Thesis
There are 3.3 billion gamers across the world in 2025, and that number continues to grow. The COVID-19 pandemic supercharged the gaming industry, with 82% of global consumers playing video games or watching video game content during the height of lockdowns. Although this acceleration has slowed since the pandemic, with a slight decline in global gaming revenue reported in 2022 (down to $184.4 billion from a peak of $192.7 billion in 2021), more people played games in 2025 than ever before, and a return to growth is expected following the pull-ahead caused by the COVID-19 lockdown period.
In the long term, gaming seems set for continued growth. As of 2023, two-thirds of all Americans under 18 played video games online. Mobile gaming is the largest segment, with 49.2% of the US population playing games on their smartphones in 2024. That year, global revenue from the mobile gaming industry exceeded $175 billion, surpassing the combined value of global music industry sales ($29.6 billion) and box office sales ($30 billion).
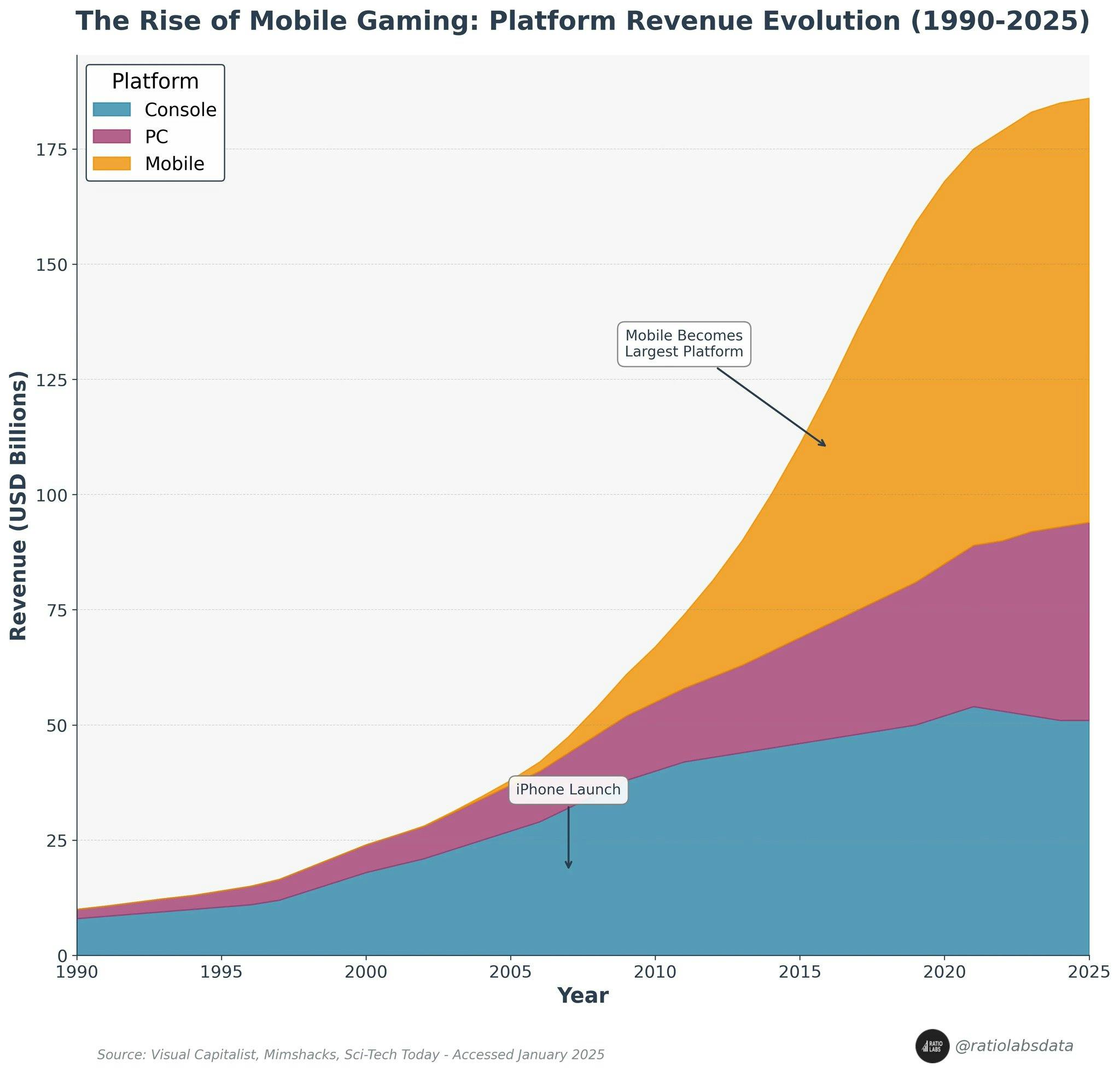
Source: Ratio Labs
Epic Games is a prominent gaming platform company. In addition to having produced titles like Fortnite, Rocket League, and Fall Guys, Epic Games provides an end-to-end digital ecosystem for developers and creators to build, distribute, and operate video games through the Unreal Engine, Epic Games Store, and Epic Online Services. In many ways, Epic’s business model is analogous to Amazon’s consumer business and its cloud computing service, AWS. Not only does Epic develop games, but it also builds game engines, which serve as the core infrastructure powering large parts of the gaming and 3D graphics industry.
Founding Story
Epic Games was founded in 1991 by Tim Sweeney while he was a mechanical engineering student at the University of Maryland. The company began under the name Potomac Computer Systems, a one-person computer consulting business run from Sweeney’s parents’ house in Potomac, Maryland. His interest in programming started as a child on an Apple II computer, and by college, he was creating small software projects for the IBM PC. One of these projects, a text editor he built for fun, evolved into a game called ZZT.
