Thesis
The demand for enterprise automation and integration is accelerating rapidly, driven by three converging trends: cloud, AI, and digital transformation. Worldwide end-user spending on public cloud services is forecast to reach $723.4 billion in 2025, up from $595.7 billion in 2024. 61% of large enterprises now use multi-cloud security, and applications siloed on different clouds have increased from 44% to 57% year-over-year. On the AI side, one 2023 study found 40% of organizations reported increased AI adoption due to advances in generative AI, with 75% expecting AI to cause significant or disruptive change in their industry within three years. Finally, global digital transformation spending reached $1.9 trillion in 2022, creating demand for platforms that can orchestrate data, automate processes, and integrate fragmented tools.
The Integration Platform as a Service (iPaaS) market demonstrated 30.7% growth in 2023, reaching $7.7 billion in revenue, and is projected to grow at a 26% CAGR, adding $10.3 billion between 2023-2027. This growth stems from increasing complexity in enterprise software ecosystems where businesses now manage an average of 342 SaaS applications. Despite significant investment, only 28% of marketing tools in enterprises are fully integrated, creating widespread inefficiencies.
Workato positions itself in this expanding market with a unified platform, empowering both business and IT users to build automation into their applications. The company offers over 1K pre-built connectors across major SaaS tools, including Salesforce, Workday, and Slack. Workato's cloud-native architecture enables scalability, real-time automation, and event-driven integration capabilities. This technical foundation supports both horizontal use cases across business functions (marketing, sales, HR) and vertical industry-specific solutions for healthcare, finance, logistics, and other sectors.
Founding Story
Workato was founded in December 2013 by Vijay Tella (CEO), Gautham Viswanathan (Strategic Advisor, former CPO), Harish Shetty (Strategic Advisor, former Head of Engineering), and Dimitris Kogias (Co-founder, Software engineer and architect), and is headquartered in Mountain View, California. The four co-founders first connected at TIBCO Software as its founding team members in 1997. Together, they developed BusinessWorks, an integration platform that connects applications, systems, and services, which became the foundation of what Workato is doing today.
Following TIBCO's successful IPO, each of them pursued different paths. Tella moved to Oracle in 2003 as Chief Strategy Officer, where he helped create Fusion Middleware. In 2009, he became CEO of consumer video company Qik, which was acquired by Skype in 2011. Reflecting on this experience, Tella noted that “that experience rewired everything [he] thought about software; how it should be, how it should work.”
Meanwhile, Viswanathan and Shetty co-founded Blink Interactive in 2007. Viswanathan later started to develop iProfile in 2009, with Shetty following in 2011. iProfile was subsequently acquired by DiscoverOrg and merged with ZoomInfo. The other co-founder, Kogias co-founded Pragmaticomm in 2005 and Missum in 2010.
In 2013, Tella and Viswanathan reconnected, and this reunion sparked the creation of Workato. The company was founded with the vision of bringing automation to business workflows. Drawing from their TIBCO experience, where they had developed integration middleware like The Information Bus (TIB) and BusinessWorks, they recognized that modern cloud applications presented new integration challenges. Viswanathan observed that despite their earlier work at TIBCO, integration problems persisted with modern cloud-based services. Tella later explained:
“We thought we had solved [the integration problem] back in the day and moved on to other things... There was a sense that middleware products and technologies had become mature and full-featured. However, the urgent and, now, universal digital transformation imperative and the explosion of cloud apps and APIs unleashed by it has changed everything. It has become both the biggest opportunity and an existential threat for companies to transform to dynamic digital companies in the mold of innovators like Amazon, Salesforce, Netflix, GE, Starbucks, and Walmart and avoid the fates of a Blockbuster, a Borders, or a Kmart.”
The team’s goal was to enable both IT and business teams to collaborate on automation, resulting in the creation of a “Recipe" — Workato's low-code / no-code foundation that provides an accessible integration canvas. Viswanathan and Tella saw space for a new approach marrying consumer-grade ease of use with enterprise capabilities.
Before launch, the Workato founders devoted significant time to “isolating some hard problems to solve,” overcoming challenges like enabling reusable integrations across customized systems. The company has also borrowed a strategy from GitHub to provide a platform for customers to share their problems. With core technical obstacles addressed, Workato emerged from stealth in mid-2013, aimed squarely at helping enterprises adopt SaaS.
Product
iPaaS: Integration Platform as a Service
The Integration Problem
Modern enterprises often rely on a multitude of applications, such as Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems, Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software, marketing platforms, and Human Resources (HR) tools to manage diverse functions. However, these systems frequently operate in isolation, leading to data silos and operational inefficiencies. On average, companies use 342 SaaS applications, and 40% of SaaS licenses are currently unused. Take the example of the marketing team; the marketing team alone utilizes over 20 tools on average, yet only 28% of these are fully integrated. In terms of addressing this problem, 84% of businesses say integrations are “very important” or a “key requirement” for their customers.
