Thesis
In 2009, the Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health (HITECH) Act was introduced to “modernize the health care system by promoting and expanding the adoption of health information technology.” This incentive led to a rise in electronic health record (EHR) adoption in the US from 6.6% in 2009 to 88.2% in 2021, driving rapid digitization and growth in healthcare data. A report in 2018 estimated that the healthcare industry generates about 30% of the world’s data, and projected a 36% CAGR of data volume by 2025.
Although 88.2% of physicians had adopted EHRs by 2021, healthcare data exchange remains challenging due to a fragmented network of systems using disparate formats and standards. In 2021, an estimated 70% of healthcare providers still relied on fax machines to share medical information. This lack of data interoperability makes it difficult to view full patient histories, thus hindering care and limiting insights across patient populations.
This issue has become so prominent that the Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology (ONC) passed regulation in 2020 to prioritize improving interoperability of health information through the Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR) API standard and a standardized dataset called US Core Data for Interoperability (USCDI).
At the same time, the expanding use of real-world evidence (RWE) in drug development has further increased the demand for integrated, interoperable datasets. RWE often goes hand-in-hand with real-world data (RWD). RWD is information on patient health and care delivery that is collected from sources outside of traditional clinical trials, such as electronic health records, claims, and patient-reported data. This data is used to generate RWE, which are clinical insights about the safety and effectiveness of medical products in real clinical environments.
RWE can be used as an alternative or complement to traditional randomized control trials (RCTs) because it captures how treatments work in real-world settings rather than just in the controlled environments of RCTs. Using RWE trials can reduce the time and cost of drug development — in one study, the use of RWE led to a 40% reduction in the planned sample size of a phase III program, which translated into six months of time savings. McKinsey estimated in 2020 that a top-20 pharmaceutical company could realize over $300 million a year by leveraging RWE analytics across its value chain.
Momentum has been growing in the RWE space. In 2018, the FDA launched a Real World Evidence Program for the use of RWE to support the approval of new drug indications. At the end of 2020, 90% of new drug approvals in the United States included RWE as part of the submission. However, data interoperability, accessibility, and quality still remain major barriers to scaling RWE.
Komodo Health supports this shift toward real-world insights by providing integrated datasets and self-service analytics solutions to life sciences organizations. As of December 2025, its healthcare map pulls from disparate sources to provide an in-depth, comprehensive dataset covering over 330 million patients, including data on pharmacy and medication use. Its full-stack analytical platform includes low-code tooling and AI enhancement to support rapid insight generation. Komodo Health’s products are tailored to accelerate the process of RWD analysis, advancing its core mission of reducing the burden of disease.
Founding Story
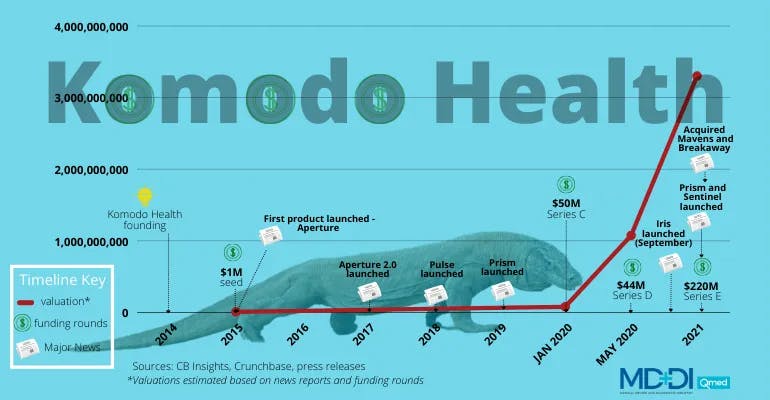
Komodo Health was founded by Arif Nathoo (CEO) and Web Sun (President) in 2014.
Nathoo started his career with the intention of becoming a doctor. After earning a bachelor’s degree in neurobiology from Harvard University, he went to Harvard Medical School, where his path took an unexpected turn. In an October 2023 interview, Nathoo said: “I got so fascinated by the way that technology and data were changing how healthcare was practiced, and I decided that I would take a little bit of time, figure out what it is that I wanted.” He decided to complete a degree in public policy while in medical school and joined McKinsey as a consultant after graduating. Though he promised his parents to go back to complete residency after two years, Nathoo ended up working at McKinsey for seven years before co-founding Komodo Health with Sun.
Sun’s background is rooted in healthtech and the life sciences. He earned a bachelor’s degree in biochemistry, biological sciences, and psychology from Rutgers University and an MBA in international business, marketing, and finance from New York University. Sun then served as vice president at life sciences management consultancy Campbell Alliance (now Syneos Health). Before founding Komodo Health, he was a managing director at Zephyr Health, a life sciences data and insights solution provider.
Nathoo and Sun wanted to address the broken insights workflow in healthcare that they had observed while working on life sciences projects. At the time, large enterprises would spend multiple years and millions of dollars on bespoke consulting engagements to understand patient costs, outcomes, and risks. Recognizing the growing shift toward data sharing, cloud storage, and broader data accessibility, the two founders formed a “full-stack thesis,” envisioning an end-to-end analytical platform powered by comprehensive data assets to simplify workflows and accelerate clinical insights. Nathoo and Sun decided to name Komodo Health after komodo dragons to “embody both resilience and a bit of enchantment.”
Komodo Health added former McKinsey partner Paul Gurney as Head of Market Strategy and Innovation in 2021 before appointing him Chief Data Product Officer in 2022. In 2024, Miles Ennis (COO/CRO) joined Komodo Health with prior experience leading sales at both Cisco and IBM. Komodo Health brought on Paul Thomas as VP of Finance in the same year before also appointing him to the role of Acting Chief Financial Officer in 2025. Thomas was previously the SVP of Strategic Finance and Investor Relations at Talkdesk and played a key role in leading the IPO of Sumo Logic. Mark Jewett (CMO) also joined Komodo Health in 2025 with decades of experience leading marketing teams at Tableau and Microsoft.
