $122 million in the private markets backed by notable funds like Kleiner Perkins. Beyond Meat IPOd in 2019 netting them $240 million of funding at around a $1.5 billion valuation.
Source: Yahoo
In terms of revenue, Beyond Meat expects to earn between $400 million and $425 million in fiscal year 2022, representing a decrease of between 14% and 9% in sales compared to 2021. The company attributes its decline in sales to the current macro environment. The company lost $101.7 million in the third quarter of 2022 alone. In order to mitigate losses, Beyond Meat announced in October 2022 that it would lay off 19% off its workforce. As of December 2022, since IPO, Beyond Meat’s stock ($BYND) is down around 80%. With Impossible Foods reportedly doing around $137 million in revenue in 2021 growing at 70% year over year, Beyond Meat is the larger company between the two, but with a significantly worse growth profile.
Morningstar Farms
Morningstar Farms was founded in 1974 as a division of Worthington Foods offering soy-based meat-like products. Morningstar was acquired by Kellogg in 1999 for around $300 million. Under Kellogg, the brand has grown to a multi-hundred million dollar business. Strategically, Morningstar has seen success by not positioning its products as true meat substitutes, but rather natural yet tasty meat alternatives. Morningstar offers products like soy or bean-based veggie burgers, soy ground beef, and soy based chicken nuggets. In 2019, Morningstar did launch a direct competitor to Impossible Foods called Incogmeato whose aim is to be a true meat substitute, mimicking the classic meat experience. In 2021, Morningstar Farms did approximately $340 million in revenue putting them ahead of Impossible and just behind Beyond Meat.
UPSIDE Foods
UPSIDE Foods is a food technology company with a differentiated approach to the space, compared to an Impossible Foods or Beyond Meat. Instead of trying to create a meat-like protein using plants, UPSIDE Foods is looking to create actual meat through scientific processes in a laboratory by taking cells from live animals and turning them into muscle tissue. UPSIDE believes that if this process is successful, consumers will not be able to identify the difference between lab grown meat and real animal meat since their chemical makeup is exactly the same. In November 2022, UPSIDE raised a $400 million Series C at a valuation of over $1 billion with the goal of creating a production facility that is able to produce tens of millions of pounds of lab grown meat, annually. The company plans on starting with chicken and plans to launch in 2023.
Valuation
Impossible Foods raised $500 million in its last funding round in November 2021 led by Mirae Asset Global at around a $7 billion valuation. At the time of this round, Impossible Foods had raised a total of just under $2 billion in venture funding. Other notable rounds include a $500 million raise also led by Mirae in March 2020 and a $200 million round led by Coatue in August 2020.
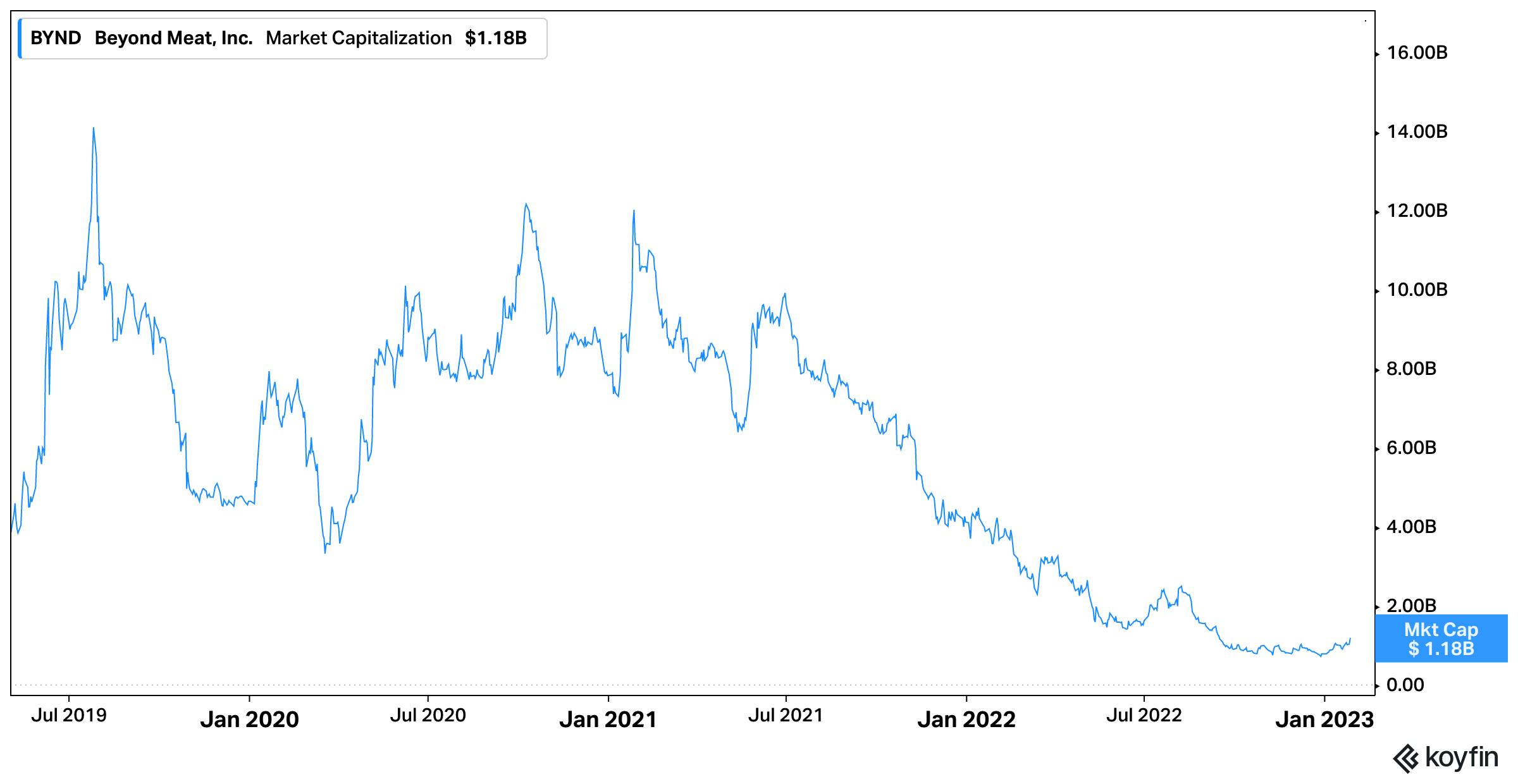
In April 2021, Impossible Foods was exploring going public either via SPAC or IPO at a $10 billion valuation. At the time, competitor Beyond Meat was trading at a 200% premium to their 2019 IPO. However, as the markets collapsed and investors have prioritized profitability, Beyond Meat is trading at an 80% discount to their 2019 IPO and is down more than 90% from all time highs. Recent reports from industry insiders project that an Impossible Foods’ IPO will occur in 2023.
