Thesis
The population of people in the US aged 65 and above is expected to grow by 48% by 2032. This demographic shift has increased the demand for medical care, creating a shortage within the healthcare workforce. As of 2025, there was a projected deficit of over 500K registered nurses in the United States. Additionally, the Association of American Medical Colleges projects a shortage of between 37.8K and 124K physicians by 2034, affecting primary care and specialty areas crucial for aging populations.
The effects of this shortage are compounded by inefficiencies in how healthcare professionals spend their time. A 2020 study monitoring how 57 physicians spend their time showed that up to 49.2% was spent on administrative tasks, leaving just 27% for direct patient interactions. By supporting administrative needs, AI has the potential to reshape healthcare roles, allowing physicians and nurses to devote more time to patient care and less to paperwork, which could mitigate the effects of the workforce shortage and improve patient outcomes.
Additionally, healthcare delivery models are undergoing a structural shift toward value-based care (VBC), which rewards quality, efficiency, and patient engagement rather than service volume. The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) aims for all Medicare beneficiaries to be covered by VBC arrangements by 2030, accelerating the transition away from fee-for-service payments. As reimbursement becomes increasingly tied to outcomes such as patient satisfaction and care coordination, health systems are adopting technologies that can deliver consistent, data-driven, and scalable patient support.
Hippocratic AI is on a mission to build the first safety-focused LLM designed for healthcare. Hippocratic AI’s agents handle non-diagnostic, patient-facing tasks such as intake, scheduling, and chronic-care follow-up, reducing clinician burden. In doing so, it can help address the US healthcare worker shortage by augmenting human healthcare workers.
Founding Story
Hippocratic AI was founded by Munjal Shah (CEO), Vishal Parikh (Chief Product Officer), Meenesh Bhimani (Chief Medical Officer), Subho Mukherjee (Chief Science Officer), Saad Godil (CTO), Alex Miller (SVP of AI Operations), and Kim Parikh (SVP of Data and Content) in 2023. Hippocratic AI was co-created in partnership with General Catalyst, Andreessen Horowitz (a16z), and General Catalyst’s Health Assurance Ecosystem.
Shah is a serial entrepreneur whose interest in technology began in college. While at UCSD, where he was a computer science major, he wrote his senior thesis on building a neural network to predict protein-ligand binding efficacy for 3D model drugs. Immediately after undergrad in 1995, Shah continued his education at Stanford, where he earned a master's in computer science and machine learning.
After graduating, he spent two years as the director of marketing for a software company until he decided to start his first company in 1999, Andale, focused on helping small and medium-sized merchants sell on marketplaces like eBay and manage their transactions. After about five years, Andale was acquired by Vendio in 2006, but Shah left the company in 2004.
Shah’s next venture, which he founded in 2004, was Like.com, a machine learning company that leveraged computer vision to analyze details like the color, shape, and patterns of products online, enabling users to compare prices of similar products across different websites. Like.com was acquired by Google in 2010.
The day after selling Like.com, Shah experienced chest pains that landed him in the hospital. This health scare sparked his interest in healthcare, which led him to launch Health IQ in 2014, which provided lower insurance rates for customers with healthy lifestyles. However, prior to starting Health IQ and after he sold Like.com, Shah spent a little over a year leading Google Shopping’s product management team and began taking health classes on the side. In 2023, Health IQ filed for bankruptcy despite having received backing from a16z. Nevertheless, a16z supported Shah in his next startup, which he launched in 2023: Hippocratic AI.
The idea for Hippocratic AI originated in a conversation between Shah and General Catalyst’s Hemant Taneja, sparked by ChatGPT’s rapid rise and the potential of LLMs in healthcare. As ChatGPT entered mainstream use among patients and care teams, the sector “crossed the Rubicon,” embracing an irreversible path toward AI-enabled care delivery. The pair envisioned a safe LLM for healthcare capable of addressing workforce shortages while maintaining patient trust and safety.
Its early development prioritized humanistic communication — what Shah calls “bedside manner.” Hippocratic AI trained its model to deliver information in an optimistic, empathetic tone, acknowledging that “hope is a placebo” that can independently improve patient outcomes. To further enhance patient experience, especially for seniors who consume healthcare at a disproportionately high rate, the company developed voice capabilities that can convey and detect emotion, tone, and intonation during patient interactions.
Shah was explicit that Hippocratic AI would not perform diagnoses or administrative EMR tasks like documentation or pre-authorization letters, which he considered “too low a bar” for impact. Instead, the company addresses healthcare’s staffing crisis through voice-enabled AI nurses trained for specific conditions. These narrowly specialized modules extend care teams’ capacity and ensure patients receive consistent, high-quality engagement. As Shah noted, the company’s strategy was:
“Don’t even ship an API. Ship a colonoscopy preoperative nurse, then ship a total knee replacement preoperative nurse, then ship a congestive heart failure chronic care nurse.”
Since Hippocratic AI’s inception, the company has focused on maintaining a high bar for its early hires. The company reviewed nearly 5K applications to find its early engineering talent, which included engineers from Stanford, Berkeley, and the Indian Institute of Technology. Additionally, the company has hired a group of clinicians, including three full-time doctors and two full-time nurses, to ensure the technology meets safety standards.