Product
In pursuit of its goal to set the “Evidentiary Standard” for real-world data and analytics, Komodo Health provides a comprehensive suite of products that support evidence generation and commercial strategy in the life sciences sector. As of December 2025, its offerings fall into three primary categories:
Proprietary integrated data assets (the Healthcare Map)
AI-driven analytics tools built for broad usability across teams
Targeted analytics solutions tailored to specific use cases
Healthcare Map
Komodo Health’s foundational Healthcare Map is a de-identified dataset built from the healthcare records of 330 million patients — including medication, specialty pharmaceutical, EHR, clinical, and payer data — with 16 million clinical encounters added daily as of December 2025. The dataset also contains 160 million closed, linkable lives. A closed, linkable life refers to a patient whose fully processed healthcare claims have been connected across sources to form a longitudinal record of their care over time. Komodo Healthcare Map’s value proposition lies not only in its breadth but also in its depth and continuity of patient data, aiming to track every patient’s encounter within the healthcare system to provide a more complete view of patient health.
Using the MapEnhance feature, users can also layer specialty datasets on top of the Healthcare Map to further enrich healthcare insights. These curated datasets from partner organizations include precision molecular diagnostics, high-volume standard lab diagnostics, EMR data, and inpatient and outpatient facility chargemasters. Data partner organizations include Invitae, PointClickCare, Trio Health, GeneDx, and COTA Healthcare.

Source: Komodo Health
MapLab
Built on top of the Healthcare Map is MapLab, a low-code analytical solution suite that consists of MapView, MapExplorer, and MapLab Enterprise. Komodo Health developed this solution to enable medical teams to run more sophisticated commercial analytics and longitudinal studies, after observing that many users were only conducting a limited set of analytics on the Healthcare Map and not unlocking its full potential.
\MapView offers pre-built dashboard templates for common industry use cases, enabling non-technical users to quickly analyze disease trends, treatment pathways, patient populations, and brand performance. Provider lists and geographic territory files can also be uploaded into MapView to increase filter granularity.
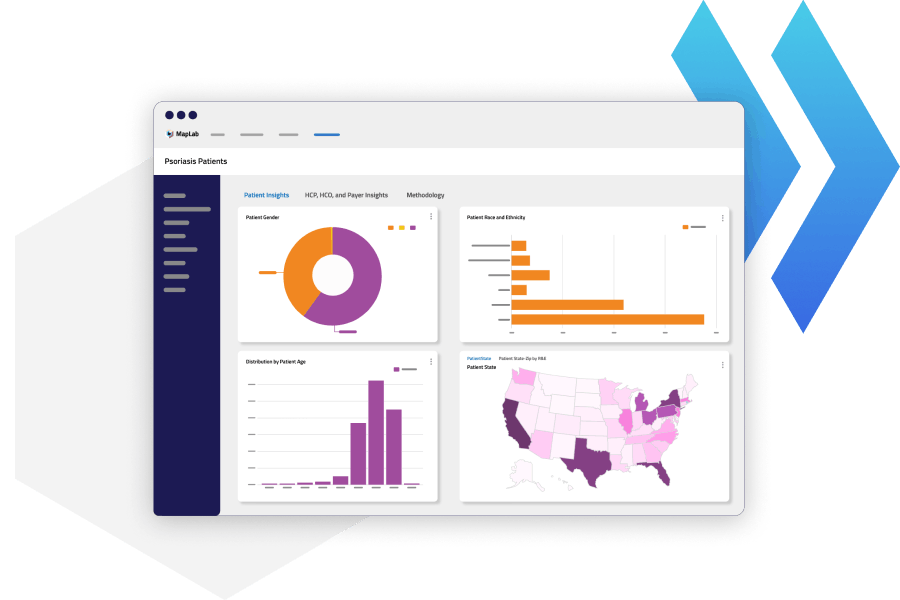
Source: Komodo Health
Released alongside MapAI, MapExplorer is a no-code analytics environment that helps nontechnical users explore the Healthcare Map. The Definitions Builder feature allows users to create codesets and patient cohorts for different patient populations.
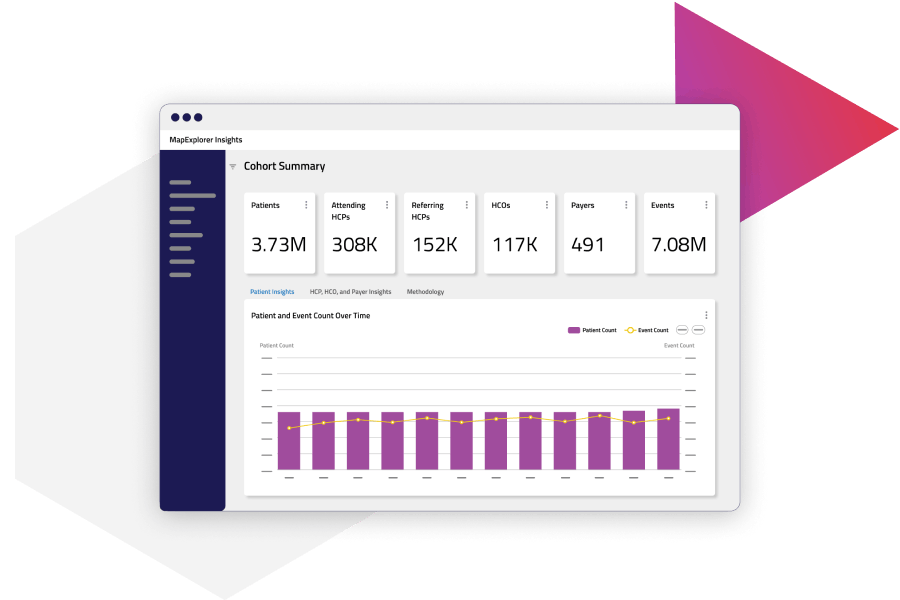
Source: Komodo Health
MapLab Enterprise was launched as an enterprise analytics platform that offers tailored capabilities for different market segments, including Health Economics and Outcomes Research (HEOR) and Risk-Bearing Entities (RBEs).
