Thesis
Gaming and entertainment have often been cited as some of the clearest use cases of augmented reality devices. Some of the earliest widely used AR apps have been games or entertainment applications. As AR devices continue to grow more sophisticated, mixed reality may even herald a new era that redefines computing interfaces more significantly than anything since Douglas Englebart designed the computer mouse.
Driven by these technological currents, the augmented reality (AR) gaming market was valued at $8.4 billion in 2022 and is projected to continue to grow, spurred by the rising number of mobile gamers and by technological advancements in AR. Pokémon Go was a viral sensation when it launched in 2016. It has since received over 1 billion downloads, generating $6 billion in revenue, and retains its status as one of the most popular apps on the market in 2023, seven years after its launch. The company responsible for it was Niantic, which is an AR gaming company that has since made other popular games like Harry Potter: Wizards Unite, Pikmin Bloom, and NBA: All World.
Niantic’s vision is to build a digital layer around the real world, enabled by 3D maps, where people can interact with content and experiences in the context of the real world. Niantic’s “soft copy” of the world can enable augmented reality content and immersive experiences attached to real-world placement and interaction. Beyond specific gaming titles, one of Niantic’s other big products is Lightship, a software development platform for building AR experiences. Lightship has the potential to be a game engine for augmented reality. Instead of coding up computer vision or machine learning algorithms, developers use the Lightship SDK to access AR features in their apps or games.
Founding Story
Niantic was founded in 2010 as an internal startup within Google by John Hanke (CEO) and Phil Keslin (CTO). Prior to Niantic, Hanke and Keslin had founded a startup called Keyhole before joining Google. Keyhole was acquired by Google in 2004 and then became Google Earth. At Google, Hanke led Google Maps and Google Earth. As he said in an interview:
“I helped start a company called Keyhole that Google bought in 2004. We worked on this earth viewer project, which became Google Earth. I worked on Maps and Earth and those related projects for about six years at Google. That group grew from a few dozen people, about 30 people in 2004, to more than 1,000 engineers and project managers and a couple thousand contractors working on Google Maps in 2010.”
Keslin, meanwhile, worked as a senior staff software engineer where he contributed to the Google StreetView and Gmail products. While still at Google, Hanke wanted “to do something a bit more entrepreneurial” and got permission from Google execs including Larry Page to form a group to start creating products at the intersection of maps, mobile phones, and gaming.
The first product Hanke’s team produced was Field Trip, which was released in September 2012. As this was being launched, they began working on Ingress, which Hanke described as a “precursor to Pokémon Go” that made use of similar concepts like the use of real-world locations in a multiplayer digital game.
As a parent worried about his kids’ screen time, Hanke wanted to build a product that “would encourage exercise, but not in a heavy-handed way.” The internal team also had latched onto the idea of what Hanke called “real world social”, which was the idea of a product that would help people connect offline in the physical world.
Ingress was launched in 2012 and became what Hanke called a “cult hit”, with 15 million downloads. Then, in April 2014, Google’s Maps teams did an April Fool’s joke that was a mash-up with Pokémon that got 18 million views. It was at this point that Niantic reached out to the Pokémon Company to build a game around this concept.
In 2015, Niantic spun out of Alphabet Inc. as an independent, private company with $35 million in Series A funding from The Pokémon Company Group, Google, and Nintendo. In 2016, Niantic released Pokémon Go, an AR game that became popular worldwide. Pokémon Go generated more than $1 billion in 2016 and over $6 billion in cumulative revenue for Niantic as of June 2022. As of October 2023, John Hanke remains as Niantic’s CEO, Phil Keslin serves as CTO, and Mike Quigley (previously VP of Marketing for EA) serves as Chief Marketing Officer.
Product
Lightship Platform
Source: Niantic
Niantic, which began in gaming, has expanded into AR infrastructure. It first started developing its “Real World Platform” in June 2018, before changing the name to Lightship in May 2021. Lightship, a software development platform for building AR experiences, was officially released to developers in November 2021. Lightship is essentially a game engine for augmented reality. Developers can use the Lightship SDK instead of building their own computer vision algorithms. The platform is used internally at Niantic to develop AR games, and externally in companies such as Historic Royal Palaces, Coachella, and Led Zeppelin.
Lightship products include the Augmented Reality Developer Kit (ARDK) and Visual Positioning System (VPS). ARDK helps developers integrate AR features into their mobile app or game, with features such as:
Real-Time Mapping: Lightship SDK scans a user’s environment to detect walls and objects, then uses advanced Meshing technologies to transpose realistic virtual items on real-world environments. Developers can additionally integrate physics into the accurate Meshing system so that digital assets can react to the real world.