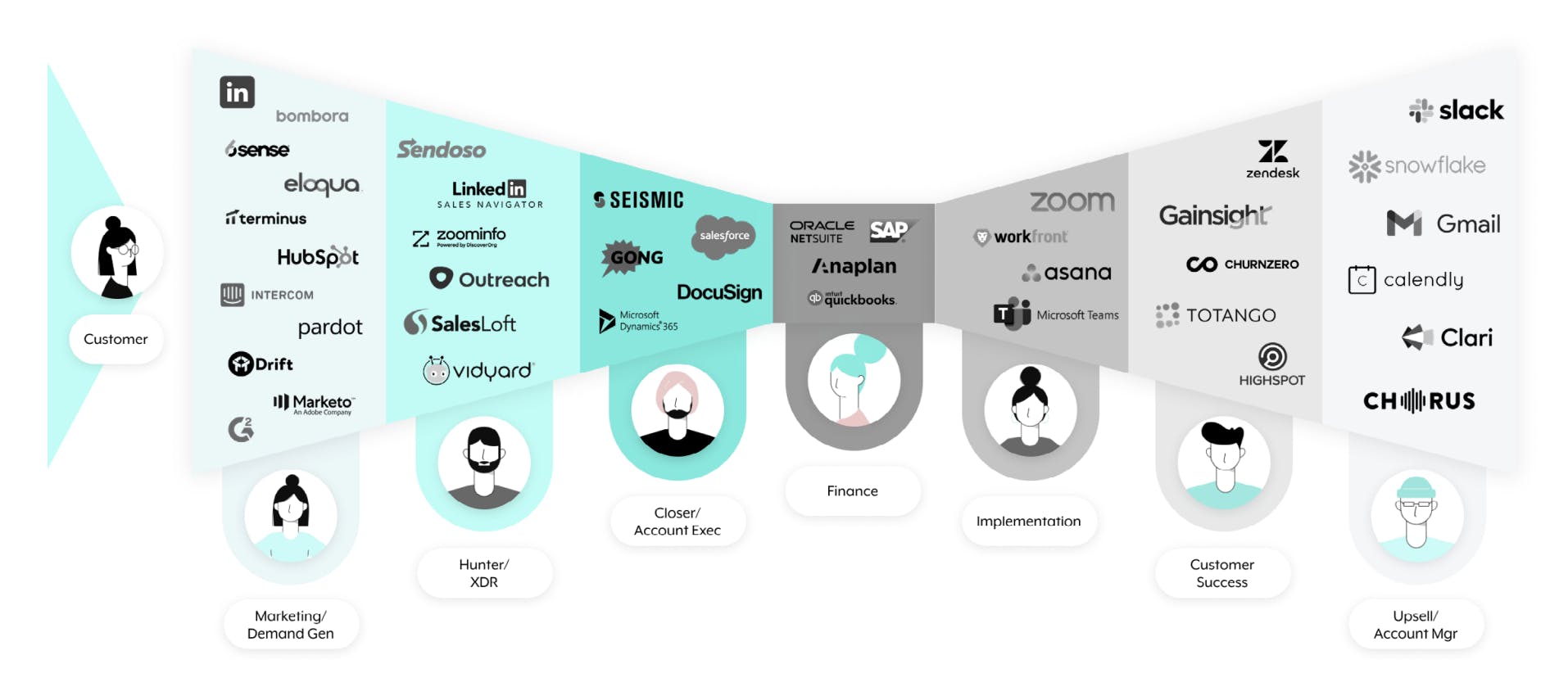
Source: Workato
iPaaS refers to cloud-based platforms designed to connect disparate applications, data sources, and services within an organization. It allows users to automate workflows, synchronize data, and orchestrate business processes across multiple tools without the need for custom code or dedicated infrastructure. Instead of developing and maintaining individual point-to-point integrations between applications (e.g., Salesforce to Snowflake), iPaaS provides a centralized solution to efficiently manage and scale integrations through a low-code / no-code interface.
Workato addresses integration challenges by offering a unified, cloud-native iPaaS platform that facilitates both integration and automation. Workato is built on AWS and offers a range of AWS services and applications with recognition for AWS low-code / no-code migration and modernization competency. It delivers an API-led, event-driven platform capable of integrating data, applications, APIs, and events.
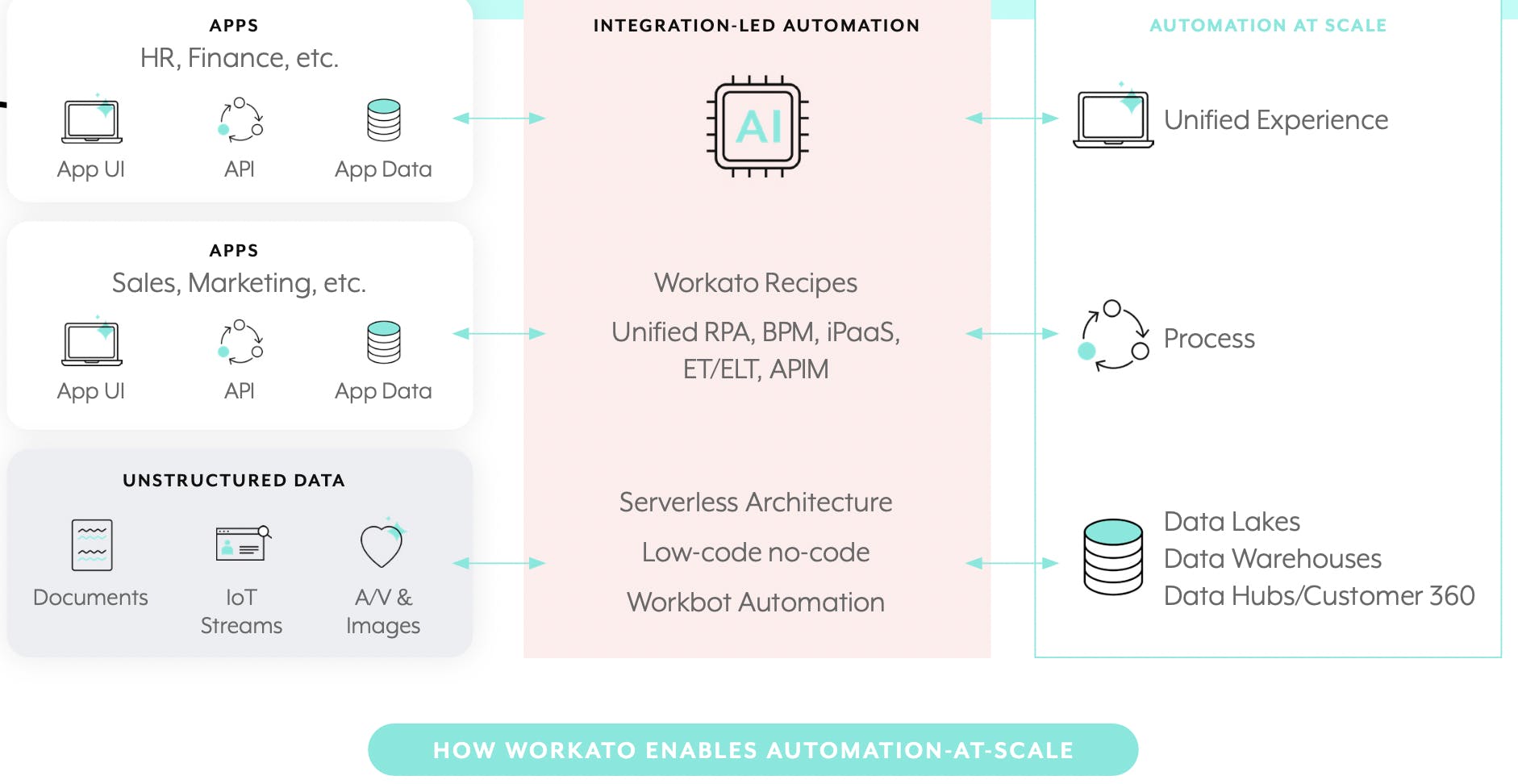
Source: Chakray
Workato’s core functionality revolves around enabling teams to build recipes using pre-built connectors to integrate leading tools across various domains, including marketing, sales, support, and HR. These recipes support messaging, event processing, and triggers, and allow for use case-specific workflow automation, including in AI/machine learning, customer service, databases, DevOps, IT, finance and accounting, HR, sales and marketing, etc.