Released in January 1991 as shareware, ZZT was a basic text-based adventure game that included a built-in level editor that allowed players to create and share their own games. This design helped form an early creative community around user-generated content. Sweeney’s father helped manage mail orders, and the shareware model gave Sweeney direct control over distribution and customer feedback. Though ZZT sold only about 4K-5K copies, it gave Sweeney enough momentum to turn Potomac Computer Systems into a video game company.
In 1992, Potomac Computer Systems was rebranded as Epic MegaGames to make it sound larger and more established. Around the same time, Sweeney brought on Mark Rein as co-founder to handle business and publishing operations. Rein had previously served as a “probationary president” at id Software, which he joined after contacting co-founder John Romero to help with the Commander Keen series. Rein had begun by playtesting Commander Keen 4 and later managed negotiations for major deals, including FormGen’s publication of Commander Keen in Aliens Ate My Babysitter and Spear of Destiny. After leaving id due to internal disputes, Rein joined Epic to take charge of business development and allow Sweeney to focus on leading engineering. Due to the company’s rapid growth, Sweeney left university one credit short of completing his degree.
Throughout the 1990s, Epic remained a small team that attracted young and skilled developers, including Cliff Bleszinski, who joined at age 17 after submitting his game Dare to Dream to Sweeney, and would later become the company’s design director. The company relocated to Cary, North Carolina in 1999 and dropped “Mega” from its name, becoming Epic Games.
In 1995, Sweeney developed the Unreal Engine, a 3D computer graphics game engine, which laid the groundwork for Epic Games’s first-person shooter Unreal (1998). Unreal achieved commercial success, reaching sales of 1.5 million units by 2002. Epic Games also began licensing out the first version of Unreal Engine to other game developers.
ZZT and Unreal Engine were the foundational pillars of Epic Games. In both cases, Sweeney developed the game engine first and then used the engine to produce a game. In recent decades, Unreal Engine was used to create the popular game Fortnite, and many other titles from a diverse range of external developers.
In the following years, Epic continued to expand its leadership team with hires like Nate Nanzer from Blizzard Entertainment to oversee competitive esports and Randy Gelber as Chief Strategy Officer. Veteran departures, including Cliff Bleszinski in 2012 and Rod Fergusson in 2014, marked the company’s shift toward live-service models and platform growth. By the early 2010s, it was clear that the industry was shifting towards a games-as-a-service (“GaaS”) and free-to-play (“FTP“) model. Epic sold a 40% stake to Tencent in exchange for their expertise on this transition. With the new capital injection, Epic embarked on a series of strategic changes: it made Unreal Engine 4 free, moved a few of its titles to an FTP model, launched the Unreal Marketplace, and cut its dependency on other publishers.
Product
In addition to flagship games like Fortnite, Epic provides an end-to-end digital ecosystem for developers and creators to build, distribute, and operate video games through the Unreal Engine, Epic Games Store, and Epic Online Services. Using a GaaS and FTP model for its products, Epic Games lowered the barrier to entry for creating and playing games. As more games are built with Unreal Engine and distributed through the Epic Games Store, developers and gamers become further entrenched in Epic Games’ ecosystem.
Gaming: Fortnite
Fortnite serves as Epic Games’ flagship product. Launched in 2017, Fortnite is a free-to-play, cross-platform game with three main gameplay modes:
Battle Royale: Up to 100 players land on an island and fight other players until no opponents remain.
Party Island: A social hang-out space where players can dance, fish, race, and attend live virtual concerts by celebrity DJs and musicians. Users portray their identities via skins and avatars.
Creative Mode: Players can create digital worlds, games, and stories using the assets and mechanics of Fortnite in a Minecraft-like experience. Additionally, users can play games made by other players. In March 2023, Epic Games launched the public beta of the Unreal Editor for Fortnite (UEFN) to improve the creative options for creating and publishing games within Fortnite.
In the long term, Fortnite is a testbed for Epic’s version of the metaverse, persistent virtual worlds that continue to exist even when people are not playing. Epic brought real-world experiences to Fortnite through partnerships with brands (Disney and the NFL) and celebrity musicians (Deadmau5 and Ariana Grande). Epic continues to test new experiences in Fortnite, blurring the line between the real and virtual worlds.

Source: Epic Games
Unreal Engine
Unreal Engine is one of the most popular 3D game engines in the world, holding a 16.3% market share in the industry in 2025. Game engines are software development programs originally used to develop video games. Over time, these powerful rendering and visualization tools also expanded to support other industries, including architecture and manufacturing. Today, Unreal Engine is used not only in video games (Fortnite, Arkham Knight, Mortal Kombat X) but also in film and television (The Mandalorian), automotive (Nascar, Ferrari), and fashion (Balenciaga).
Over time, Epic built or integrated additional developer tools into the Unreal Engine, making developing 3D digital content more efficient. Examples include Metahumans, a framework for creating high-fidelity digital humans, and Twinmotion, a real-time immersive 3D architectural visualization platform. First launched in 1998, Unreal Engine is now in its fifth generation, which was announced in 2020 and released to developers in 2022.
Unreal Engine 5.7, released in Q3 2025, marked the largest update since the Unreal Engine 5 launch. It introduced Nanite Foliage for real-time rendering of wind-reactive vegetation and MegaLights for large-scale dynamic lighting with improved performance and expanded support for directional, particle, translucent, and hair lighting. The update also added an AI Assistant for contextual guidance and in-editor C++ code generation and improved skeletal mesh editing.