Multiplayer API: Niantic’s engine supports private peer-to-peer sessions along with its multiplayer features, and provides built-in server features such as synchronized clocks and session-persistent databases.
Semantic Segmentation: The product’s intuitive system automatically recognizes elements in an outdoor location such as the sky, artificial ground, water, and buildings.
8th Wall

Source: Niantic
In March 2022, Niantic acquired 8th Wall, a startup in web-based augmented reality (WebAR), which now allows developers to bring AR experiences to the web, expanding AR capabilities beyond smartphones. Well-known brands such as Bloomingdales, National Geographic, and Crocs have since partnered with 8th Wall. In November 2022, Niantic announced it integrated its Lightship Maps feature on 8th Wall.
Games

Source: Niantic
Niantic began building AR games with Field Trip, a location-based game that would offer users recommendations for places to visit, like a virtual tour guide. Next, it launched Ingress, a game that remains online and is listed on Niantic’s website. In 2019, Niantic shut down the Field Trip app, but it became the building blocks for its most popular game, Pokémon Go.
Pokémon Go is a free-to-play AR game using mobile devices with GPS to locate, capture, train, and battle virtual creatures, called Pokémon, which appear as if they are in the player’s real-world location. After the success of Pokémon Go, Niantic has also developed AR games, including Peridot, Monster Hunter Now, and Pikmin Bloom.
Previous games that Niantic had developed but has since ceased working on include Marvel World of Heroes, which was sunsetted in June 2023 after Niantic had layoffs and closed its LA studio. The same thing happened previously to Niantic’s Harry Potter: Wizards Unite, which was shut down in January 2022, and NBA All-World which was shut down in July 2023 within a year of its launch.
AR Glasses
In November 2022, Niantic announced it was developing augmented reality glasses in partnership with Qualcomm, allowing users to mix the real world with AR objects. The glasses will use a Qualcomm Snapdragon processor (the same family of chips as Meta’s VR headsets) and Niantic’s Lightship Visual Positioning System (VPS) will be integrating with Qualcomm’s SDK.
Rewarded AR: In-Game Ads
In June 2023, Niantic announced its own “Rewarded AR” ads format during the Cannes Lions International Festival of Creativity. Powered by 8th Wall, the AR ads have already been used by leading brands to deliver branded AR experiences to consumers. This strengthened Niantic’s shift towards finding unique ways to monetize its AR products; in the month prior, it partnered with Amazon to deliver “Amazon Anywhere,” its virtual world shopping experience.
Other Applications
Niantic released Campfire in 2021. Campfire is a social network integrating into Niantic’s games and sharing AR experiences with friends. Users can see their friends on a map and RSVP for local in-game experiences.
Niantic’s investment in social gaming experiences were done primarily through acquisitions. In 2021, Niantic acquired Mayhem.gg, an online platform for gamers to self-organize custom game formats, and Lowkey, a social gaming platform. In a blog post following the acquisition announcement, Ivan Zhou, the former CEO of Mayhem wrote about Niantic’s vision for social gaming experiences:
“In this new shared vision, games didn’t just connect people online - they could physically move people and bring them together in real life. It became obvious to our team that Niantic would be one of the most important companies shaping how people interact with each other in the future.”
Niantic Wayfarer is an app that allows eligible players will be able to review nominations of local points of interest (museums, art installations, historical markers, etc.) so they can be added to Niantic products (e.g. Portals, PokéStops and Gyms). It was introduced in October 2019.
In November 2022, Niantic introduced Truffel, a revised version of its Field Trip app, which is the first app ever created by Niantic that shut down in 2019. Truffel is a shared map of a person’s favorite places in a city that may be pinned together and explored with their friends.
In August 2021, Niantic acquired Scaniverse, which is an app that is able to scan objects and environments in high-resolution 3D. Scaniverse lets users capture, edit, and share 3D content directly from his or her phone. Being able to quickly create 3D objects is useful for creating content in AR and VR worlds.
In March 2020, Niantic acquired the startup 6D.ai for an undisclosed amount. 6D.ai allowed smartphone cameras to rapidly detect the 3D layouts of spaces around them. Niantic shut down 6D.ai’s existing developer tools after the acquisition, but the tech was integrated with the company’s Lightship platform, which was released in November 2021.