Architecture of iPaaS
Workato’s cloud-native iPaaS foundation is designed to support large-scale, real-time integrations. At a high level, every iPaaS has three main logical components: management plane, runtimes, and infrastructure. Manage plane is the "control tower" of Workato, and it serves as the main UI access point where users build, configure, and monitor automations.
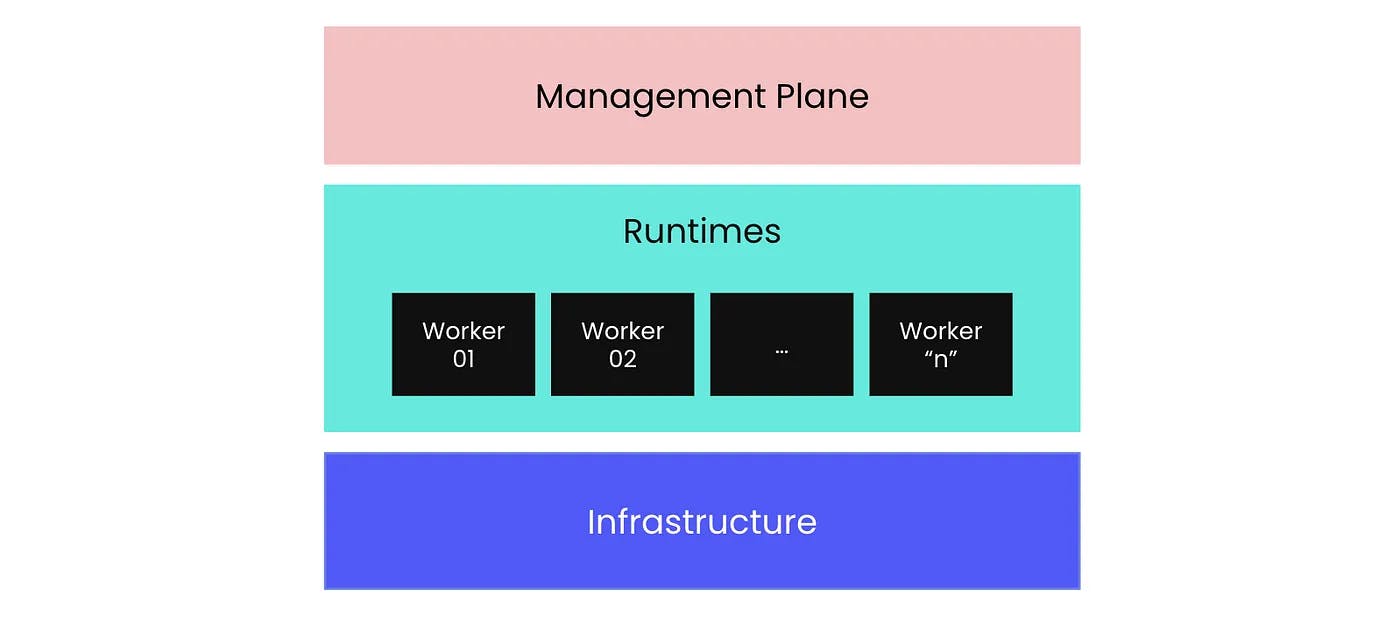
Source: Andres Ramirez
Runtimes is the execution engine where customer automations (recipes) run. Workato splits the workload using microservices-based runtimes to run over containers, which allows each workflow to run independently from other recipes. This allows the recipes to achieve benefits like higher availability, scalability, deduplication, and guaranteed delivery.