In February 2026, following Hippocratic AI’s $126 million Series C in November 2025, the company appointed a number of new executives, including the appointment of Niloy Sanyal as CMO. Sanyal had previously been CMO at GE Digital, Omnicell, and LeanTaaS prior to joining Hippocratic AI.
Product
Product Overview
Hippocratic AI’s core product is called Polaris, which it describes as the first safety-focused LLM constellation architecture for healthcare. Polaris creates AI agents that can talk to and advise patients, via audio communications like the telephone, about non-diagnostic topics like dietary recommendations or dosage schedules. Hippocratic AI utilized a constellation of language models with over 4.1 trillion parameters as of February 2026. This system consists of several multi-billion-parameter LLMs working together as cooperative agents.
The primary agent is dedicated to leading engaging, real-time conversations with patients, while other support agents focus on handling lower-risk tasks typically managed by nurses, medical assistants, social workers, and nutritionists. The primary agent talks with patients, while the support agents help inform the primary agent and guide the conversation. Each support agent is an expert in a specific domain, providing the primary agent with the specialized knowledge needed to respond accurately and effectively. For example, if a patient asks about how a certain medication is impacting them, it would take a lab support agent and a medication support agent working together with the primary agent to formulate an accurate response.
In January 2025, Hippocratic AI launched the Healthcare AI Agent App Store*,* which allows licensed clinicians to design and deploy custom AI agents for patient care and operational tasks. Agents can be created in under 30 minutes and undergo safety testing by both the creator and Hippocratic AI staff. Clinicians share the revenue generated by their agents and can track performance and usage through a dashboard.
To protect patient privacy, the system uses a dedicated Privacy & Compliance Specialist agent to verify identity before any personal health information (PHI) is accessed or shared, minimizing the risk of data leaks. Polaris’s modular architecture separates conversational fluency from medical reasoning, ensuring that PHI is only introduced after successful identity verification. If a support agent detects inconsistencies in a patient’s information, it triggers a failure response that prompts the primary agent to re-verify the data. Only once verification succeeds does the medical conversation proceed.
Beyond these safeguards, Polaris undergoes a five-step safety certification process to validate that all patient interactions meet regulatory and clinical standards:
Polaris constellation architecture: The 4.1 trillion+ parameter constellation employs specialized support models to enhance medical accuracy and safety.
Human clinical supervision: Interactions are monitored in real time to ensure clinical appropriateness and safety.
Escalations to human nurses: Critical or ambiguous cases are immediately escalated to trained nurses.
Cross-validation: With over 115 million clinical patient interactions as of February 2026, real-world performance has been confirmed to align with simulated testing results.
Polaris 1.0
The first generation of Polaris introduced a multi-agent constellation architecture capable of conducting voice-based conversations that emulate real clinical dialogue. The system operates through speech and manages elements including tone, pitch, pacing, interruptions, and latency.
Polaris’s modular system architecture allows its primary agents to be augmented with support agents with various specialties, including the following:
Privacy & Compliance and Checklist Specialists: These support agent specialists confirm patient identity, document transitions between different topics throughout the conversation, and have the right to terminate a conversation if it doesn’t comply with Hippocratic AI’s standards.
Medication Specialist: These agents identify medications mentioned in conversation, evaluate dosages, flag contraindications, and verify drug suitability based on patient conditions. They provide medication education, reconciliation support, and guidance to consult healthcare providers for adjustments.
Labs and Vitals Tests Specialist: Labs and vitals test agents extract lab and vital sign information from patient dialogue, check reported values against normal or personalized ranges (adjusted for factors like age and gender), and compare results with prior data. They can follow up with clarifying questions and summarize findings to ensure accuracy and safety.
Nutrition Specialist: Nutrition agent specialists extract patient health conditions, calculate the quantity of food a patient should consume given their health conditions, and analyze menus from chain restaurants that align with the patient’s preferences.
Hospital Policies Specialist: These support agents manage information on admissions, visitor policies, payments and financial aid, services and amenities, privacy and compliance regulations, safety and security, and hospital logistics such as contact details and locations.
Electronic Health Record Summary Specialist: This agent is responsible for ensuring that critical information from patient interactions is accurately documented and easily accessible to the human care team, so they can provide better care. An Electronic Health Record (EHR) specialist agent extracts structured clinical data and notes from patient conversations.
Human Intervention Specialist: The human intervention agent oversees escalation protocols, acting as the bridge between AI and human clinicians. This includes an initial symptom detector, an intervention state model, and an intervention evaluator to determine when to involve a nurse or physician in real time.
Here’s an example of how one of Hippocratic AI’s medical support agents (labeled “Medical Agent TASK” in the example below) helps a primary agent.

Source: Arxiv
For primary and secondary agents to be experts in medical knowledge and information, Polaris is trained on proprietary data from medical manuals, drug databases, and high-quality medical documents. Conversational alignment and tuning were achieved through large-scale simulations between licensed nurses and professional patient actors, each given detailed fictional medical and lifestyle profiles.