For comparison, Beyond Meat is expected to do between $400 million to $425 million in revenue, in 2022. With a market cap of ~$1 billion, the company is trading at around 2.3x revenue. The approximate $400 million revenue figure represents a 14% decrease in growth year over year. Additionally, Beyond Meat is generating significant losses from operations losing over $100 million in the third quarter alone. Impossible Foods reportedly did earn more than $137 million in revenue in 2021 at a 70% growth rate. However, it has not publicly shared any 2022 revenue figures or profitability metrics making a direct comparison to Beyond Meat difficult.
Source: Koyfin
Key Opportunities
Strength in Times of Weakness
Over the past several years, there has been a significant decrease in demand for plant-based meat for many of Impossible Food’s competitors like Beyond Meat, Morningstar, and Planterra – who shut down their operations. However, it appears that Impossible Foods has created a product that resonates with consumers and is in a significantly different position than its competitors. According to an Impossible Foods spokesperson in November 2022, “We’re not experiencing anything like what Beyond Meat has reported or some of the other brands in the space…Quite the opposite: We’re seeing hypergrowth, with over 60 percent year-over-year dollar sales growth in retail alone.” If Impossible Foods can continue to show strength in this environment, there could be significant opportunities to gain market share and possibly be a consolidator in the industry.
Additional Products
As of the end of 2022, Impossible Foods operates in a handful of alternative meat markets and it is now focusing on entering other markets. Specifically, Impossible Foods has taken steps to move into the fake fish markets. As of 2022, the seafood marketplace is a $113 billion industry globally and expected to grow to a $138 billion industry by 2027. Impossible Foods has already taken steps to penetrate the market, including the development of an anchovy flavored broth in 2019 made only from plants. Impossible Foods has a goal of creating an animal-free alternative for every protein by 2035, so additional lines of business for the company is a key priority.
Key Risks
Significant Competition Leading to Commoditization
Impossible Foods operates in a competitive industry with publicly traded companies like Beyond Meat, as well as multi-billion dollar food conglomerates like Kellogg (Morningstar). As of the end 2022, there were more than 60 alternative meat brands generating a minimum of $500K in sales. The existing competition will force Impossible Foods to continue to innovate and expand its brand or be at risk of being disrupted by either a larger or smaller player. Additionally, there is the risk of venture-backed companies taking a different approach to alternative meat such as Meati, which uses mushrooms as a base, or UPSIDE Foods, which grows meat from animal cells. Such approaches may resonate more with consumers and eat into Impossible Food’s current market position.
Full Market Penetration
There are concerns in the fake meat industry that the excitement around brands is fading and there is a serious decrease in sales on the horizon. Early signs of this include the fact that the fake meat market has seen sales collapse 22 consecutive months now, although this is difficult to disentangle from broader macro conditions. It’s possible that consumers are returning to cheaper alternatives or more familiar habits as a more difficult economic climate has set in. Additionally, a Deloitte study on the fake meat market suggested that that the 53% of Americans who do not buy the product might not be interested in making the switch at all, which may cap the TAM for Impossible Foods lower than it hopes.
Summary
Although animal protein has historically been a key component to the human diet, over the past several decades, the negative social and environmental consequences of this industry have become clear. With the increased awareness around these problems, combined with significant advancement in food technology, it has become possible to create quality plant-based meat products over the past decade.
Through billions of dollars in venture investment into the alternative meat markets, a $7.5 billion industry has emerged with multiple billion-dollar ventures like Impossible Foods and Beyond Meat. However, over the past several years, sales in the industry have slowed significantly. Impossible Foods has avoided this fate to this point represented by 70% year-over-year revenue growth. In order for Impossible Foods to continue to grow, product innovation and sustained cost-lowering will be critical.