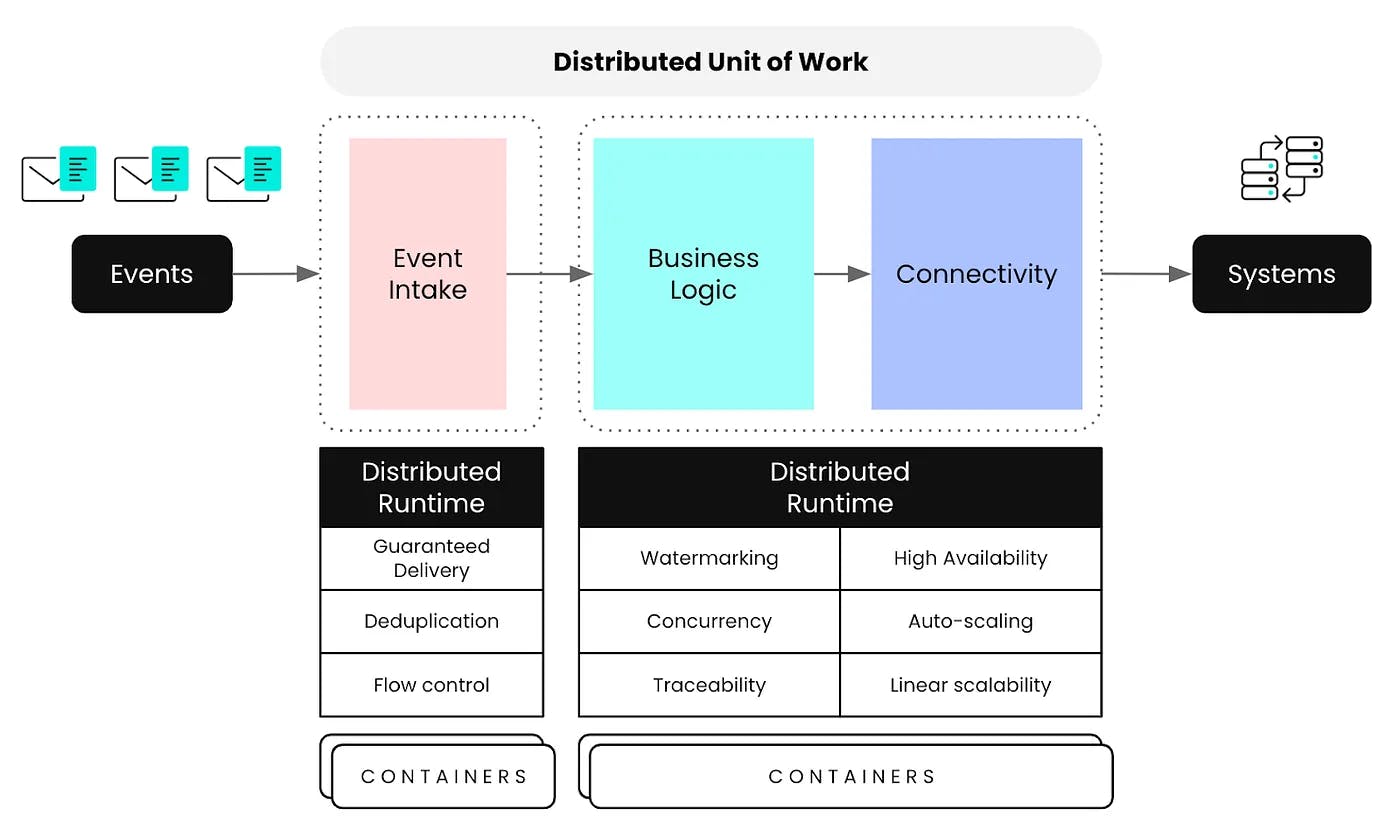
Source: Andres Ramirez
Infrastructure includes the underlying resources being used to support both the management plane and the runtimes provisioning. All of the containers runs on a containerized infrastructure, using industry standards like Docker and Kubernetes. This architecture enabled Workato to run millions of automations concurrently. Each recipe operates in isolation, so one failure doesn’t crash the system.
Platform Overview
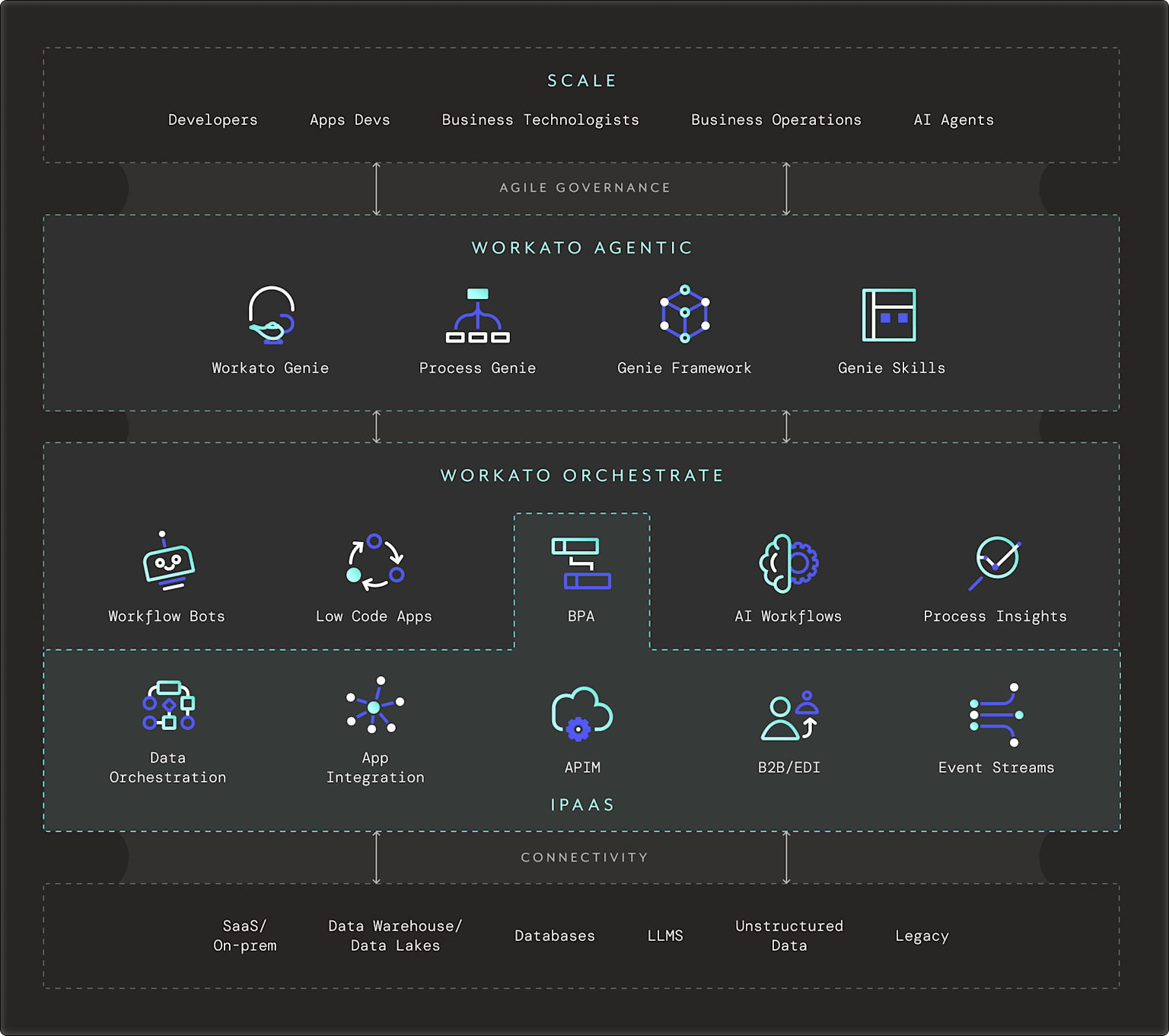
Source: Workato
Workato’s product ecosystem is structured around three core pillars: Platform, Orchestration, and Generative AI. Each of these work together to automate business processes at scale.