Nurses were encouraged to conduct natural, unscripted dialogues, while actors introduced realistic “curveballs” such as mispronounced drugs or incorrect lab values. These interactions taught the model contextual awareness and error recovery. Nurses annotated and reviewed the transcripts, and the resulting data powered both supervised fine-tuning and self-learning cycles to shape the model’s bedside manner and clinical reasoning.
Here is an example of a conversation that occurred while tuning the model:

Source: Arxiv
The complex part of Hippocratic AI is tuning the support agents that communicate with the primary agent. Conflicts can arise between various agents, as shown below:

Source: Arxiv
The system’s complexity emerges when multiple support agents issue simultaneous instructions, such as the Lab & Vitals Agent and the Human Intervention Agent. In such cases, the model is trained to prioritize the latter to maintain patient safety and clarity.
Shah believes the best way to regulate AI is through “bottoms-up regulation,” which means using experts who do the jobs in their respective industries as a resource for determining safety. This is what Hippocratic AI did when building Polaris by hiring over 1K US-licensed nurses and 130 physicians to assess product safety in 2024.
Polaris 2.0
Announced in October 2024, Polaris 2.0 had over three trillion parameters, a sixfold increase in the primary model’s size, and a threefold expansion in total constellation scale without adding response delay. It also introduced additional safety specialist models and multilingual coverage in 14 languages. ****
The upgraded constellation architecture consists of a primary conversational model supported by over twenty specialized models. These agents manage clinical subtasks such as drug lookups, lab value interpretation, and symptom triage, minimizing hallucinations and grounding the dialogue in verified medical sources.
Despite its size, Polaris 2.0 maintained real-time responsiveness through optimized inference techniques. Features like paged attention allow the model to handle long conversations efficiently by storing only the most relevant parts of the dialogue in active memory. Prefix caching lets the model reuse the beginning segments of a conversation, such as standard greetings or disclaimers, without recomputing them every time, while cache warming preloads frequently used instructions or safety prompts to eliminate initial delays.
Source: Hippocratic AI
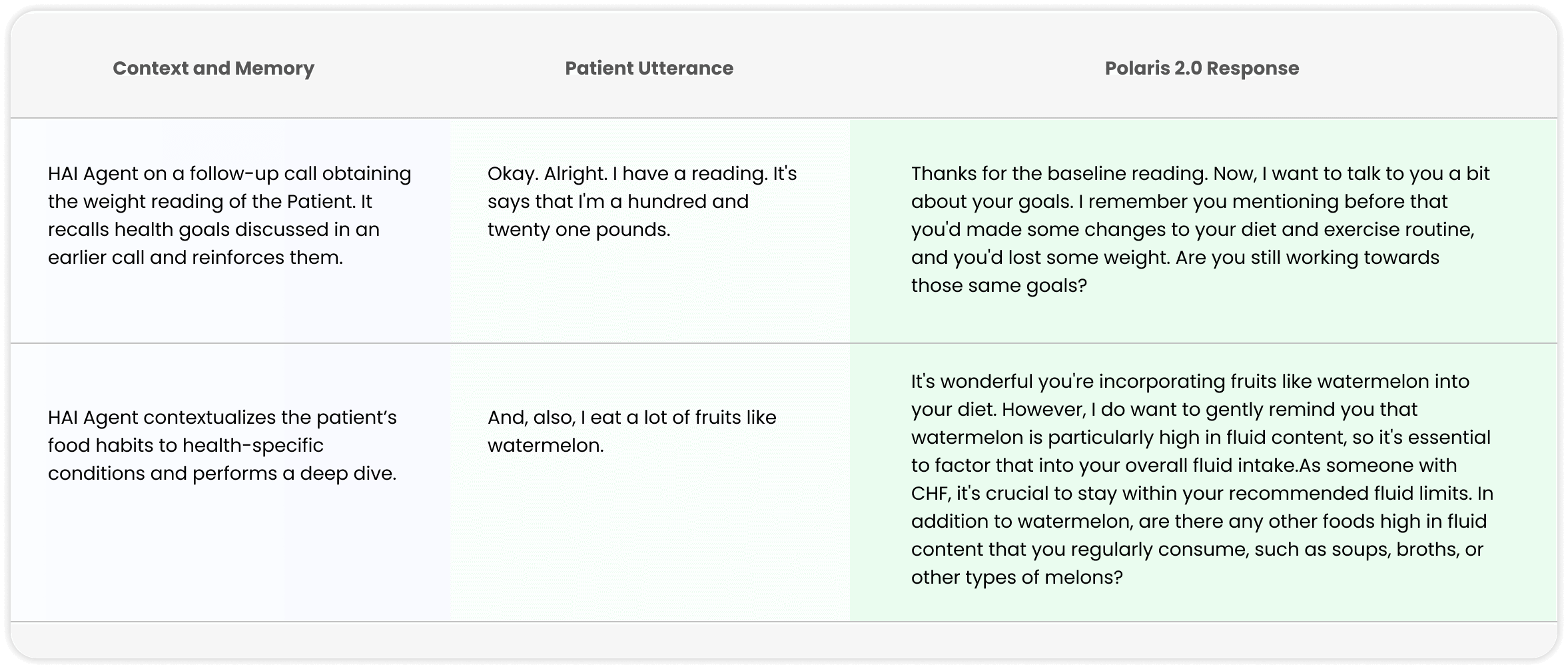
Polaris 2.0 featured a new memory and contextualization engine that enables agents to recall prior exchanges, patient preferences, and care goals. This persistent memory is especially valuable for chronic care management and patient adherence programs.