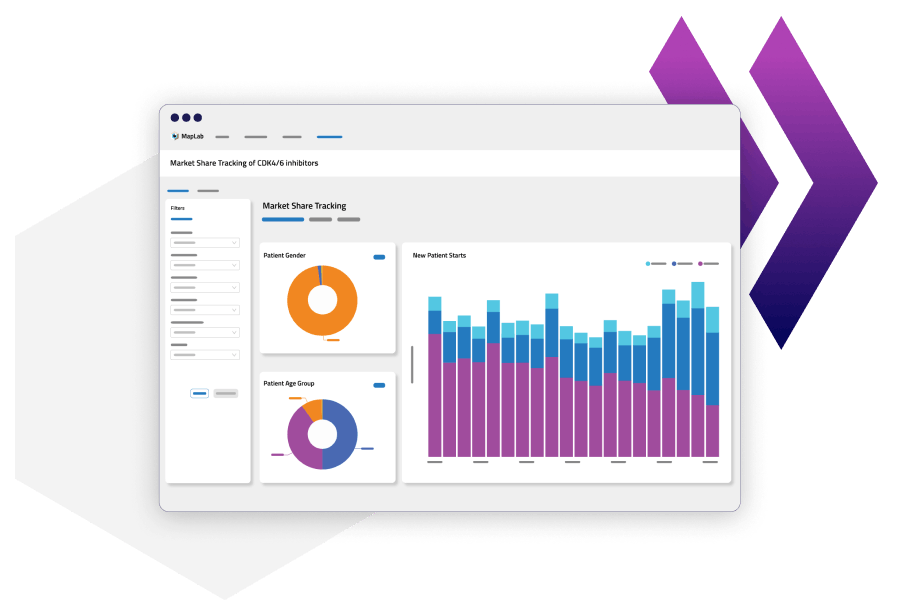
Source: Komodo Health
MapAI
Seeking to further streamline the process of data preparation, Komodo Health released its first integration of generative AI technology called MapAI, an NLP-based AI assistant that embeds across all MapLab workflows. Using plain language, users can ask MapAI to build patient cohorts or answer questions such as “What is the patient breakdown of GLP-1 prescriptions by payer?”, reducing reliance on data experts for early-stage analyses.
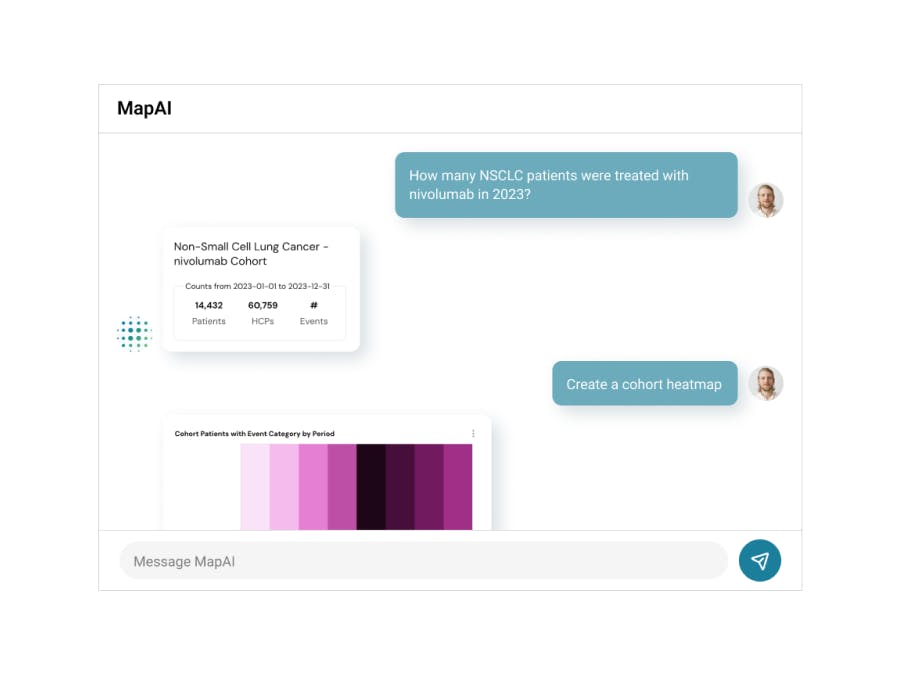
Source: Komodo Health
Marmot AI
Marmot AI was launched as the “first AI to speak the language of healthcare analytics.” The AI engine is powered by the Healthcare Map and trained on data from more than one million active cohorts across the Komodo Health platform.
A key design principle of Marmot AI is earning user trust through transparency and reproducibility. According to an article written by Marmot AI and Ramraj Velmurugan, Head of Komodo Health Labs and the creator of Marmot:
“In healthcare, you must be able to trust the results, and that requires seeing the work behind the answer. Every insight I generate is accompanied by transparent, auditable code that allows any analyst to reproduce the results. This includes confidence metrics that quantify certainty levels, citations to third-party studies, and a research planner that ensures reproducible results”.
In October 2025, Komodo Health used Marmot AI to support its analysis of real-world colorectal cancer treatment disparities across 878K patients, finding that early-onset disease occurred at “nearly three times the rate among Black, Asian, and Hispanic patients (14.49%) compared to White patients (4.91%).” Komodo Health claimed that the processing time for its analysis took about one hour, whereas traditional analysis methods would normally take weeks.

Source: Komodo Health
Sentinel
Komodo Health’s Sentinel application allows developers to link proprietary datasets with the Healthcare Map and develop new algorithms, ML applications, and custom analytics within a cloud-based environment. Users can integrate both their own proprietary data and MapEnhance datasets through the process of universal tokenization. In the process of tokenization, personally identifiable information (PII) is transformed into a unique token identifier that is used to link data sources, stitching together different elements of a patient journey while protecting patient identity.
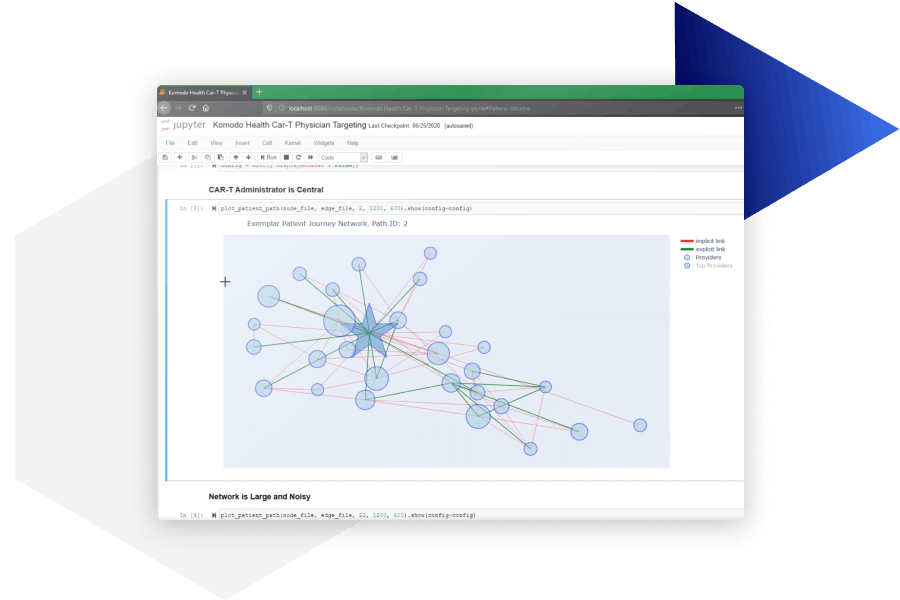
Source: Komodo Health
Aperture
Aperture started as Komodo Health’s first proof-of-concept solution for its full-stack thesis. The application was designed for medical affairs teams, who are tasked with identifying and engaging key opinion leaders (KOLs) — prominent physicians and subject matter experts in specific disease areas — to drive awareness of new treatments and clinical trials. Traditionally, these teams relied on a very manual process of searching for KOLs within publications and clinical trial sites that often yielded outdated information.