The Platform layer provides the foundational infrastructure, including the Workato Platform itself, the cloud-native integration and automation service. Providing enterprise-grade security ensures that users can securely build, deploy, and manage automation across applications without requiring extensive infrastructure setup.
Built on top of the platform foundation is the Orchestration layer, which provides the tools to design, manage, and execute automations. This includes components such as Enterprise iPaaS, data orchestration capabilities, app connectors, and API management. These tools allow users to connect disparate systems (e.g., Salesforce, SAP, Workday) and automate workflows across departments like IT, finance, and HR. Additional features like Workflow Bots, Low Code Apps, and Process Insights make it possible to monitor and refine business processes in real time. Orchestration acts as the connective tissue between systems, turning data into structured processes.
Finally, the Generative AI layer extends orchestration by embedding AI-powered agents and workflows directly into business operations. Workato’s Copilots and AgentX offerings (e.g., AgentX IT, Sales, and Support) use large language models and proprietary orchestration logic to carry out tasks like ticket triage, lead qualification, or internal knowledge retrieval. These AI features are built within the existing Workato environment, allowing them to leverage the same underlying data connections and process orchestration capabilities. Workato’s Agent Studio serves as a development environment where users can design, test, and deploy these AI-powered agents, tying together the platform’s integration, orchestration, and AI components into a unified automation experience.
App Connectors

Source: Workato
The fundamental building blocks of Workato’s platform are recipes, an automated workflow that executes a series of steps to integrate and process data across multiple applications. Every recipe includes a trigger that initiates the workflow (events that start the recipe) and one or more actions that execute when a trigger event occurs (tasks performed in response to triggers). Recipes use connectors to interact with different apps, ensuring seamless data flow across systems.
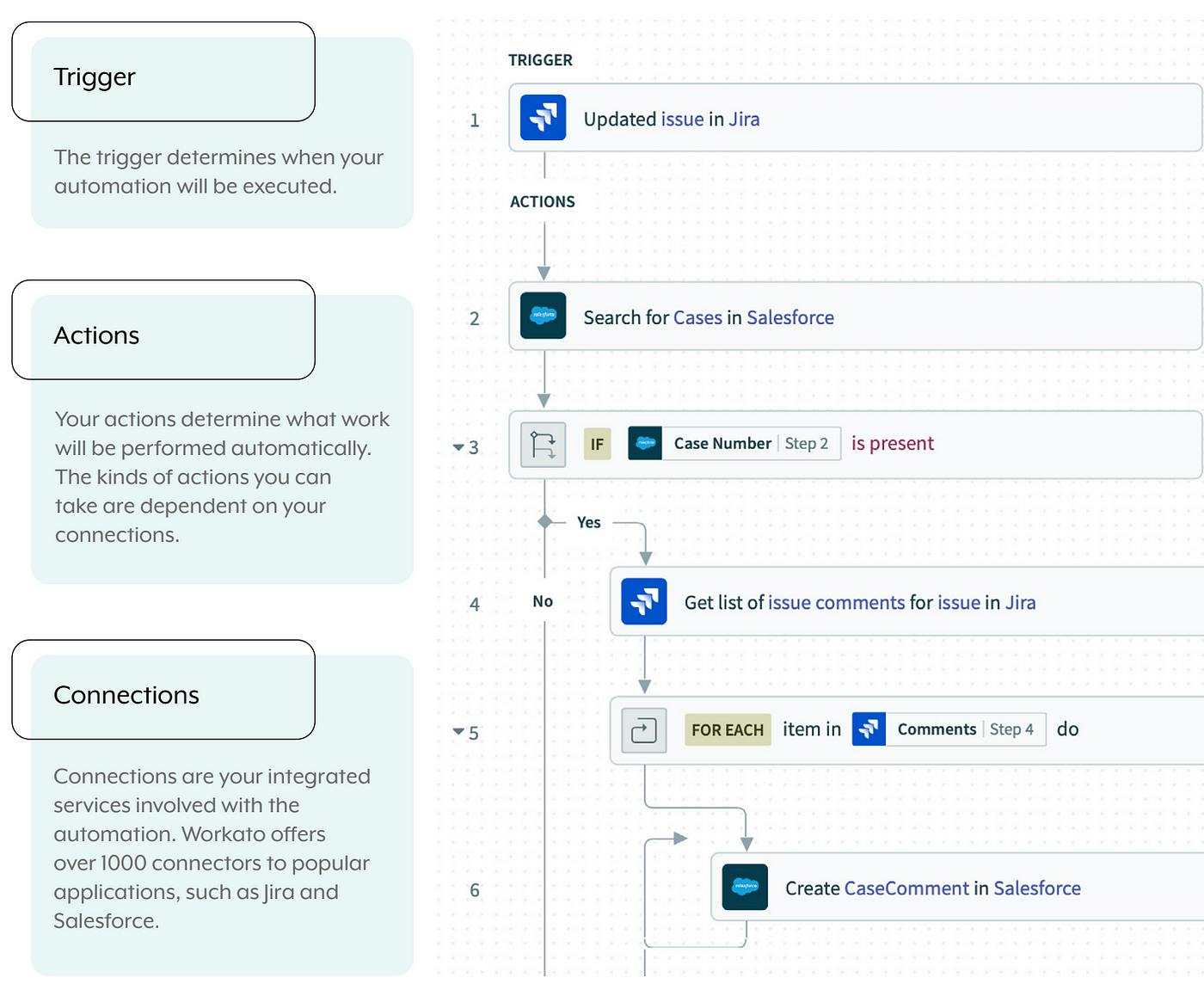
Source: ihub4us
Connections are links to external systems established during recipe creation, which can be reused across different recipes. A connection authorizes a recipe to interact with apps like Salesforce and Zendesk through triggers and actions.