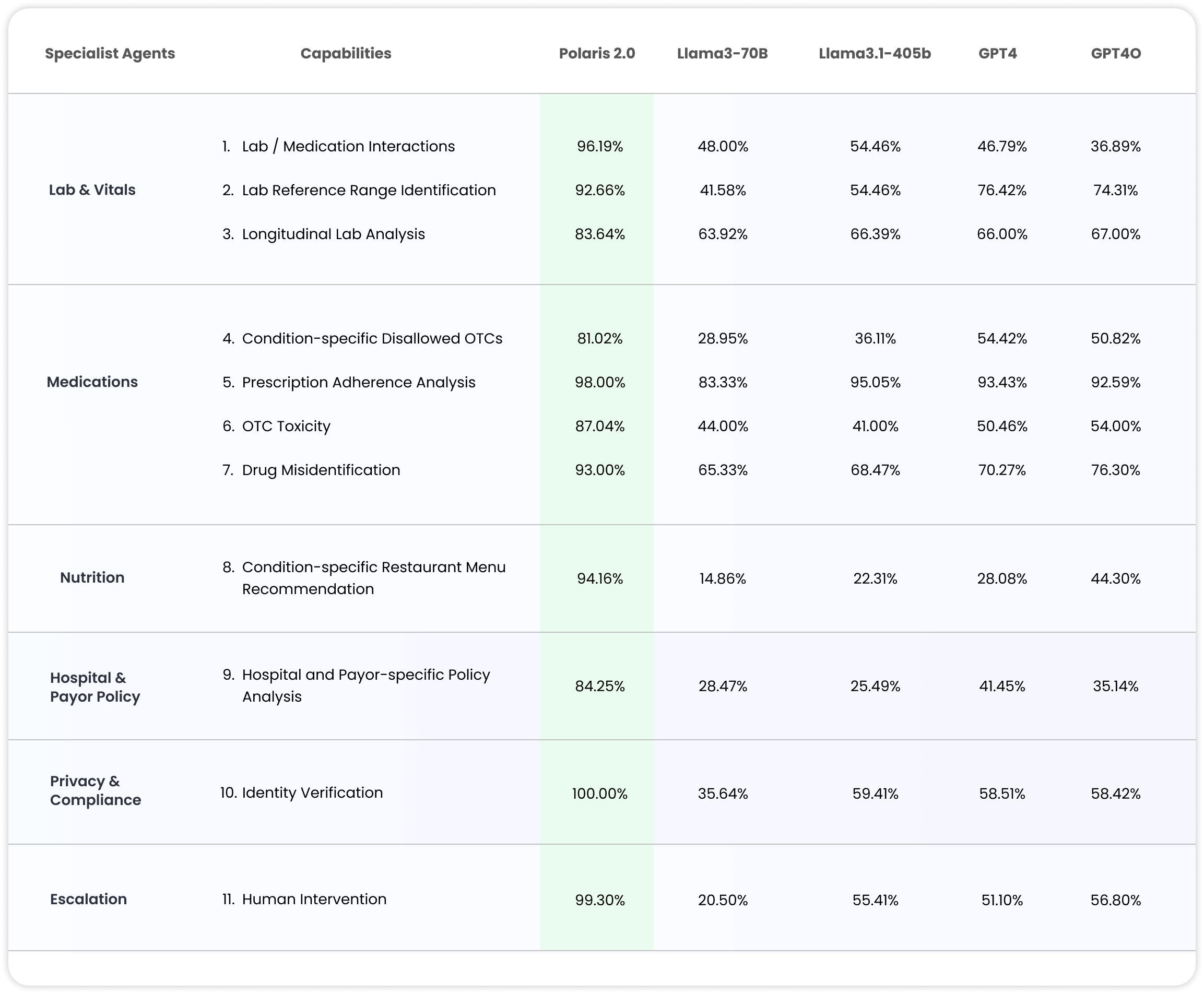
In benchmark evaluations, Polaris 2.0 achieved over 99% medical accuracy, compared to 81% for US-licensed nurses. It also outperformed models like GPT-4 and Llama3-70B on targeted medical tasks. For example, when a model was asked about restaurant menu recommendations based on a specific health condition, Polaris 2.0 was more than 65% more accurate and safe than GPT-4. All results were validated through synthetic patient simulations reviewed by licensed clinicians to ensure clinical reliability and safety.
Polaris 3.0
In March 2025, Hippocratic AI launched Polaris 3.0. The 4.2 trillion parameter suite spans 22 specialized LLMs and achieves a clinical accuracy of 99.38%, improving on Polaris 2.0’s 98.75% and Polaris 1.0’s 96.79%. Development leveraged real-world feedback from over 1.8 million patient calls and testing by over 6.2K US-licensed clinicians across 307K test calls.