Niantic Ventures
The company also has an in-house investing arm known as Niantic Ventures. Niantic Ventures launched in November 2021 with a $20 million fund that aims to be a “catalyst for the AR ecosystem”. It invests in AR companies that use Niantic’s Lightship ARDK. Companies that Niantic Ventures invests in become part of the Niantic AR ecosystem. Portfolio companies as of October 2023 include Pixelynx and TRIPP.
Market
Customer
Niantic’s biggest game by revenue as of October 2023 was Pokémon Go. Niantic’s AR games target young adults. As of 2021, 48.4% of Pokémon Go players were between the ages of 18-29 while 43.1% were aged 30-49.. 19% of Pokémon Go downloads in 2023 occurred in the US, followed by Brazil and India at 10% and 6% each.
Niantic’s Lightship platform and 8th Wall target developers and studios developing AR experiences. In May 2022, Niantic invested in TRIPP, an extended reality (XR) and mobile experience for wellness apps, and PIXELYNX, a new gaming venture created by famous musicians and technologists. Both TRIPP and PIXELYNX develop parts of their apps using Lightship. Notable brands such as Tiffany and Co, Bloomingdales, National Geographic, and Crocs have partnered with 8th Wall to create AR experiences.
Market Size
The AR gaming market was estimated to be $8.4 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow to $38 billion by 2027. More broadly, the addressable market for mobile gaming was $108 billion in 2022, while the total addressable market for game development was $957 million in 2020. Globally, there were 3.2 billion gamers as of 2023, which is expected to grow to 3.3 billion as of 2024. Participation in AR gaming was expected to grow to 216 million by 2025 according to an April 2022 report. While this would represent more than a 32% CAGR from 2021 to 2026, it is still only ~6.8% of the global gaming market.
However, interest in AR gaming is continuing to grow. 32% of Americans were interested in playing AR games as of May 2023. As early as 2019, 66% of gamers were interested in AR gaming, with one-third citing their main hesitation about AR gaming being the quality of mobile devices for the gaming experience. As the appetite for the medium continues to increase, there will likely be a higher demand not only for AR games but for technology like Lightship to more effectively enable game development.
Competition
AR Platforms
Google ARCore: ARCore, which Google announced in February 2018, is Google’s AR SDK which provides cross-platform APIs to build AR apps on Android, iOS, Unity, and web. ARCore is also known as Google Play Services for AR and supports a wide range of devices. Alphabet, Google’s parent company, had a market cap of ~$1.8 trillion as of October 2023.
Apple ARkit: ARKit, which was first introduced in June 2017, is Apple’s platform for developers to create or integrate AR experiences into iOS apps. Its offerings include RealityKit, which provides APIs to help build AR experiences. It also offers Reality Composer, which allows users to create interactive AR without prior 3D experience by converting existing 3D models to work on iPhones or iPads. Another offering, AR Quick Look, allows developers to place 3D objects in the real world. Apple’s Vision Pro AR glasses, which are set to be released in early 2024, may help bolster Apple’s position in the AR market. Apple had a market cap of ~$2.8 trillion as of October 2023.
Snap AR: Snap AR is Snap Inc.’s AR platform. It claims to have been used by 300K creators to create 3 million Snap “Lenses” which were viewed over 5 trillion times as of October 2023. Its Lens Studio offering is a desktop application for artists and developers to build AR experiences, and its Lens Web Builder is targeted towards brands and agencies who want to build AR experiences with no coding experience required. Snap had a market cap of $15.6 billion as of October 2023.
Meta Spark: Meta’s Spark platform provides tools for developers to build AR experiences for Meta’s larger AR ecosystem, which the company has invested significant resources in developing. Meta began its foray into AR/VR very early on with its acquisition of Oculus in 2014, and its Meta Quest 2 VR headset was the most popular headset on the market as of 2023. Meta has a market cap of $815.6 billion as of October 2023.
AR Glasses
In November 2022, Niantic announced the development of new AR glasses in collaboration with Qualcomm, which will be compatible with its Lightship SDK platform. Niantic’s AR glasses directly compete with Snapchat Spectacles, Meta Smart Glasses, Microsoft Hololens, Apple’s Vision Pro, and Magic Leap.
AR Games
According to one source, at the top of the list of AR games on the market as of October 2023 are Niantic’s Pokémon Go and Ingress. Other popular games include Zombies, Run (the highest-grossing fitness app on the Apple store with 10 million users as of October 2023), Spectrek, and Temple Treasure Hunt.