Source: Workato
Within the Workato platform, users can leverage the Project area where users build recipes. Users can create multiple projects and inside each project users can create a hierarchical folder structures to host recipes and connections.
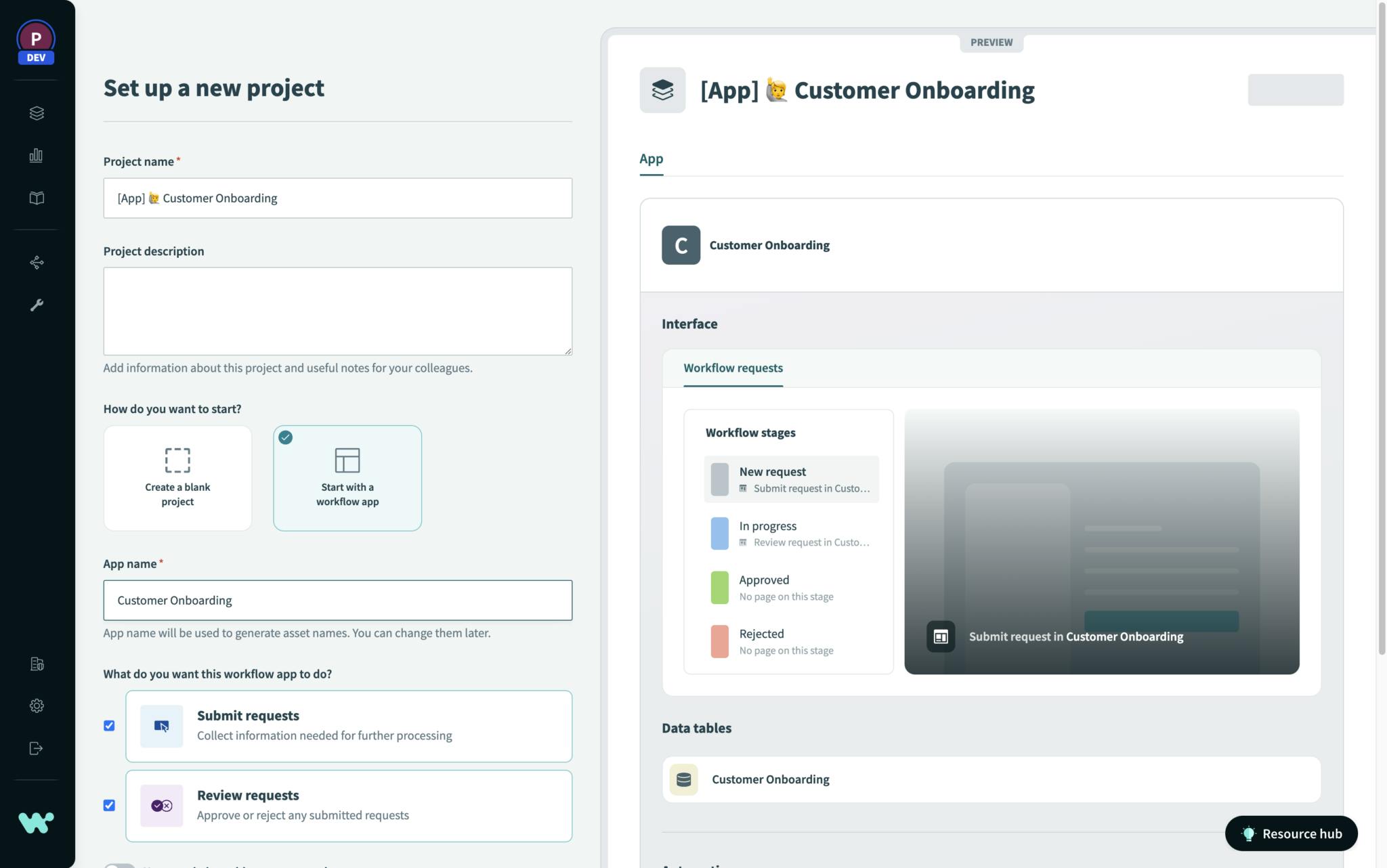
Source: Workato
Projects within Workato's platform revolve around Workato Workspaces, which serve as hubs for users to access and oversee their integration processes. Automation HQ provides centralized control and oversight across all workspaces, ensuring seamless administration, monitoring, and governance.
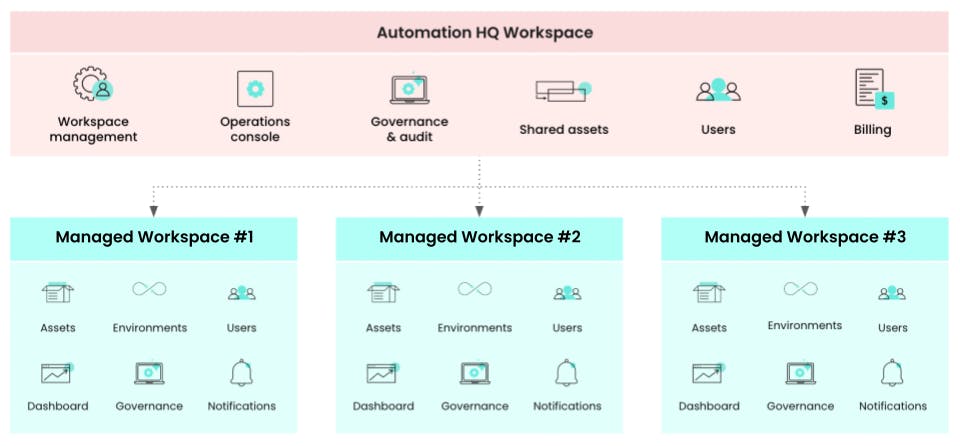
Source: Workato
Workato allows businesses to integrate applications and automate complex workflows without the need for coding. It supports over 1K pre-built connectors to popular SaaS applications like Salesforce, Slack, Workday, SAP, and more. Workato offers industry-specific solutions and connectors to accelerate deployment for common use cases in marketing, HR, finance, and IT.