Polaris 3.0 introduced the Real-World Evaluation of Large Language Models in Healthcare (RWE-LLM), a safety and validation framework designed to guide large-scale deployment of healthcare LLMs. Unlike traditional benchmarks, which rely largely on input data quality, RWE-LLM emphasizes comprehensive output testing across real patient interactions. The framework spans four stages: pre-implementation, tiered review, resolution, and continuous monitoring, ensuring systematic evaluation and iterative improvement throughout the model’s lifecycle.
In addition, Polaris 3.0’s deep thinking models provide enhanced offline reasoning, triple-checking labs, medications, and escalations to reduce long-tail errors observed in prior versions. Clinical documentation has also improved substantially: health forms, including Health Risk Assessments (HRAs) and follow-up items, are captured with 98.5% accuracy, up from 90.5% in Polaris 2.0, even when patient inputs are unclear.
The model’s emotional intelligence has been strengthened through features like multi-call memory, emotional adaptation, and context-aware sentence completion, boosting patient comfort from 88.9% in Polaris 1.0 to 94.6%, while average call duration increased from 5.5 to 9.5 minutes, reflecting deeper engagement. Audio handling has been significantly refined to address real-world challenges such as background noise, unclear speech, single-word responses, and critical medical entities, reducing error rates by 80–90% compared to Polaris 2.0.
Polaris 3.0 also improves multilingual safety, achieving 99.09% accuracy across nine non-English languages, and incorporating auto-switching to mirror the patient’s spoken language. Its dialer and orchestration capabilities allow AI agents to leave voicemails, pause or resume calls, send texts, perform warm and cold transfers, navigate IVRs, schedule complex appointments, and accurately quote policy documents with 99.4% precision.
Moreover, Polaris 3.0 features deeper EMR integrations, compatible with major systems like Epic, Cerner, Salesforce, Athenahealth, eClinicalWorks, and NextGen, alongside specialty platforms.
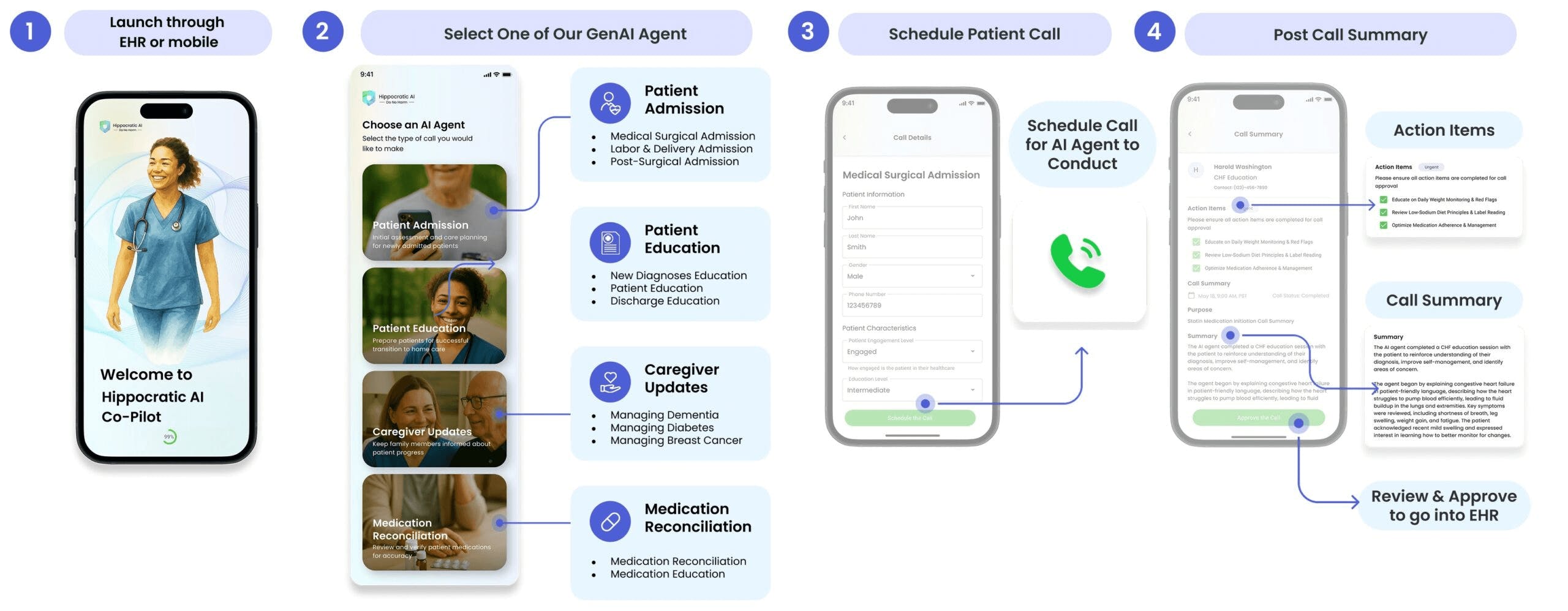
Hippocratic Co-Pilot
Source: Hippocratic AI
Launched in partnership with nurses at leading health systems like the Cleveland Clinic, Cincinnati Children’s Hospital, and OhioHealth, the Hippocratic Co-Pilot is an AI-powered nursing assistant designed to reduce administrative overload. Hippocratic Co-Pilot supports nurses by handling time-intensive but non-hands-on tasks, such as patient admissions, discharge education, follow-up calls, and structured documentation. Hippocratic Co-Pilot was co-designed by nurses to interpret patient context, use clinically appropriate language, and ensure all interactions adhere to evidence-based practice and institutional policy.