Komodo Health’s Aperture solution gave medical affairs a holistic view of KOLs that they could filter, segment, and monitor, enabling launches of new medical programs. Aperture also uniquely provides information on each KOL’s clinical activity, which they found to be extremely predictive of a KOL’s clinical influence.
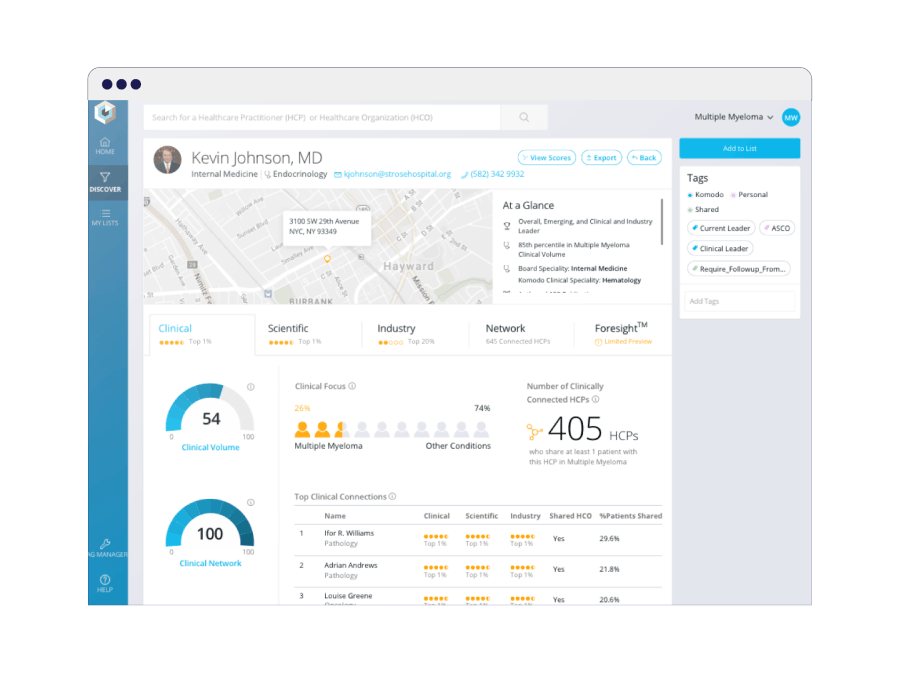
Source: Komodo Health
Iris
Iris is a field sales insights tool that helps commercial teams construct cohorts for outreach and optimize sales strategies based on real-world evidence. Users can monitor market share, brand performance, and key product metrics while identifying new opportunities for expansion.

Source: Komodo Health
Pulse
Through Pulse, commercial teams can design custom alerts for different patient cohorts and tailor their sales strategies to target healthcare providers at the right time. Pulse customers have seen a 47% increase in script activity when field teams acted on Pulse alerts and 4x more clicks on Pulse-timed email campaigns.
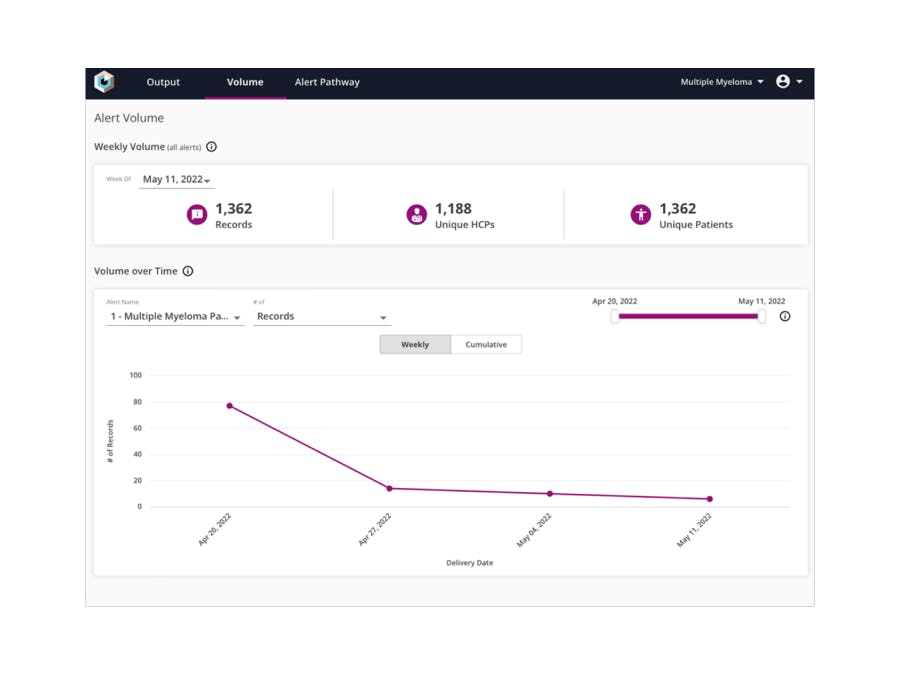
Source: Komodo Health
Drug Projections
Komodo Health’s Drug Projections solution provides real-time market intelligence on more than 10K drug therapies, including both pharmacy benefit and medical benefit drugs. Users can compare medications side-by-side and view weekly projections of drug metrics, including revenue forecast, market share, marketing ROI, and salesforce size.