In October 2024, Epic Games launched Fab, a platform for buying and selling digital assets such as 3D models, textures, animations, and other content used in game development and real-time 3D projects. It supports creators across Unreal Engine, UEFN, and other engines.

Source: Epic Games
Epic Games Store
Launched in 2018, Epic Games Store (”EGS”) is a digital video game storefront, providing a game catalogue, friends list management, player matchmaking, and other features. After the success of Fortnite, Epic used the profits to enter the gaming distribution market and to break its reliance on Steam, the largest PC game storefront.
EGS rapidly gained popularity by offering developers and publishers time-exclusivity agreements, which stipulate that games cannot be released on other storefronts for a defined period of time in exchange for minimum revenue guarantees. This strategy has been effective but also controversial, as gamers expressed frustration over games constantly moving storefronts due to EGS exclusivity contracts. Before EGS, timed storefront exclusivity was rare in PC gaming.
Source: Epic Games
In September 2024, Epic Games launched the Epic Games Store on mobile, making it available on Android worldwide and iOS in the European Union. Before September 2024, EGS was accessible only on PC and Mac through the Epic Games Launcher. Epic Games has announced plans to launch the app in the UK and Japan by the end of 2025, contingent upon new legislation permitting third-party app stores on iOS devices.
In October 2025, Epic Games Store introduced Epic Web Shops, a direct-to-consumer platform that allows developers to sell in-game content to players on both PC and mobile devices. Developers can also use Epic Web Shops independently of distributing their games on the Epic Games Store; the shop also enables cross-platform purchases across other stores, including Google Play and Apple’s App Store.
Epic Online Services
Epic Online Services (”EOS”) is a set of cross-platform gaming services that help developers to launch, operate, and scale cross-platform games. EOS is roughly divided across 3 categories: account services, game services, and store services. Functionalities include authentication, player progression tracking, matchmaking, voice chat, and more.
Epic offers EOS to developers for free with the goal of “encouraging wider adoption of all of Epic’s offerings, and of making cross-play, cross-progression, and other open and interconnected, online features more accessible to everyone.”
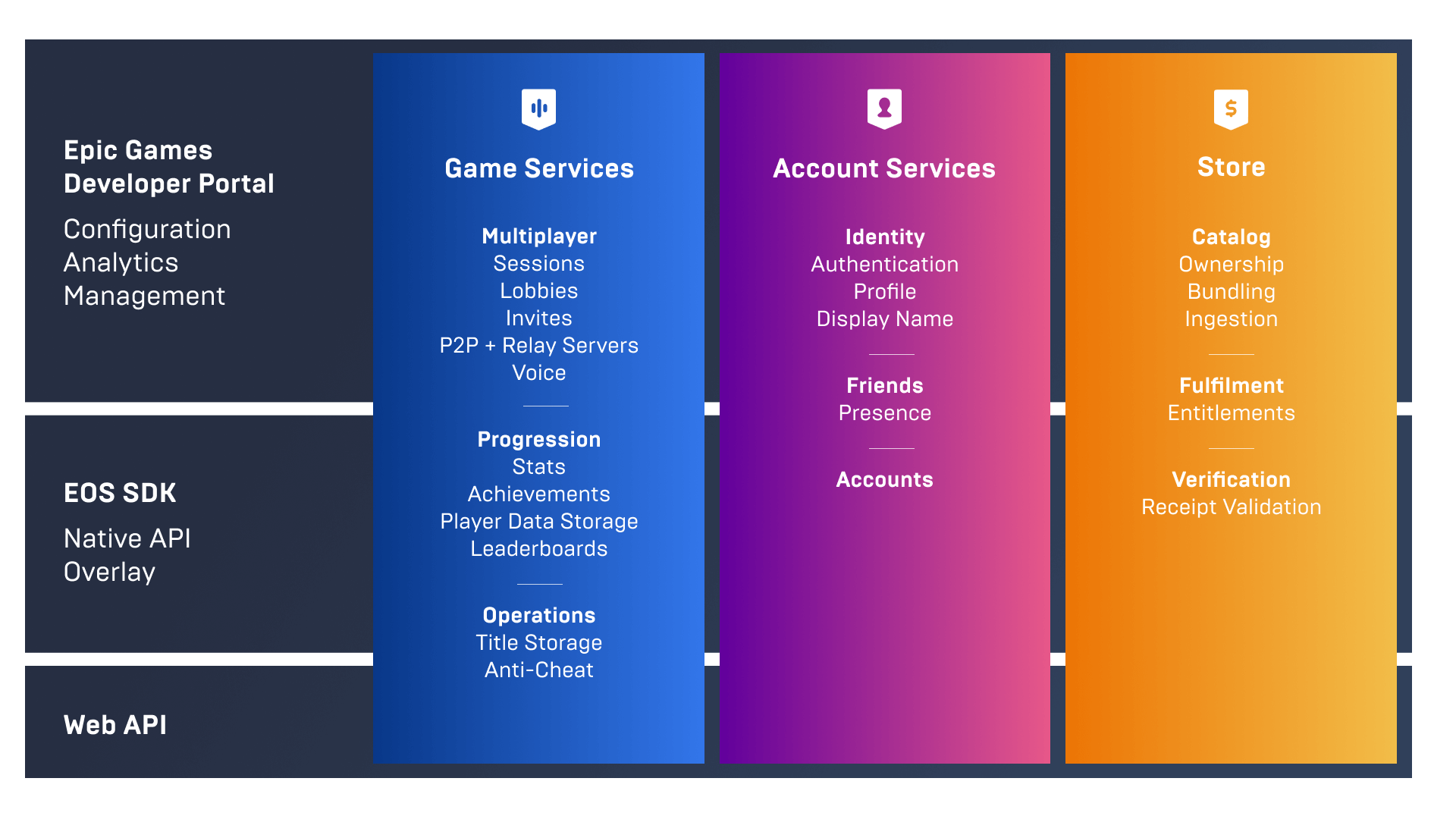
Source: Epic Games
Market
Customer
Epic Games serves 3 customer bases: gamers, developers, and publishers.