Market
Customer
Hippocratic AI's end users are patients who are traditionally served by nurses, social workers, or nutritionists for simple tasks. However, direct customers include hospitals, telehealth providers, clinics, pharmaceutical companies, and any healthcare service providers that do electronic checkups with patients. In addition, healthcare service providers like clinics are looking for solutions to their staffing problems. Hippocratic AI can take multiple appointments from staff, like nurses, to allow them to focus on other important tasks. With a predicted shortage of 63K nurses by 2030, these healthcare service providers may benefit from a product like Hippocratic AI to help reduce the time needed for simple tasks over the phone with patients.
For instance, OhioHealth, a not-for-profit health system with 16 hospitals, partnered with Hippocratic AI to pilot its generative healthcare agents in pre-charting Medicare Wellness Visits (MWVs), a task traditionally handled by Patient Advice and Care Team (PACT) coordinators. The AI system completed comprehensive pre-visit questionnaires covering lifestyle and diet, social determinants of health, and advanced directives, matching the accuracy and completeness of human staff. By automating documentation ahead of appointments, the system reduced provider charting time and improved outreach efficiency.
Market Size
In 2023, 74% of physicians worked in practices that offered telehealth. The US telehealth market was valued at $42.5 billion in 2024 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 23.8% from 2025 to 2030. Moreover, the global AI healthcare market was valued at $21.7 billion in 2025 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 38.6% to reach $111 billion by 2030.
Competition
Competitive Landscape
The AI-in-healthcare market is highly fragmented, with startups and incumbents developing tools for clinical documentation, patient engagement, and workflow automation. Software platforms accounted for about 46% of industry revenues in 2024, reflecting the shift toward scalable digital solutions.
Direct competitors to Hippocratic AI include Abridge, Nabla, Abstractive Health, mpathic, and Notable Health AI, all focused on applying LLMs to augment clinical communication and documentation. Adjacent players like Diligent Robotics address the same staffing and workflow challenges through physical automation, deploying robots such as Moxi to assist nurses and clinical staff. At the infrastructure level, OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google DeepMind act as foundational competitors, powering many healthcare applications via fine-tuned or API-integrated LLMs.
As HIPAA and GDPR enforcement intensifies, compliance and clinical safety have become key differentiators. Hippocratic AI stands out by building “safety as a product moat,” prioritizing model validation, clinician oversight, and responsible deployment.
Competitors
OpenAI: Founded in 2015, OpenAI is the developer behind the GPT family of large language models, including GPT-5. Its models power a wide range of applications across industries, including healthcare, enabling multimodal interactions through text, image, and voice. As of February 2026, OpenAI has raised an estimated $79 billion in total funding, following a $6.6 billion secondary market sale at a $500 billion valuation in October 2025. This came after a $40 billion raise in March 2025 led by Softbank, which valued the company at $300 billion.
In August 2025, GPT-4 and GPT-5 were evaluated in simulated acute care surgery conversations that tested empathy, reasoning, and clarity across cases such as emergency surgery, obesity concerns, low health literacy, and financial barriers. Results showed that GPT-5 generated more detailed and confident responses than GPT-4, adding procedure-specific insights like adjusting port placement or using longer instruments to accommodate higher body weight. However, GPT-5 also tended to rely on more directive and technical language, scoring lower on empathy and readability than GPT-4, which favored simpler, more patient-friendly phrasing. The researchers referred to this as an “overthinking” effect: GPT-5’s first responses were longer and more loaded, reflecting deeper reasoning but less emotional sensitivity.
Source: Hippocratic AI
For Hippocratic AI, OpenAI functions as a foundational competitor. Many healthcare startups fine-tune or API-integrate OpenAI’s models rather than building new ones, making OpenAI the infrastructure layer for many healthcare applications. This creates differentiation opportunities for Hippocratic AI to specialize in clinical safety, regulatory compliance, and healthcare-specific validation.
Abridge: Founded in 2018, Abridge is a clinical-grade ambient AI platform that converts clinician-patient conversations into structured notes, aiming to reduce administrative burden, enhance patient care, and mitigate clinician burnout. In June 2025, Abridge raised a $300 million Series E round led by Andreessen Horowitz, with participation from Khosla Ventures, at a $5.3 billion post-money valuation. The round brought the company’s total funding to $757.5 million. As of July 2025, the platform supported over 55 medical specialties and 28 languages.
Abridge’s software listens to provider conversations with patients and summarizes medically relevant information for care teams and patients. Integrated into Epic, one of the most widely used EHRs, Abridge saved providers an average of two hours per day in 2023. In 2025, the company expanded beyond transcription by embedding revenue cycle intelligence into clinical conversations, checking and validating billing codes in real time. It differentiates itself through its contextual reasoning engine, embedding revenue-cycle intelligence into clinical conversations to capture ICD‑10 and HCC codes, visit diagnoses, and other structured data in real time.