Business Model
Games
Niantic primarily generates revenue from games like Pokémon Go through in-app purchases. Players can buy PokéCoins, Pokémon Go’s in-game currency, allowing users to purchase things like premium items and/or upgrades in the Pokémon Go Shop.
Additionally, Pokémon Go makes money through in-game advertising, where digital events are overlaid on top of a real-world location, incentivizing players to visit a store or restaurant. Sponsor partners, like McDonald’s, pay Niantic 50 cents per visitor attracted by the game. Pokémon Go’s payout uses the cost-per-visit (CPV) ad model, where advertisers only pay when a user enters the advertised store. Niantic also generates revenue through in-app purchases in its other games, such as Pikmin Bloom.
Pokémon Go has also been monetized by digital events with large business brands such as Lawson, a popular convenience store chain in Japan. At the peak of Pokémon Go’s launch in the summer of 2016, McDonald’s Japan activated 3K stores in the country, which produced $900K and $3 million in payouts to Niantic per day.
Pokémon Go also sells branded Pokémon Go toys, collectibles, apparel, and more through its official online store Pokémon Center. The merchandise ranges in price from $12.99 to $54.99.
Lightship & 8th Wall
Besides gaming revenue, Niantic also generates revenue through selling its Lightship and 8th Wall development platform as a service. For example, brands such as Coca-Cola use 8th Wall and Lightship to build AR experiences for consumers.
Costs