Gamers: Fortnite has over 650 million registered users and 110 million MAUs as of August 2025. Roughly 62.7% of Fortnite gamers are between the ages of 18 and 24, and another 22.5% are aged 25-34. Players aged 45 and over comprise only about 2% of the total customer base. Fortnite’s customer demographic skews male, with approximately 72-73% of players being male as of 2025. Most of its users come from the US (~30%), followed by Brazil (8%) and Russia (6%). Fortnite attracts a large number of non-avid gamers, with 37% of its players reporting not playing any other games. The median player spends 6–10 hours per week on the platform. Console play remains the top choice for Fortnite gamers, with 78% preferring consoles. Around 77% of players report making in-game purchases, with most spending activity focused on items like outfits and characters. In its first full year (2018), an average of $84.67 was spent by each Fortnite player. By 2020, this figure had increased to $102.42.
Developers: Developers who require 3D computer graphics and advanced rendering are all potential customers for the Unreal Engine. PC is the most popular platform for Unreal developers (with 80% targeting PC), followed by consoles and other real-time 3D segments. Games built with the Unreal Engine typically feature advanced lighting, shadows, and interactive graphical user interface (GUI) surfaces.
Publishers: In June 2025, Epic Games Store (EGS) began offering a 100% revenue share to publishers on the first $1 million in net revenue per title annually, reverting to the standard 88/12 split after that point. In contrast, Steam continues with the 70/30 split, which makes Epic’s platform especially appealing to emerging or mid-sized publishers seeking better profit margins. Epic also provides additional benefits to publishers, such as timed exclusivity and minimum guarantees.
Market Size
Epic Games competes in two markets: video games (Fortnite and Epic Games Store) and game engines (Unreal Engine).
The global video games market generated $299 billion in revenue in 2024 and is projected to reach $600 billion by 2030. Globally, the video game industry boomed during the COVID-19 pandemic, with 82% of global consumers playing video games or watching video game content during the height of lockdowns. Industry growth was also fueled by improved internet access and lower smartphone and PC prices. Twitch streaming and esports leagues are now recognized professions, with some star gamers earning over $5 million annually.
The global game engine market was estimated at $3.1 billion in 2025; the market is expected to grow to $8.3 billion in 2030. Unity is much more bullish on the total addressable market, citing $29 billion across games and entertainment in their S-1.
Epic Games' gaming unit and Unreal Engine are among the most popular players in their categories, but even at scale, they have only scraped the tip of the iceberg. Fortnite at its peak represented only ~2% of gaming industry revenue.
Competition
Gaming: Fortnite
Fortnite competes against other games within two categories: consumer gaming (Roblox, Minecraft, and Apex Legends) and esports professional gaming (League of Legends, Counter-Strike, and Call of Duty).
Consumer Gaming: At any point in time, each game’s MAUs can skew towards one direction over another. A game ranking can look different every month.
eSports Professional Gaming: Game popularity is judged on a variety of factors, including MAUs, prize earnings, number of tournaments, game hours watched, and more.
Source: NewZoo
Unreal Engine
Unreal Engine competes against standalone game engine companies (Unity) and in-house game engines developed by major publishers (Activision Blizzard’s IW Engine, EA’s Frostbite).
Unity: Founded in Denmark in 2004, Unity is a cross-platform game engine designed to make 2D and 3D development accessible to smaller studios and mobile developers. As of 2025, the company has a market capitalization of approximately $15.8 billion. As of 2025, Unity remains the most widely used engine in the industry, holding ~26% of global market share, compared to ~16% for Unreal Engine. On Steam, about 51% of released games were built with Unity and 28% with Unreal, but games using Unreal generated far more revenue, with Unreal-powered games accounting for 31% of all game revenue on Steam in 2024 versus 26% for Unity. As of June 2025, games made with Unity accounted for over 70% of the top 1K mobile games, including Pokémon Go and Temple Run.
However, Unity and UE serve different developer needs and project goals. Unity is a better fit for developers who have little to no experience in game development and 3D graphics, offering a lower learning curve and a small subscription fee instead of a revenue share. Unreal Engine, designed for more experienced developers, is preferred for high‑budget and technically sophisticated projects. In 2025, 25% of Unreal-powered games launched at a premium price point ($29.99+), compared to 6% for Unity projects.