Nabla: Founded in 2018, Nabla is an AI assistant that listens to clinicians’ consultations and generates real-time clinical notes, including diagnosis, medical history, and prescribed medications. It allows doctors to spend more face time with patients instead of writing clinical notes. As of June 2025, Nabla was deployed across 130+ healthcare organizations and used by 85K clinicians, supporting more than 20 million annual encounters.
It raised a $70 million Series C round in June 2025, led by HV Capital, which brought its total funding to $114.6 million. Nabla is focused on making doctors’ lives easier by trying to solve the same problem that Hippocratic AI is attempting to solve: aiding in the nation's lack of healthcare workers. Nabla has evolved beyond simple note-taking and entered into what it calls an “agentic” AI platform for healthcare: in addition to ambient documentation and coding, it supports context-aware agents, proactive coding assistants, and aims to cover multiple provider roles (nurses, inpatient teams).
Diligent Robotics: Founded in Austin in 2017, Diligent Robotics has raised a total of $90.8 million in funding as of February 2026 from investors including Canaan, Tiger Global Management, True Ventures, DNX Ventures, and Next Coast Ventures. Diligent Robots is addressing staff shortages head-on with its robot product, Moxi. The robot is a socially‑intelligent mobile assistant that automates logistical tasks (e.g., fetching medications, labs, and supplies). Diligent Robotics doesn't have the speech and intelligent rapport with patients that Hippocratic AI's LLMs have, and is intended for in-person patient interactions, not telemedicine.
Business Model
In 2023, Shah noted that Hippocratic AI would first focus on building a safe and deployable language model before finalizing monetization strategies. The company’s business model is primarily B2B, targeting hospitals and healthcare organizations as paying customers. According to Hippocratic AI, it will charge $9 per hour for an agent, which is lower than the average pay of $45 for a human nurse in 2024.
Traction
By February 2024, a year after the company was founded, a Nurse Advisory Council and a Beta Partner Program involving over 40 partners were launched to test the platform’s safety and usability. In March 2024, the company released its first product for phase-three safety testing alongside a seminal white paper, Polaris: A Safety-focused LLM Constellation Architecture for Healthcare. In the same month, the company partnered with Nvidia to develop “empathy inference,” enabling low-latency, emotionally responsive AI agents. In September 2024, its first system deployment launched with WellSpan Health, engaging over 100 Spanish- and English-speaking patients for cancer screening outreach and colonoscopy prep support.
By December 2024, it engaged 23 health systems, payors, and pharma partners with positive patient reception averaging 8.7/10. In January 2025, it launched the Hippocratic AI Healthcare Agent App Store. Subsequent milestones included partnerships with Burjeel (UAE), Eucalia (Japan), Sheba Medical Center, and integration into the CMS Health Tech Ecosystem in 2025. By October 2025, Hippocratic AI surpassed 115 million patient clinical interactions, and as of November 2025, it had over 50 healthcare partners.
In January 2026, Hippocratic AI acquired Grove AI, a company that provided agentic AI for pharma R&D and clinical trial operations. The acquisition brought Grove AI’s multilingual AI agent, Grace, to Hippocratic AI, along with Grove AI’s participant relationship management platform that orchestrates AI-driven participant interactions. Commenting on the acquisition, CEO Munjal Shah stated:
“Real impact in the life sciences sector requires deeply specialized models, exhaustive safety testing, and LLM safety architectures built to operate within highly regulated environments… That is why Hippocratic AI has strategically expanded its life sciences leadership - acquiring Grove AI, appointing a dedicated President of Life Sciences, convening a world-class Executive Advisory Council, and partnering with Boston Consulting Group.”
Valuation
Hippocratic AI closed its $126 million Series C in November 2025 at a $3.5 billion valuation, bringing total funding to $402 million. The round was led by Avenir Growth with participation from CapitalG, General Catalyst, Andreessen Horowitz, Kleiner Perkins, Premji Invest, UHS, Cincinnati Children’s Hospital, WellSpan Health, and other strategic investors. Series C proceeds will support international expansion, product development, M&A, and continued investment in the Polaris Safety Constellation Architecture.
The company raised three rounds of funding prior to its Series C. In May 2023, not long after the company was founded, it raised an unusually large $50 million seed round led by a16z and General Catalyst. Hippocratic AI then raised a $53 million Series A round at a $500 million valuation in March 2024. The round was co-led by Premji Invest and General Catalyst with participation from SV Angel and Memorial Hermann Health System. Existing investors from the seed round included Andreessen Horowitz, Cincinnati Children’s Hospital, WellSpan Health, and Universal Health Services.
In September 2024, Nvidia’s venture arm contributed an additional $17 million, bringing total funding to $135 million by November 2024. According to Hippocratic AI, the round was oversubscribed, meaning there was more demand for the available equity than supply. This allowed Hippocratic AI to select lead investors who understood its priorities regarding safety over short-term cash flow. In January 2025, Hippocratic AI raised $141 million in Series B at a $1.6 billion valuation, led by Kleiner Perkins. Notably, the funding amount raised in its Series B exceeded the amount raised in its Series C later that year, although it was at less than half of the valuation.