In terms of significant costs, Niantic pays a licensing fee for various Intellectual Properties (IP) used in its games, such as the Pokémon Company (Pokémon Go), Nintendo (Pikmin Bloom), and Warner Bros (Harry Potter: Wizards Unite). Additionally, Niantic spends money on research and development, developing new games such as Peridot and extending capabilities of new technology platforms (Lightship, 8th Wall) and hardware like AR glasses.
Traction
By June 2022, Pokémon Go had generated 672 million downloads and $6 billion in revenue since launching in 2016. It had over 150 million players globally in June 2022, and player spending grew by 19%-34% YoY from 2016 to 2021.
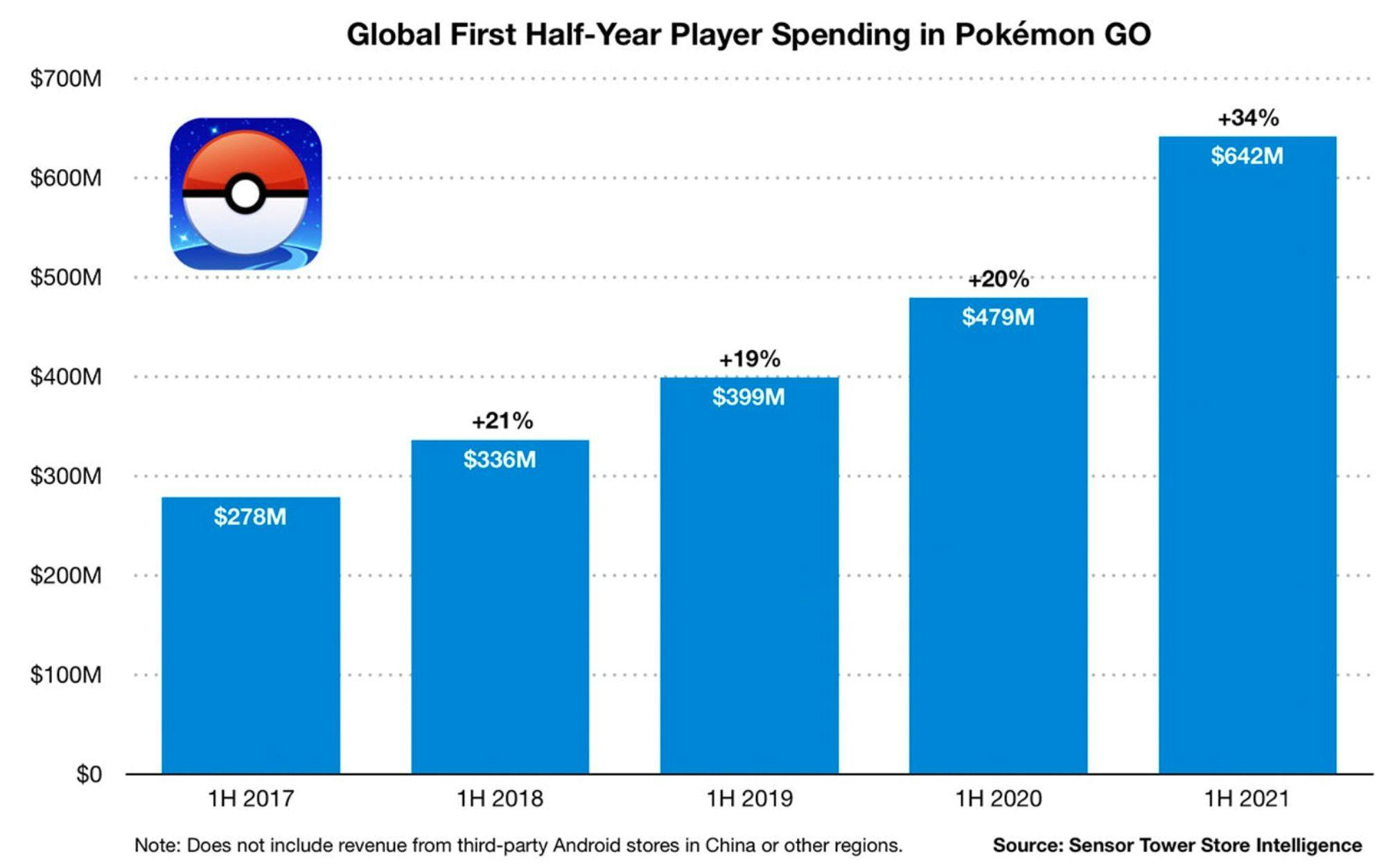
Source: SensorTower
However, player spending decreased 45% YoY from 2021 to 2022, generating $430 million in revenue in the first half of 2022. This was the first meaningful YoY revenue drop the game had seen since its release in 2016. Sources point to several possible causes for the revenue decline, including a spike in early 2021 revenue given consumers receiving COVID stimulus checks, as well as the easing of COVID restrictions early in 2022 leading to more spending on in-person experiences as opposed to gaming.
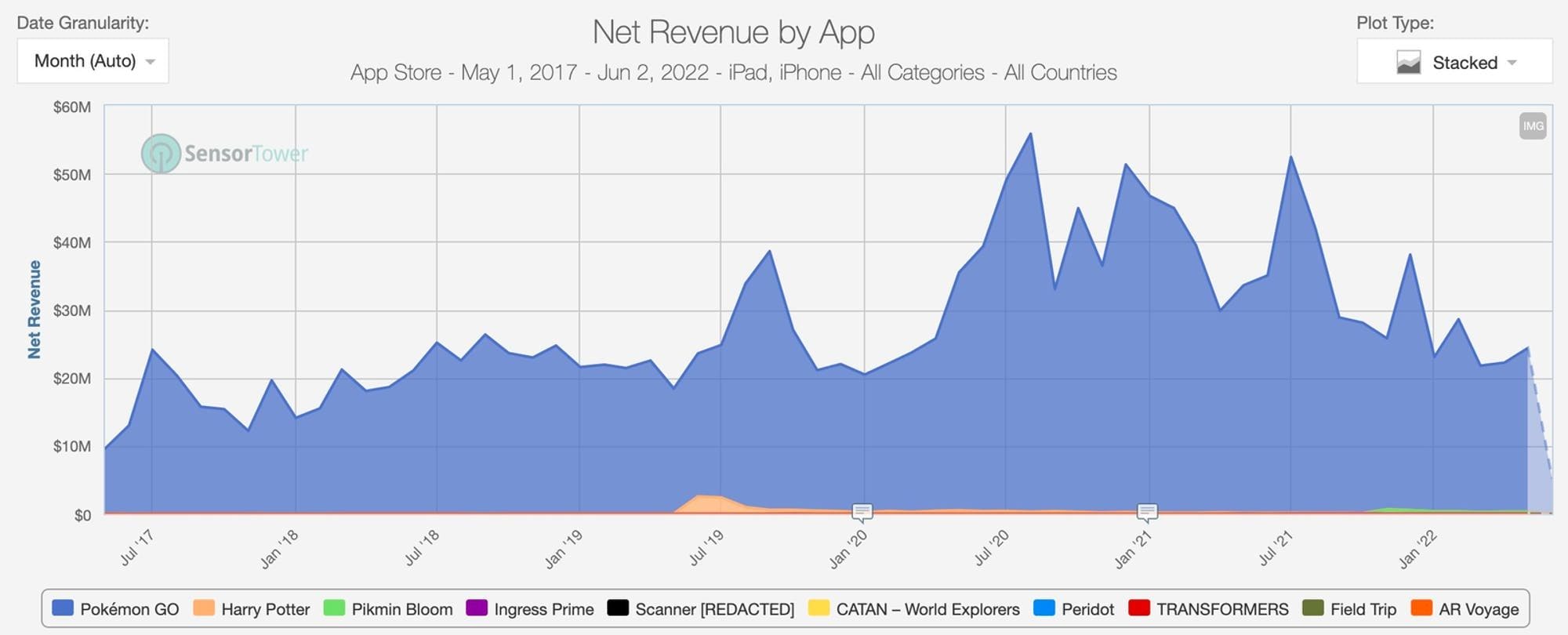
Source: Naavik
Pokémon Go’s active player count peaked at 232 million in the year of its launch (2016). Since then, it has seen a steady decline from its viral peak and had 79.3 million active players as of July 2023. On the platform side, notable companies such as Historic Royal Palaces, Coachella, and Led Zeppelin have used Lightship to develop AR experiences.