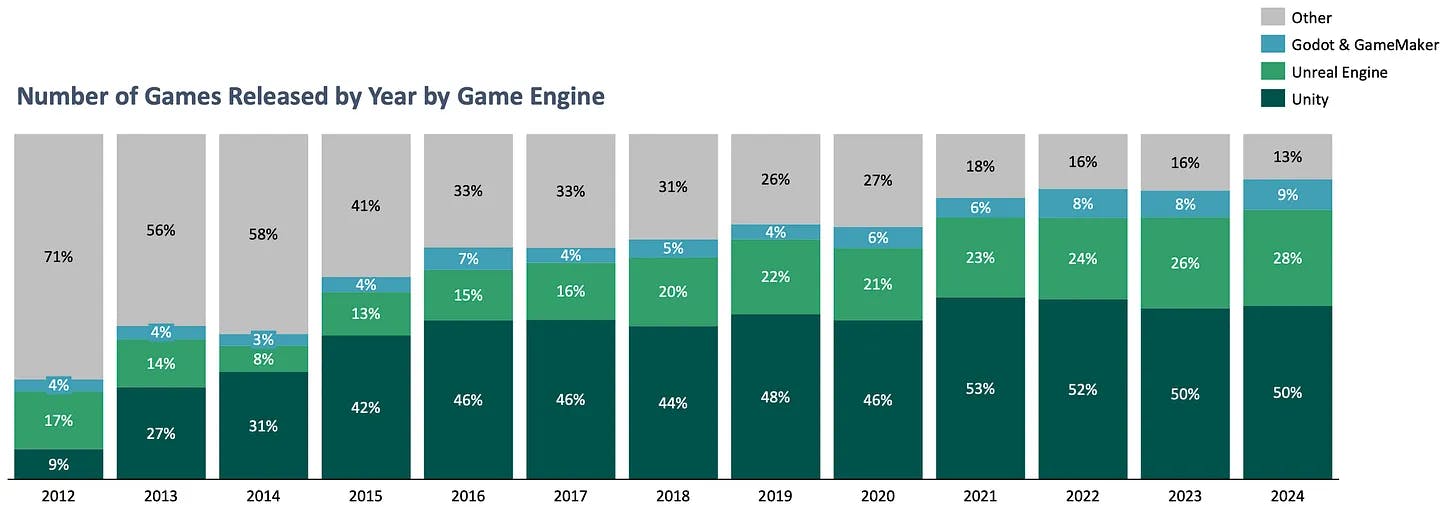
In-House Game Engines: Major game publishers typically use proprietary engines. Since many top games generate more than hundreds of millions in revenue, UE’s royalty structure (5% for revenue over $1 million) quickly becomes costly. Typically, in-house engines are not as feature-rich as Unreal or Unity; they also take time to build and significant engineering resources to maintain. As a result, some publishers have shifted to using Unreal or Unity instead of their proprietary engines. In 2012, over 70% of games released on Steam were made with custom engines; in 2024, this figure had declined to only 13%.
Epic Games Store
Epic Games Store (EGS) primarily competes with Valve’s Steam.
Steam: Steam is a digital distribution platform for video games operated by Valve Corporation. As of 2022, Valve was estimated to be worth $7.7 billion. Launched in 2003 primarily to distribute updates for Valve games, Steam has since evolved into the largest PC game distribution platform globally and controls about 70% of the market. As of 2025, Steam has approximately 147 million MAUs and generated roughly $10.8 billion in PC game sales, compared to about 74 million MAUs and $1 billion in sales for EGS. The gap between Steam and EGS has persisted despite Epic spending hundreds of millions on exclusive titles and free game giveaways.
Many gamers prefer Steam’s UI and find Steam to be faster and less buggy than EGS, EA’s Origin, and other storefronts. Steam also boasts a larger game library than EGS, with over 200K titles compared to EGS’s 4K games. Although Steam charges a much higher revenue share (30%) than EGS (12% only after a developer’s first $1 million in annual per‑app revenue), developers are willing to sell their games to Steam for its larger user base and established purchasing ecosystem. Additionally, if a developer sells to EGS under a timed-exclusivity contract, they risk restricting themselves to a smaller audience during that time window.
Business Model
Gaming: Fortnite
Fortnite is free to play. The majority of Fortnite’s revenue comes from sales of cosmetic items, such as avatars or costumes, and Battle Passes, which unlock rewards, new accessories, and items each season. In-app purchases can only be bought through Fortnite’s in-game currency, V-Bucks. To encourage more players to buy, Fortnite creates a sense of urgency by extending access to in-app purchases for a limited window of time.
Since 2023, Epic Games has attempted to shift Fortnite from a game into a user-generated content platform through Fortnite Creative 2.0 and Creator Economy 2.0. Players and developers can design custom maps using the UEFN, and Epic distributes 40% of Fortnite’s total net revenue, from V-Bucks and related purchases, to creators based on player engagement. In the first six months, creators earned over $120 million. This model reduces Epic’s reliance on microtransactions and Battle Passes, lowers development costs, and keeps players active between updates. It also connects to Epic’s broader ecosystem as creators use Unreal Engine tools and may publish through the Epic Games Store.
Epic has been engaged in ongoing legal disputes with Apple and Google. The conflict with Apple began in 2020, when Epic added a direct payment system in Fortnite, bypassing Apple’s 30% commission on in-app purchases. Apple removed Fortnite from the App Store, and Epic filed an antitrust lawsuit. In September 2021, the court required Apple to allow developers to link to external payment options but upheld Apple’s control over app distribution. In April 2025, the court found Apple in civil contempt for violating the injunction by imposing a 27% commission on external links. Fortnite returned to the US App Store in May 2025 with a third-party payment system.
Epic also sued Google over Play Store practices. In December 2023, a jury found Google unlawfully maintained a monopoly by restricting app distribution and tying in-app payments to its billing system. A permanent injunction issued in October 2024 required Google to allow alternative app stores and end exclusive agreements with device manufacturers. In July 2025, the Ninth Circuit upheld the decision and, in October 2025, the Supreme Court declined to intervene. Epic plans to launch Fortnite and the Epic Games Store on Google Play in the US.