Data Orchestration
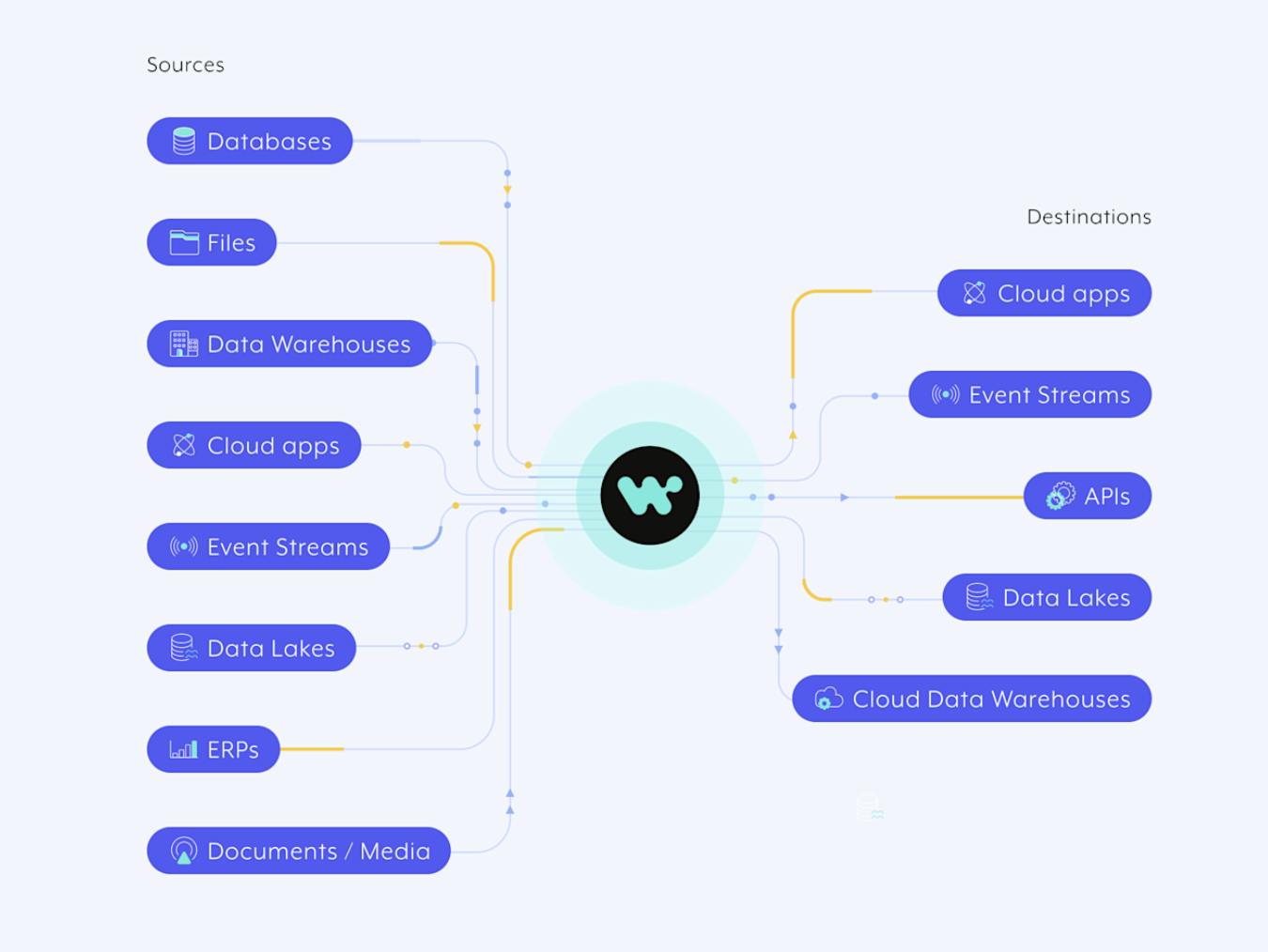
Source: Workato
Workato’s Data Orchestration capabilities are designed to help businesses move and transform data across different systems more efficiently. Users can build pipelines that are more resilient to errors and adaptable to schema changes, with visibility into each step. Workato’s support for over 1.2K prebuilt connectors across cloud applications, on-prem databases, APIs, and data streams, allowing organizations to automate data movement on flexible schedules, including real-time and batch processing.
Launching a pipeline is designed to be straightforward: Workato recipes automatically map and adapt schema changes, reducing the risk of data loss. Performance at scale is a key focus, with features like SmartShunt for direct data transfers and built-in parallelization for high throughput. Users can apply transformations using more than 400 built-in functions or code in Python, JavaScript, SQL, and other languages. Push-down ELT and complex data transformation steps, such as joining, enriching, or validating, can be performed directly within the workflow.
Additionally, Workato enables Reverse ETL, allowing data from cloud warehouses to be pushed into operational tools like CRMs or marketing platforms. Event-based triggers and schema introspection simplify change data capture and reduce manual configuration. The platform also supports querying and transforming data stored in CSV, JSON, or Excel files within Workato FileStorage, bypassing the need for intermediate databases. These orchestration tools are complemented by resources like prebuilt recipes, webinars, and accelerators to help teams get started quickly and scale reliably (source).