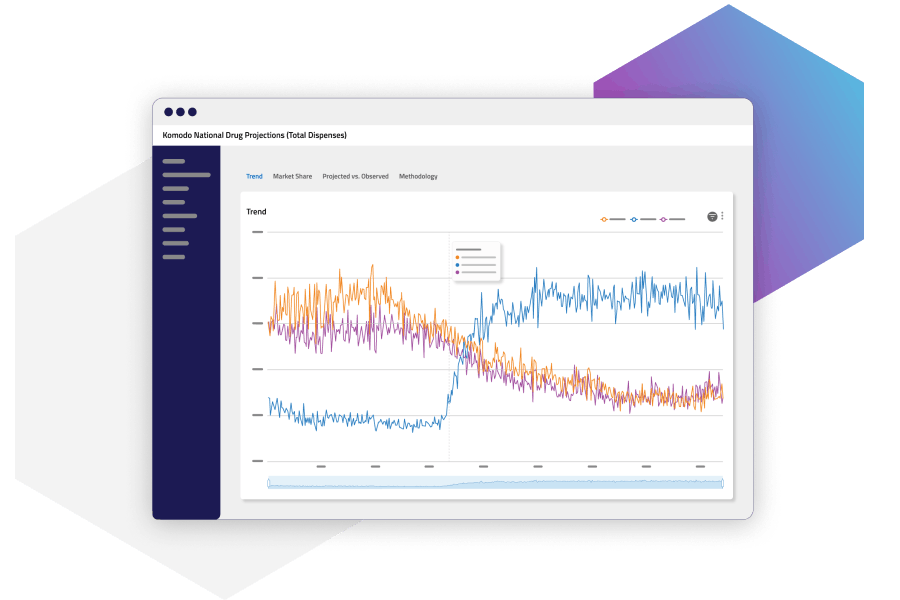
Source: Komodo Health
Medical Information Cloud and Scientific Publications Cloud
In 2021, Komodo Health acquired Mavens, a Salesforce-powered enterprise software platform, and added Mavens’ Medical Information Cloud and Scientific Publications Cloud to its product suite.
The Medical Information Cloud is a content management solution that uses Salesforce’s conversational AI to support and automate medical information responses (MIRs). MIRs are non-promotional, evidence-based answers to questions asked by medical professionals and can cover anything from product information requests, adverse event reports, and off-label information.
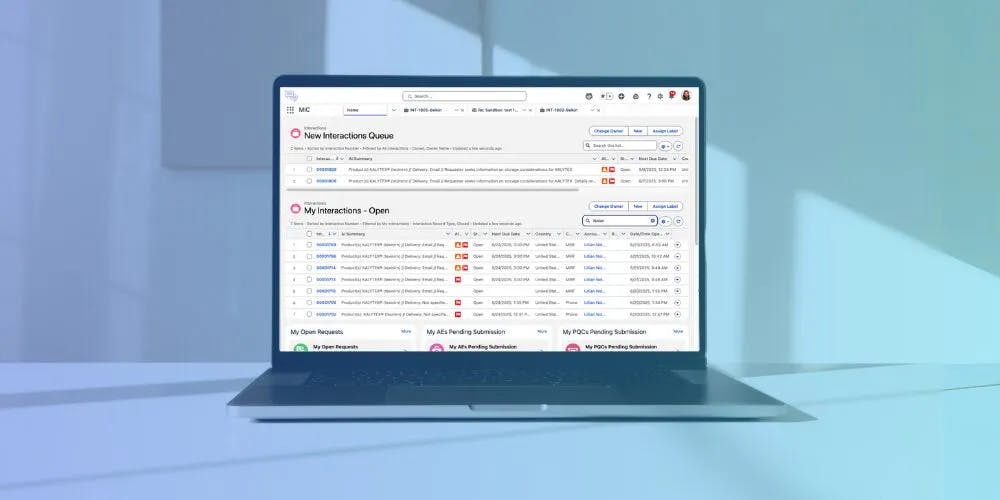
Source: Mavens
The Scientific Publications Cloud is another content management solution that supports the scientific publication process by tracking publication submissions, streamlining feedback workflows, and facilitating journal selection.
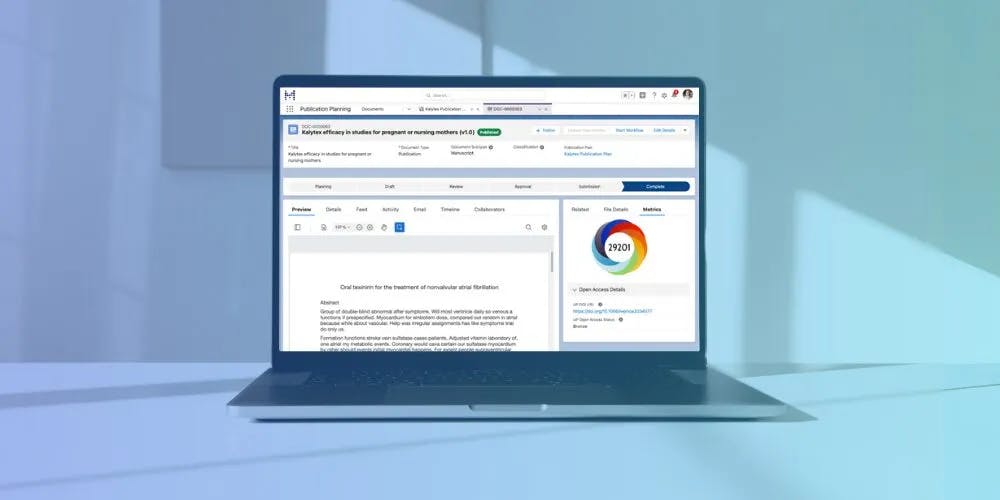
Source: Mavens
Market
Customer
Komodo Health primarily serves life sciences companies and healthcare organizations, initially focusing on medical affairs teams within pharmaceutical companies before expanding to support R&D and commercial strategy functions. As of 2024, Komodo Health claimed that over 200 life sciences and healthcare organizations were using its product suite, including Johnson & Johnson, Merck, Novo Nordisk, MoonLake Immunotherapeutics, Regeneron, and Takeda Pharmaceuticals.