In November 2025, Google and Epic reached a proposed court settlement to resolve Epic’s 2020 antitrust lawsuit. The agreement, pending judicial approval, would formalize sweeping Play Store reforms, allowing easier installation of third-party app stores and permitting developers to direct users to alternative payment systems. Google said it would implement a capped service fee of 9-20% on such transactions. Epic CEO Tim Sweeney praised the deal as it “genuinely doubles down on Android's original vision as an open platform”.
Unreal Engine
Unreal Engine makes money from both royalties and licensing:
Royalty: UE’s source code is available on GitHub and free to use until developers earn $1 million in gross revenue. After that threshold, Epic collects a 5% royalty (”engine royalty”) on any product that incorporates Unreal Engine code. Royalties are waived for games sold on the Epic Games Store, where Epic collects its standard platform fee instead. In 2025, Epic Games introduced the ‘Launch Everywhere with Epic’ program. If a game releases on the Epic Games Store simultaneously or before other supported platforms (PC, Mac, Android, and future iOS), the Unreal Engine royalty rate on those other platforms drops from 5% to 3.5%.
Licensing: UE has three license options, including Standard, Enterprise, and Custom. Enterprise and Custom licenses offer more bespoke support, private training, and more. Standard licenses are free, but uphold the 5% royalty. Enterprise licenses charge $1,500/seat per year.
Unreal Engine is free for personal use, projects, and linear content creation.
Epic Games Store
Epic Payments is Epic Games’ integrated payment system for handling transactions within games distributed on the Epic Games Store. It processes purchases, microtransactions, and in-app content, allowing developers to retain more control over revenue. EGS originally took a 12% commission (”platform royalty”) on game sales. Beginning in June 2025, however, the store changed its revenue-share model so that developers keep 100% of the first $1 million in net revenue per product per year, after which Epic applies its standard 12% cut. EGS is a loss leader for Epic Games, generating losses of $273 million in 2020 and $139 million in 2021. Court documents show EGS was expected to remain in the red through at least 2025, with projected cumulative losses of about $965 million by 2027.
The key drivers of EGS’s losses are Epic’s generous “minimum guarantee” program and the weekly free games. Epic fronts payments for timed exclusivity contracts in order to attract developers and publishers, even if the game is performing at a loss. EGS also fully subsidizes free games. In 2021, Epic distributed approximately 765 million free games to users, losing out on an estimated $18 billion.
Traction
As of 2025, Epic Games is the seventh-largest video game company by revenue. It generated an estimated $5.7 billion in revenue in 2024, up roughly 30% from $5.2 billion in 2023. In 2024, Epic Games had reached 898 million total cross-platform accounts, an increase of 94 million over that year.
Gaming: Fortnite
Fortnite historically has been and continues to be Epic Games’s largest revenue driver. It is one of the world’s largest games with over 650 million registered accounts and 110 million monthly active users (MAUs) as of early 2025. As of September 2025, it is the fourth most-played PC game globally, trailing behind Counter-Strike 2, Roblox (380 million MAUs) and Minecraft (204 million MAUs). Fortnite’s gameplay peaked during the COVID-19 pandemic. In April 2020, it amassed more than 3.2 billion hours of playtime compared to 2 billion hours each from Roblox and Minecraft. In 2019, users spent 3x more time playing Fortnite than on social media apps such as Facebook and Snapchat. Netflix had even cited Fortnite as a competitor in its Q4 2018 shareholder letter.
Source: Variety
Unreal Engine
As of October 2024, Unreal Engine had over 850K monthly active developers, with projections to surpass 1 million in 2025. As of 2025, over 6,000 companies globally use Unreal Engine for development. Revenue reached $275 million in 2023, up from $225 million in 2022 and $150 million in 2021. The engine holds about 16.3% of the global game development market and ranks among the top three engines worldwide. Its market penetration has steadily increased since 2015. In 2024, 28% of all games released on Steam were made with Unreal Engine.
Source: Gamedev Reports
Epic Games Store
As of 2024, the Epic Games Store (EGS) reached 295 million registered PC users. Peak daily active users (DAU) hit 37.2 million, with an average of 31.5 million, and monthly active users (MAU) peaked at 74 million, averaging 67.2 million. The store offered over 4K titles, including 1.1K new releases in 2024. Player spending on third-party games using Epic Payments totalled $255 million, while total spending, including Epic’s first-party titles, reached $1.1 billion.
Valuation
As of November 2025, Epic Games has raised a total of $7.9 billion across 13 funding rounds. The company is valued at $22.5 billion, following a $1.5 billion investment by The Walt Disney Company in February 2024 for a 9% stake. This valuation implies a 3.9x revenue multiple based on an estimated $5.7 billion generated in revenue in 2024.
This latest valuation reflects a market correction from Epic Games’s $31.5 billion valuation peak in April 2022, after it had raised a $2 billion round from Sony Group Corp and KIRKBI, the family-owned holding company behind the Lego Group. The 2022 round was raised on the back of Epic’s promises to build the metaverse, almost doubling Epic’s valuation within two years. In 2022, M&A and private investments in gaming soared to $127 billion as publishers made a bigger push towards game development. On top of Epic’s raise, transactions that year included Microsoft’s acquisition of Activision for $68.7 billion, Embracer’s acquisition of Tomb Raider and the franchise’s development studio for $300 million, and Tencent’s acquisition of Subway Surfers maker Sybo.