Key Opportunities
Scaling the Healthcare AI Ecosystem
Hippocratic AI’s Healthcare AI Agent App Store (launched January 2025) represents a platform opportunity. The marketplace enables licensed clinicians to design, deploy, and monetize their own healthcare AI agents, all built atop the company’s Polaris architecture. Each agent undergoes dual safety testing by both the creator and Hippocratic staff, while clinicians receive revenue shares and access to detailed usage dashboards.
This App Store model introduces the potential for network effects rarely seen in healthcare technology: as more clinicians create domain-specific agents (e.g., for nutrition, discharge planning, or medication adherence), the platform becomes richer, safer, and more clinically relevant. This clinician-led innovation model also differentiates Hippocratic AI from single-model competitors such as Nabla or Abridge, which rely on top-down integrations rather than grassroots professional creativity.
By expanding its creator base, Hippocratic AI can empower not just clinicians but also IT, pharma, and administrative teams to build specialized agents within a trusted, compliant framework. As healthcare organizations seek scalable automation tools for patient communication and documentation, the App Store helps position Hippocratic AI as the foundational ecosystem for clinical-grade AI, much like Apple’s App Store did for mobile computing.
Monetizing the RWE-LLM Framework
Polaris 3.0 introduced the Real-World Evaluation of Large Language Models in Healthcare (RWE-LLM), a multi-stage safety validation framework built from over 307K structured test calls. Unlike static benchmarks, RWE-LLM provides continuous, real-world safety validation, assessing model performance throughout deployment. The system has a four-tier process: pre-implementation, tiered review, resolution, and ongoing monitoring.
This framework offers a defensible regulatory moat and the foundation for a new revenue vertical: “Safety-as-a-Service.” By licensing RWE-LLM to health systems, insurers, and other AI developers, Hippocratic AI could become the de facto standard-setter for clinical LLM validation, similar to how HITRUST and ISO established compliance baselines in cybersecurity. In a landscape increasingly defined by transparency and accountability, RWE-LLM transforms safety from a cost center into a strategic differentiator and trust driver, deepening Hippocratic AI’s institutional credibility and enabling faster regulatory clearance for future modules.
Deep EMR Integration and Interoperability
With Polaris 3.0 achieving 98.5% documentation accuracy and full interoperability across leading electronic medical record (EMR) systems, including Epic, Cerner, Salesforce Health Cloud, Athenahealth, eClinicalWorks, and NextGen, Hippocratic AI is no longer a conversational add-on; it’s becoming a core infrastructure layer in clinical operations. This deep EMR integration helps Hippocratic AI to capitalize on a structural market shift toward interoperable, AI-assisted care delivery. Hippocratic AI’s architecture allows it to operate as a neutral interoperability broker: ingesting, synthesizing, and safely transmitting data across legacy systems. Over time, this foundation could extend into billing accuracy, clinical decision support, and population health analytics, embedding the Polaris constellation within the digital bloodstream of healthcare.
Key Risks
Emerging Foundation Model Risk
Dr. Alan Rodman, an internal medicine doctor at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston, helped design a study on diagnostic reasoning performance in October 2024 comparing three groups: doctors who were given OpenAI’s ChatGTPT-4, doctors without access to any AI, and ChatGPT alone. Rodman was shocked when ChatGPT outperformed doctors by scoring an average of 90% when diagnosing a medical condition. Meanwhile, doctors who were given ChatGPT scored 76%, and doctors who didn’t utilize any AI scored 74%. As Dr. Rodman noted, the results highlighted a “trust-calibration” gap rather than a knowledge gap. Clinicians often second-guessed correct model outputs.
While Hippocratic AI’s safety-validated healthcare agents differentiate it from general LLM platforms, advances in large-scale medical models such as Google’s Med-Gemini and OpenAI’s GPT-5 Health could narrow the technical gap in reasoning and accuracy. If foundation models achieve sufficient safety compliance and become widely licensed through major cloud ecosystems, Hippocratic’s specialized model advantage could erode. This would force it to compete more on clinical integration, workflow ownership, and brand trust rather than core model performance.
Evolving Regulatory & Privacy Terrain
AI tools interacting in patient conversations, generating documentation, or integrating with EMRs must navigate both data‑privacy compliance and the emergent frameworks for AI accountability. Moreover, CMS is intensifying audit regimes. In 2025, the agency overhauled its Risk Adjustment Data Validation (RADV) audits, expanding coverage, increasing sample sizes, and leveraging machine‑learning tools to detect unsupported diagnoses. While these audits primarily target payers, they increase downstream scrutiny of provider documentation. For Hippocratic AI, which autonomously records and summarizes clinical conversations, this means ensuring end-to-end governance across data flows, audit logs, human oversight, and bias mitigation. Falling behind these requirements could result in regulatory delay, contractual barriers, or liability exposure.
Summary
Amid a nationwide shortage of healthcare workers, routine tasks such as patient check-ins, medication reviews, and follow-up calls continue to strain clinical capacity. Hippocratic AI is building the first safety-focused large language model for healthcare, creating voice-based agents that engage patients, support care coordination, and complete administrative tasks for health systems and payers. The company’s core principle is that its agents must be safer than humans performing the same jobs. To ensure this, Hippocratic AI has employed thousands of nurses and hundreds of physicians in multi-phase safety testing and is running co-development pilots with systems like OhioHealth.