The primary pain point that Komodo Health seeks to address through its full-stack analytical platform is the large number of disparate resources that life sciences teams traditionally need to deploy for real-world data analysis. To surface the challenges faced by life sciences teams in acquiring RWE, Komodo Health commissioned a study by Frost & Sullivan in 2024, which included the following findings:
“Seven months, four data vendors, and four consultants. That’s the average resource commitment for Clinical Development, Commercial, and Health Economics and Outcomes Research (HEOR) Life Sciences teams to obtain and prepare the data needed to conduct real-world evidence (RWE)–driven analyses. Those numbers are even higher for the largest pharma enterprises as data scientists, researchers and senior leaders wrestle with uneven access to disparate data types, lack of confidence in data accuracy, and imperfect data integration.”
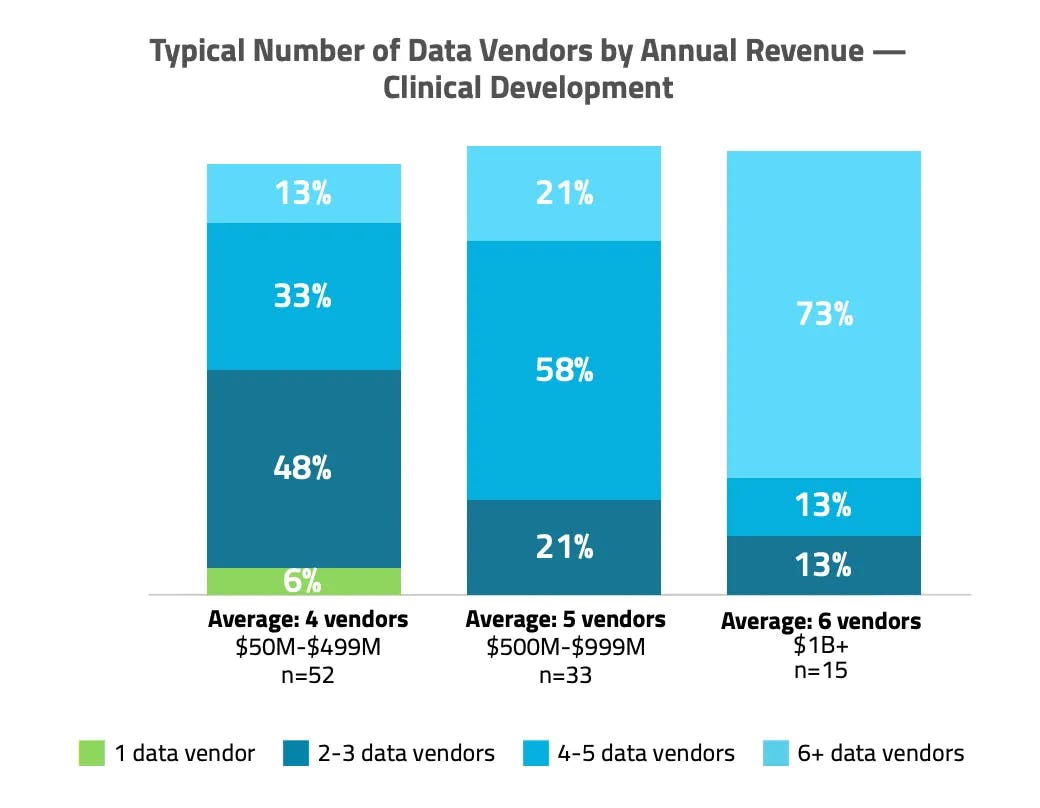
Source: Komodo Health
Leveraging the broad utility of its Healthcare Map, Komodo Health has since expanded its use cases outside of life sciences through partnerships with organizations like public health organizations (Robert Wood Johnson Foundation), patient advocacy groups (Cholangiocarcinoma Foundation), management consultancies (Deloitte), and even financial organizations (Nasdaq).
Market Size
Komodo Health operates within the global real-world evidence solutions market, which encompasses a diverse mix of players, including data vendors, infrastructure providers, interoperability networks, payers, pharmaceutical companies, researchers, regulators, and consultancies.
A 2025 survey found that 77% of biopharmaceutical organizations already used real-world data (RWD) in at least some drug development tasks. Demand for RWD/RWE is expected to continue to grow, especially with the FDA’s commitment to support RWE generation in drug development and the ONC’s prioritization of healthcare data interoperability through the 21st Century Cures Act. In September 2025, the European Medicines Agency launched a data network to generate RWE on vaccines and medications, signaling its interest in promoting RWE in drug regulation. The global RWE solutions market was valued at $1.3 billion in 2024 and was expected to grow to $3.7 billion by 2031, a CAGR of 13.9%.
Competition
Competitive Landscape

Source: Markets and Markets
Komodo Health competes in a fragmented RWE market landscape that is composed of a mix of RWD clearinghouses (IQVIA, Optum), EHR-native data providers (Epic, Cerner), and analytics platforms (Health Catalyst).
IQVIA and Optum are the incumbent leaders in the space due to their long histories and close relationships with pharmaceutical companies and payers. IQVIA has established a global presence since its founding in 1982, and Optum’s parent organization, UnitedHealthcare, is the largest health insurer in the US.
Existing EHRs like Epic and Cerner have also been making plays in this space by building in-house RWE tools. In 2019, Epic released Epic Cosmos, a real-world dataset of medical events for 16.3 million patient encounters from 310 health systems. Cerner acquired Kantar’s health division in 2021 to launch Cerner Enviza and support therapy development using RWD.
Given the importance of data volume and integration in this space, partnerships and M&As are key strategies to expand data networks and product offerings. For example, in 2025, Datavant acquired Aetion to expand its end-to-end RWE capabilities. Even non-healthcare companies have advanced into the space, as seen in Oracle’s acquisition of Cerner Corporation, one of the leading EHRs in the US, to form Oracle Health in 2022.
Smaller companies and startups like Komodo Health (Verantos, TriNetX, Flatiron Health) have had to compete on price, usability, and niche data offerings — for example, Flatiron Health and COTA Healthcare focus on RWE in the oncology space.
Competitors
Optum: Founded in 2011, Optum is a subsidiary of the public company UnitedHealth Group, which has a market cap of $297.5 billion as of December 2025. It provides pharmacy services, health care operations, and analytical services and serves 80% of US health plans, 90% of US hospitals, and 67K pharmacies as of October 2025.