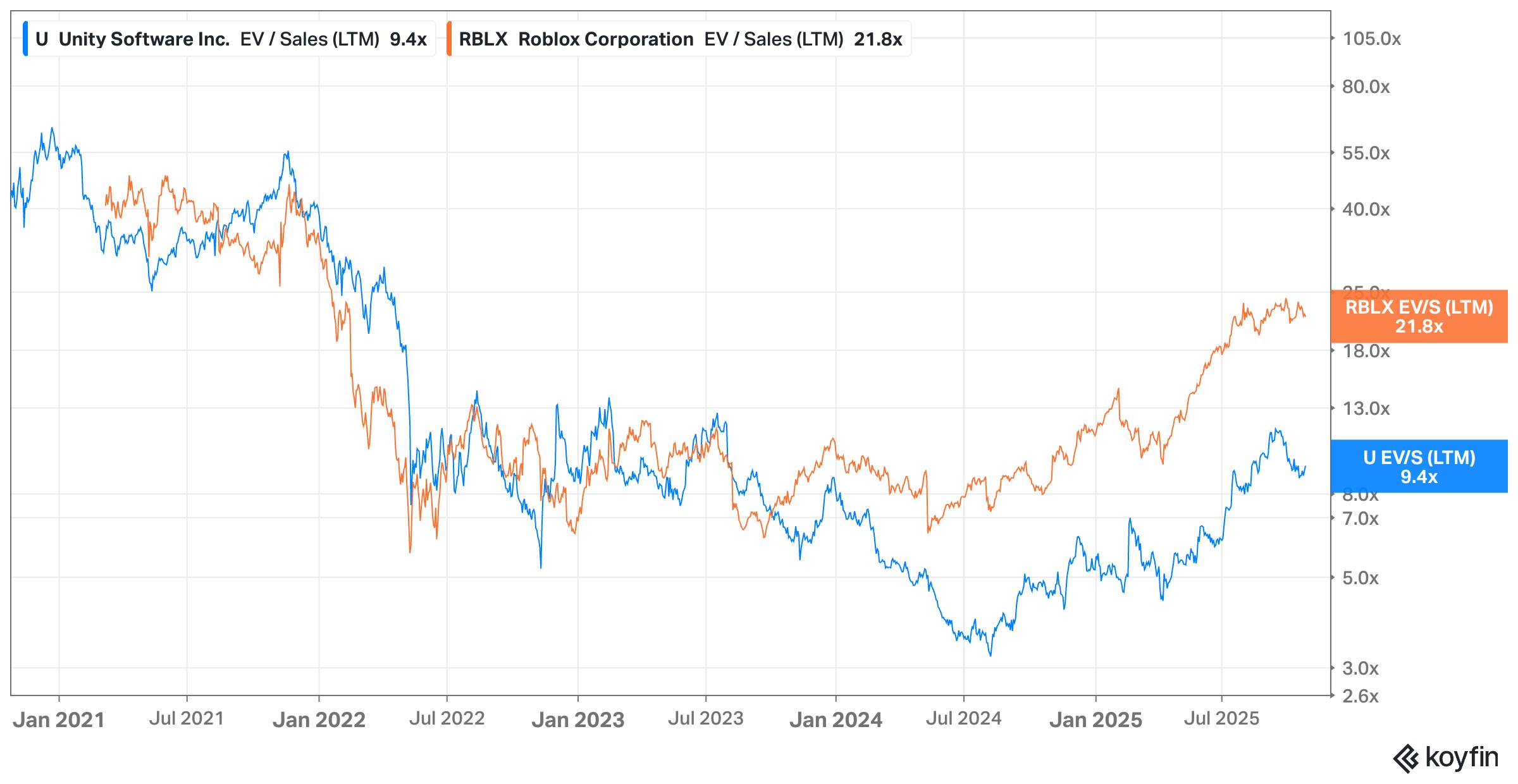
Epic Games’ 2024 valuation adjustment, which places it at a 3.9x revenue multiple (down from 6-7x in April 2022), mirrors a broader trend across the gaming industry. Revenue multiples for key public comparables have significantly compressed since the 2021–2022 peak. Unity Software’s multiple fell from above 60× in 2020 to roughly 9.4× in October 2025, while Roblox declined from around 40× in late 2021 to approximately 22× in October 2025. Despite moderate recovery since mid-2024, both remain far below their pandemic-era highs. This normalization reflects a sector-wide correction following the metaverse speculation hype cycle in 2021. Slowing engagement metrics, post-pandemic demand softening, and widespread layoffs in the gaming industry since 2022, peaking with over 15K job cuts in 2024, have further reinforced this trend.
Source: Koyfin (October 2025)
Key Opportunities
Growth Opportunities in Spatial Computing
Epic Games’ Unreal Engine supports AR/VR applications, digital twins, and metaverse experiences across multiple industries. The global spatial computing market is projected to grow from $149.6 billion in 2025 to $825.5 billion by 2032, a CAGR of 23.8%. In May 2025, SAS Institute partnered with Epic to integrate AI-driven analytics with Unreal Engine’s rendering, enabling manufacturers like Georgia-Pacific to optimize operations through digital twins. Unreal Engine is also used at Argonne National Laboratory’s METL facility to monitor and visualize emissions-free electricity generation in real-time. Epic can leverage its existing ecosystem of creators and developers to capture demand for real-time simulations in manufacturing, architecture, and urban planning.