Source: Niantic
Valuation
Niantic raised a $300 million Series D at a $9 billion valuation in November 2021, bringing its total funding to $770 million, led by Coatue. Other investors of note include Battery Ventures, CRV, Founders Fund, IVP, Spark Capital, Google, and Y Combinator.
Niantic’s total 2021 revenue was estimated at ~$909 million, which would represent a 10x revenue multiple. For comparison, Snap Inc., a public competitor, had a market cap of $15.6 billion as of October 2023 at a revenue of ~$4.5 billion, implying a 3.5x revenue multiple.
Key Opportunities
Expand Brand Partnerships
In 2021, Niantic raised its Series D with a mandate to build the “real-world metaverse.” It sees expanding the Lightship development platform as a way to position Niantic as owning the game engine and infrastructure for augmented reality moving forward. A key opportunity is to grow the Lightship AR platform by developing partnerships with brands interested in building AR customer experiences. Niantic has already started experimenting with brand partnerships using its 8th Wall and Lightship for Web program, such as a Coca-Cola experience where vending machines drop virtual items and an HBO experience that allows users to raise their own virtual dragons.
New Experience Capabilities
Niantic can continue to extend the capabilities of the Lightship platform, such as extending the VPS feature to more locations worldwide, allowing for building AR experiences across more cities globally. This will allow more opportunities to partner with local small businesses in a specific location, expanding Niantic’s customer base. Additionally, Niantic has explored building additional AR experiences, such as LEGO minigames, 3D scanning of real-world objects, and virtual clothing try-ons. These experiments are a way to explore new opportunities to build AR games and brand partnerships.
Key Risks
Lack of Revenue Diversification
An overwhelming majority of Niantic’s revenue comes from Pokémon Go. In July 2022, Pokémon Go accounted for 99% of Niantic’s overall revenue. Niantic has not made another popular game since the success of Pokémon Go in 2016. It shut down games like Harry Potter: Wizards Unite in January 2022 after in-app spending and installs dropped 57% YoY and stopped developing games such as Transformers: Heavy Metal.
In June 2023, Niantic also announced that it would cancel NBA All-World, its AR basketball franchise in the metaverse, as well as an unnamed Marvel-based title, simultaneously reiterating that Pokémon Go was its “top priority”. This further exacerbates the concentration risk of the company on one game, and although Pokémon Go still has a robust user base it has steadily declined every year since 2016.
Revenue Slowdown and Economic Conditions
Niantic laid off 8% of its workforce in June 2022 due to macroeconomic conditions and laid off an additional 230 employees (~22% of its workforce) a year later in June 2023. Niantic faces a considerable risk of declining revenue from Pokémon Go, especially since player spending was down 45% YoY from 2021 to 2022. Consumer spending and business marketing spending are both sensitive to macroeconomic conditions, which remained volatile in 2023.
Summary
Niantic is trying to build the infrastructure layer for augmented reality, capitalizing on the success of its popular AR game, Pokémon Go. However, Niantic faces headwinds due to macroeconomic exposure and a lack of diversification in its revenue. As a result, Niantic has fewer research and development resources for expanding its Lightship development platform. Niantic also faces competition from large companies such as Google, Apple, and Snap, which may build out similar capabilities for their established customer bases. However, if Niantic can grow Lightship successfully, it may become one of the best AR infrastructure layers able to operate on multiple platforms, or become the game engine for the first true “real-world metaverse”.