As of 2023, Optum’s RWE division has access to 285 million lives worth of real-world data. While it does provide data consulting through services like Evidence Engine, Optum also offers IT solutions like Clinformatics Data Mart, which includes real-world data on over 84 million patients, with about one-third of them having enrollment information spanning three or more years. While this limited dataset is much smaller than Komodo Health’s Healthcare Map, Optum still leaves a large footprint in the RWE and life sciences space. It had supported 120 global life sciences companies and over 1K publications through its RWD as of January 2024, and earned $253 billion in revenue in 2024.
IQVIA: IQVIA is a public company founded in 1982 with a market cap of $38 billion as of December 2025. It is a global provider of clinical research services, commercial insights, and healthcare intelligence for the life sciences and healthcare industries. As of December 2025, IQVIA spans 100 countries and more than 10K clients worldwide and boasts more than 1 million data feeds and over 1.2 billion real-world patient records, though it does not mention the number of unique patients or closed lives within its data. In 2025, IQVIA partnered with Nvidia to develop AI agents for healthcare.
Clarify Health: Clarify Health was founded in 2015 as an enterprise analytics company that provides self-serve insight generation. Its valuation reached $1.4 billion in 2022 after its $150 million Series D round led by Softbank Vision Fund. As of December 2025, it has raised a total of $328 million in funding with investors like BlackRock, Insight Partners, and Spark Capital.
Clarify Health’s analytics platform, Clarify Atlas, is similar to Komodo Health’s MapLab suite in that it maps patient journeys based on its dataset of over 300 million linked lives and 15 billion government and commercial medical and prescription claim records, and over 400 social determinants of health attributes. While Komodo Health focuses on serving life sciences companies, Clarify Health places more emphasis on serving providers and payers. Clarify Health has also moved further into the RWE space through its 2021 launch of Clarify Growth and Clarity Portfolio to surface RWE of health disparities.
Datavant: Datavant, founded in 2017, provides a digital ecosystem that allows providers to securely share patient data outside of their organizations and enables the exchange of over 60 million patient records per year in over 70K hospitals and clinics in the US. Datavant has raised $80.5 million of equity funding as of December 2025 from investors like Johnson & Johnson Innovation, Cigna Ventures, and Softbank Vision Fund, including a $40 million Series B round in 2020 led by Transformation Capital. In 2021, Datavant merged with Ciox Health, a health record IT firm, in a $7 billion deal.
Originally founded to improve clinical trial processes using AI, Datavant operates in both the healthcare data interoperability and RWE space. Datavant and Komodo Health first established a partnership in 2019 to enhance Komodo’s Healthcare Map and then expanded their partnership in 2023 to allow companies to connect proprietary datasets to the Healthcare Map. Datavant’s $400 million acquisition of RWE provider Aetion in 2025 signaled its intent to become a bigger player in the RWE market.
Business Model
As a health data provider and analytics platform, Komodo Health’s business model is data and infrastructure-intensive with fixed costs and recurring investments in compliance, engineering, and data acquisition. Substantial upfront investments were needed during product development to obtain the underlying data, develop platform capabilities for minimal human intervention, and build the application layer. In particular, the Healthcare Map required significant investment, with tens of millions of dollars being funneled into this data asset. Komodo Health also needs to invest in continuous data updates to ensure that generated insights are up-to-date.
Komodo Health employs an enterprise SaaS subscription model for its products. Komodo Health determines its pricing based on the cost of development for each product and the value delivered to its customers, especially compared to traditional consulting projects. This comparative pricing is evident in remarks made by Komodo Health President Web Sun in June 2024:
“If you think about traditional KOL consulting projects, they can cost anywhere from $150,000 to $450,000 per year. The crazy thing is, you do the study once, and then 18-24 months later, your consulting team might get brought back to rerun that exact same study.”
Traction
As of 2022, a report found that Komodo Health had “SaaS-like margins” and was growing its top line at a rate of more than 50% with an ARR of $150 million, though it was not yet profitable. In 2024, Komodo Health claimed that over 200 life sciences and healthcare organizations were using its product suite. Andreessen Horowitz partner Jorge Conde reported in 2020 that Komodo Health sold SaaS subscriptions to 19 of the top 20 biopharmaceutical companies. Notable partners and clients include Johnson & Johnson, Merck, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, and Cerner.
Komodo Health acquired Mavens in 2020 to enhance its enterprise life sciences offerings and Breakaway Partners in 2021 to create a comprehensive market access solution for formulary and prescription policies. To expand its data network, Komodo Health has also formed partnerships with other data companies and vendors. In 2020, Komodo Health partnered with Blue Health Intelligence (BHI) to integrate BHI’s patient data into the Healthcare Map. Komodo Health even launched its Healthcare Map on Snowflake Marketplace in October 2025, expanding access to its data beyond healthcare.
There is also widespread adoption of Komodo Health within the health outcomes and economics research space. At the 2025 Professional Society for Health Economics and Outcomes Research (ISPOR) conference, Komodo Health’s analytical platform was used for more than 250 peer-reviewed studies and 31 presentations. Consultancies like Deloitte have also used the Healthcare Map to analyze gender disparities in health benefits and measure the impact of health inequities on GDP.
One of Komodo Health’s significant partnerships was with Nasdaq Data in May 2025, demonstrating Komodo Health’s ability to advance healthcare insights in the financial services industry. The goal of the collaboration is to provide hedge funds, private equity, and venture capital firms with an in-depth view into the US pharmaceutical and healthcare industries through the Nasdaq Medical Claims Insights (NMCI) dataset, which is sourced from the Healthcare Map.
Valuation
As of December 2025, Komodo Health has raised a total of $514 million in funding, including a $220 million Series E round in 2021 led by Tiger Global Management and Casdin Capital that brought its valuation to $3.3 billion. Prior to its $50 million Series C round in January 2020, Komodo Health had raised seed, Series A, and Series B financing without announcing any of those rounds, prompting Sundeep Peechu of Felicis Ventures to dub the company an “anti-unicorn” for its modest approach and disciplined focus on operational excellence rather than chasing valuations.
In 2022, there were rumors that Komodo Health was planning to IPO. However, Komodo Health CEO Nathoo later stated that Komodo Health “was IPO-ready but wouldn't move to go public until the economy improved.” Komodo Health ended up securing a structured equity infusion of $200 million led by Coatue Management in November 2022 and laid off 9% of its workforce “to stay nimble and efficient as [the company] moves into an uncertain economic landscape”.