Deepening Developer Value Proposition
Today, Epic’s Online Services serve as a toolkit, helping developers launch, operate, and scale games. However, EOS could also offer more analytics, ad tracking, and infrastructure support to help developers monetize and maintain increasingly complex systems. Today, Epic’s Online Services are free, offered to entice developers to stay in Epic Games' ecosystem. By contrast, Unity generates most of its revenue from Unity Operate Solutions, various cloud-based products that help provide analytics, ad distributions, and other infrastructure services for game developers. Epic Online Services could offer similar support for its developer community.
Key Risks
Fortnite Revenue Concentration
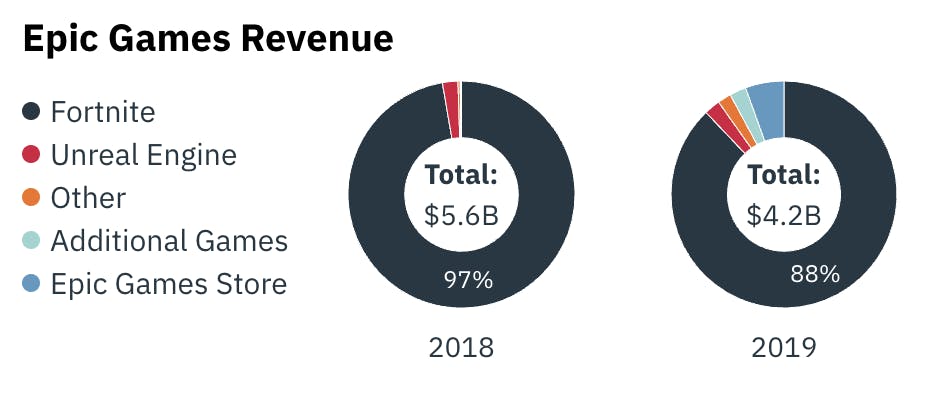
In 2020, Fortnite constituted roughly 77% of Epic Games’ revenue, down from 97% in 2018 when Fortnite’s MAUs peaked. Fortnite’s popularity has since fluctuated, causing revenues to be less predictable. Epic Games recognizes this issue, and the company has spent the past few years diversifying its revenue streams across the Unreal Engine, Epic Games Store, and third-party game titles. A significant decline in Fortnite revenue before growth in other areas could create financial risk, making the release of another hit or expansion of Fortnite’s offerings critical to reducing revenue concentration.
Defensibility of Epic Games Store
EGS undercuts Steam with a 12% revenue share versus Steam’s 30%. The storefront attracts developers and gamers through low royalties, minimum guarantees, and weekly free games. These incentives function as a loss leader to build a developer base, but are unsustainable long-term. Some estimates project EGS losses could reach nearly $1 billion by 2027 if current practices continue.
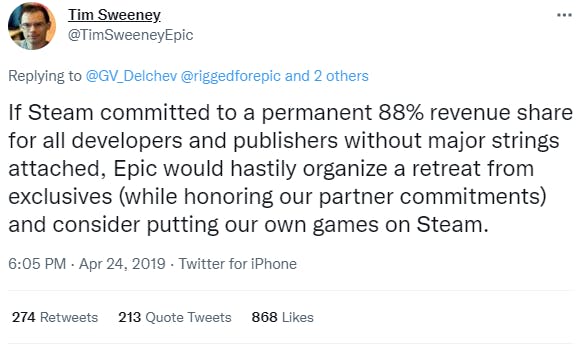
Sweeney has conceded that if Steam lowered its revenue cut, EGS would “retreat from exclusives” and consider putting their own games on Steam. Scaling back EGS, however, could cause repercussions in the broader Epic Games ecosystem, since the platform serves as a central distribution channel for Epic’s games, services, and content.
Source: Twitter
Legal Disputes
Prolonged disputes with Apple and Google over App Store terms and third-party payment access create uncertainty around timelines for expanding iOS distribution, potential regulatory changes, and ongoing litigation costs. Epic’s reliance on new legislation to enable third-party stores in regions like the UK and Japan by 2025 underscores its dependence on these platform holders. These external legal risks could constrain the growth of Epic Games’ mobile offerings.
Separately, in June 2025, Epic Games filed a lawsuit in the US District Court for the Eastern District of North Carolina against cheat software developer Ediz Atas (Sincey Cheats/Vanta Cheats), whose programs enable players to see through walls and auto-target opponents in Fortnite. Epic alleges the software violates Fortnite’s end-user license agreement, circumvents anti-cheat systems, and gives users an unfair advantage. Since February 2022, Epic has banned tens of thousands of Fortnite accounts using these cheats. Following DMCA takedown requests on YouTube, Atas impersonated Epic employees to challenge the removal of cheat-related content. Epic also sued five unnamed resellers distributing Sincey and Vanta cheats through websites, Discord servers, and Telegram channels. Widespread cheating poses a risk to Fortnite by undermining player experience and potentially damaging the game’s reputation.
Summary
The global gaming industry, worth over $298 billion in 2024, is rapidly evolving toward live-service models and creator-driven ecosystems, sectors in which Epic Games holds a leading position. The company generated an estimated $5.7 billion in revenue in 2024, the vast majority from Fortnite and the remainder from Unreal Engine licensing and the Epic Games Store.
However, Epic’s growth faces several structural risks. The company remains heavily reliant on Fortnite’s engagement cycles and microtransaction model, making it vulnerable to player churn or future regulation of in-game spending. Legal disputes with Apple and Google over distribution fees limit access to key mobile markets, while Unreal Engine faces mounting competition from Unity and proprietary engines. Overall, Epic’s vertically integrated model and expanding ecosystem provide significant long-term opportunities, but its sustainability depends on reducing Fortnite dependency and strengthening non-gaming revenue streams.