Key Opportunities
Acceleration of AI-Native Tools in Health Analytics
Deeper AI integration could provide a key avenue for growth for Komodo Health, driving faster insights and improved usability across its platform. Komodo Health is already playing a larger role in the healthcare AI space, especially with its deployment of Marmot AI. In 2025, AI-native life sciences company Anervea.ai partnered with Komodo Health as “the first partner in Komodo [Health]'s ecosystem to construct licensable, AI-native tools directly on top of Komodo [Health]'s healthcare intelligence platform.” Later that year, Alnylam Pharmaceuticals decided to embed Marmot AI into its operations with the goal of deploying custom AI agents for its business functions. As “the first AI to speak the language of healthcare analytics”, Marmot AI could eventually evolve into a health-specific copilot for medical and commercial teams.
There is certainly an appetite for AI within the RWE space. A 2025 survey found that over 50% of biopharmaceutical organizations have already paired AI with RWD, and 93% believe that AI technologies can make RWD more accessible and impactful.
Shift to Value-Based Care and Outcomes-Based Pricing
Value-based care over fee-for-service is a rising healthcare trend. As payers and pharmaceutical companies are increasingly negotiating value-based contracts, they need reliable real-time outcomes data to justify and calculate pricing.
Some of Komodo Health’s products already support these use cases. The launch of the Drug Projections product in 2024, which showed projected metrics rather than only displaying retrospective data, indicates a strategic move towards developing more predictive solutions that could power outcomes-based forecasting and strategies. The Komodo Patient Insurance (KPI) dataset was launched in the same year, enabling accurate identification of a patient’s pharmacy and medical insurance status, thus supporting the need for payer mix analysis and reimbursement tracking in value-based care. Komodo Health’s website also lists its solutions for risk-bearing entities to support actuarial risk modeling and early disease detection.
Value-based care models have already seen a 25% increase in health care provider participation from 2023 to 2024. According to McKinsey, growth in value-based care may be on track to reach $1 trillion in enterprise value in 2027 as the landscape matures.
Integration with Precision Medicine
Precision medicine focuses on tailoring treatments to specific groups of patients based on genetic differences. Komodo Health’s longitudinal Healthcare Map and RWE generation can support precision patient finding and outcomes tracking, especially for rare diseases. The company has been making progress in this direction through its partnership with Janssen in 2021 to help with patient recruitment for clinical trials. Komodo Health’s partnership with population genomics company Helix to combine Helix’s genomic datasets with the Healthcare Map is also a step towards facilitating the development of precision medicine.
Komodo Health has also partnered with many patient advocacy groups that are focused on rare diseases, including the Cholangiocarcinoma Foundation, PSC Partners Seeking a Cure, and the Foundation for Sarcoidosis Research. There has also been significant interest in using AI to identify rare diseases — Komodo Health researchers collaborated with Regeneron in 2025 to publish a study in the scientific journal Nature that demonstrated how AI-powered algorithms, when paired with a database like the Healthcare Map, can be used to identify patients with the rare disease Homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HoFH) based on the pattern of symptoms, diagnoses, and treatment before diagnosis.
There has already been a rising number of clinical trials that incorporate precision medicine, and increases in big data, AI, and longitudinal patient cohorts continue to drive the growth of this field.
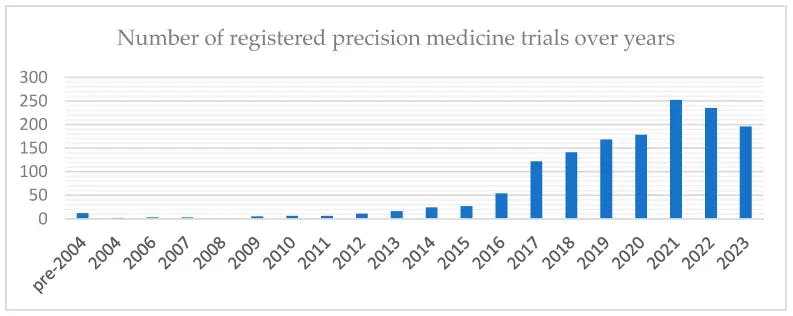
Source: Journal of Personalized Medicine
Key Risks
Reliance on Payer-Sourced and EHR Data
Much of Komodo Health’s success relies upon continuous data access and updates from third-party sources — for example, the Healthcare Map is directly derived from payer sources, including fee-for-service Medicare data, Medicare Advantage claims, commercial claims, and Medicaid claims. If any data or marketplace providers change pricing or access models, Komodo’s data quality and delivery model could suffer.
There is already a growing trend of large payers and health systems building their own real-world analytics services in-house, giving them a data access advantage and directly competing with Komodo Health’s data services. Competitors like Optum have direct access to payer data, and several EHRs like Epic and Cerner have recently launched their own real-world data solutions. If Komodo Health’s products are unable to stay competitive against these new players, they may lose customer traction.
Real-World Data Quality and Bias
Real-world evidence challenges primarily involve problems of data quality and bias. In one study, Flatiron Health found that structured mortality data in the EHR typically exhibited sensitivity levels around 65%, meaning that about 35% of actual deaths were missing from structured EHR fields. EHR data is inherently subject to many biases, including selection and informational biases. RWD is also generally more prone to selection bias than randomized controlled trials (RCTs), which reduce bias through randomization and blinding.
These underlying biases can also influence AI quality, with studies finding that AI models trained on biased or incomplete RWD can amplify existing disparities. As highlighted by Komodo Health’s Chief Marketing Officer, the quality of LLM and AI outcomes relies heavily on the quality of underlying data. Komodo Health will need to ensure high-quality of its real-world data by investing in validation and quality control in order to maintain credibility and customer trust.
Summary
The US healthcare system remains deeply fragmented, with data siloed across payers, providers, and health systems. Komodo Health is tackling this challenge by bridging gaps between patient journeys and health outcomes and accelerating real-world insight generation through its Healthcare Map and analytical platform.
Looking ahead, Komodo Health continues to forge major partnerships and extend its capabilities beyond the life sciences domain. CEO Nathoo once articulated this ambition to broaden Komodo Health’s reach:
“My vision of the future is that the Komodo platform is the back end of everything, of every study, of every piece of academic research, all the way to the way that the government makes decisions on how it addresses the health care of the population.”
Whether Komodo can achieve this vision will depend on its ability to preserve its edge in data quality and continue proving the real-world evidence value of its platform to its customers.