API Management
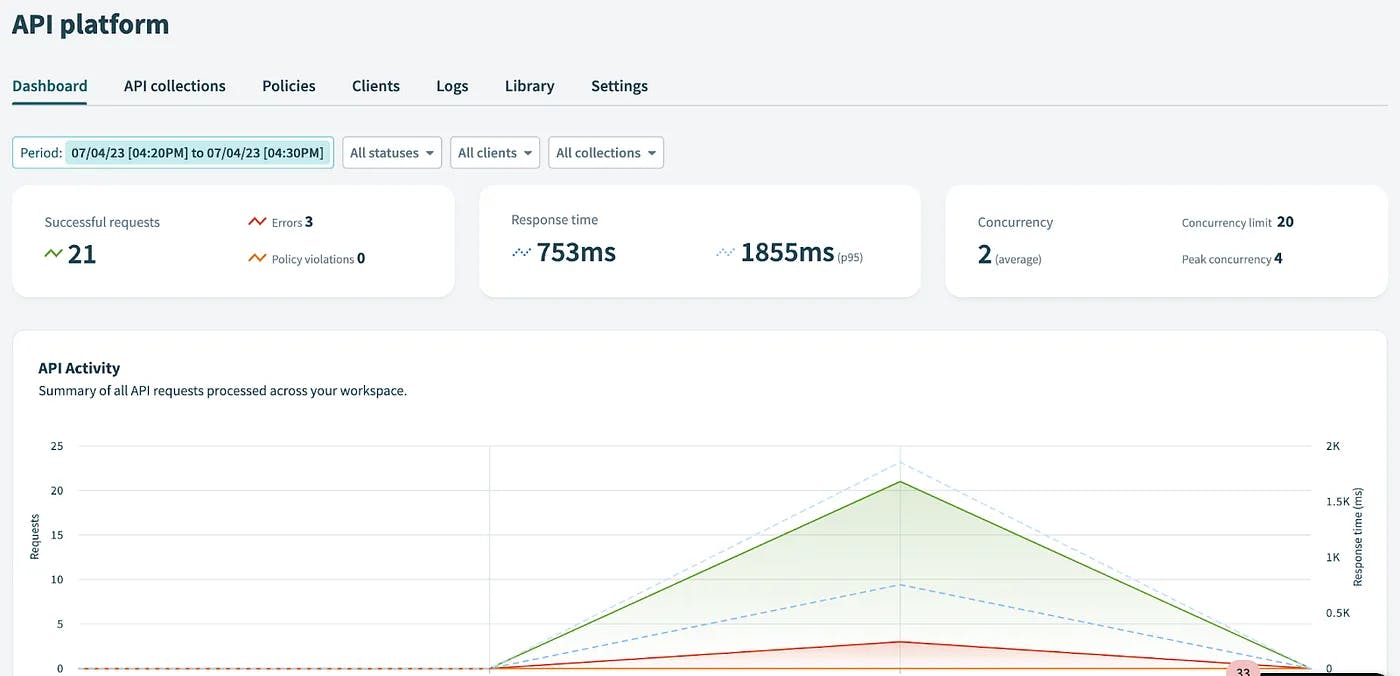
Source: ihub4us
Workato’s API platform enables users to turn recipes into APIs, defining endpoints, HTTP methods, and access controls to facilitate API management. The API platform dashboard allows owners of the API platform to visualize real-time data about the endpoints and API collections at a glance, monitor the performance of their API platform as a whole, and get granular data about a specific endpoint collection or requesting customer.
The platform is designed to help teams build, run, and manage APIs at scale while reducing complexity and cost. It allows users to create and govern APIs for data sharing across cloud apps, on-premises systems, ERPs, and databases within a unified interface. The platform includes features for managing API usage, such as quotas and rate limits, to maintain reliable performance. Its cloud-native architecture supports fast scaling and consistent uptime, while authentication, authorization, and encryption protocols help secure APIs and client access.
Workato emphasizes ease of use and flexibility through a low-code / no-code development environment. Users can design and publish APIs using prebuilt connectors and visual tools that incorporate business logic, data transformation, and error handling. Existing APIs can also be proxied using a built-in API gateway, enabling high-volume, low-latency performance. Inline documentation tools generate customizable user guides and OpenAPI specs, enabling both internal and external users to discover and test APIs efficiently. Developers can also brand APIs using custom domains with automated SSL/TLS certificate management.
Monitoring and optimization are integrated into the platform via a real-time analytics dashboard. Users can track API health, performance, and security posture, with logging tools to isolate and resolve issues quickly. This provides operational visibility across the entire API lifecycle, helping teams maintain compliance and reliability standards.
Data Hub / MDM
Source: Workato
Workato’s Data Hub, powered by Reltio, provides a centralized platform for unifying and activating trusted enterprise data. It supports data consistency across systems through multidomain master data management (MDM) and Customer 360 capabilities, enabling organizations to create a single source of truth. The platform helps break down data silos by standardizing, cleansing, and validating data across business domains. AI-powered match and merge functionality, including the use of private large language models (LLMs), allows for flexible, rule-free entity resolution and enhanced data stewardship productivity.
The Data Hub also integrates governance and quality assurance through machine learning–based anomaly detection, real-time dashboards, and interactive validation tools. Businesses can connect new data sources using prebuilt connectors and adapt quickly through no-code and low-code workflows. Velocity Packs, which include industry- and domain-specific starter kits, accelerate deployment by including data models, rules, and integrations. These components are meant to streamline onboarding and reduce time-to-value for data initiatives.
Additionally, the platform supports real-time activation of customer insights by generating unified customer profiles that can be deployed across operational systems. Pre-built assets help activate customer segments quickly, enabling personalized engagement across channels. With support for extensible integration patterns and a business-user-friendly interface, the Data Hub is designed to scale with evolving enterprise data needs while aligning with AI-readiness goals.
Workflow Bots
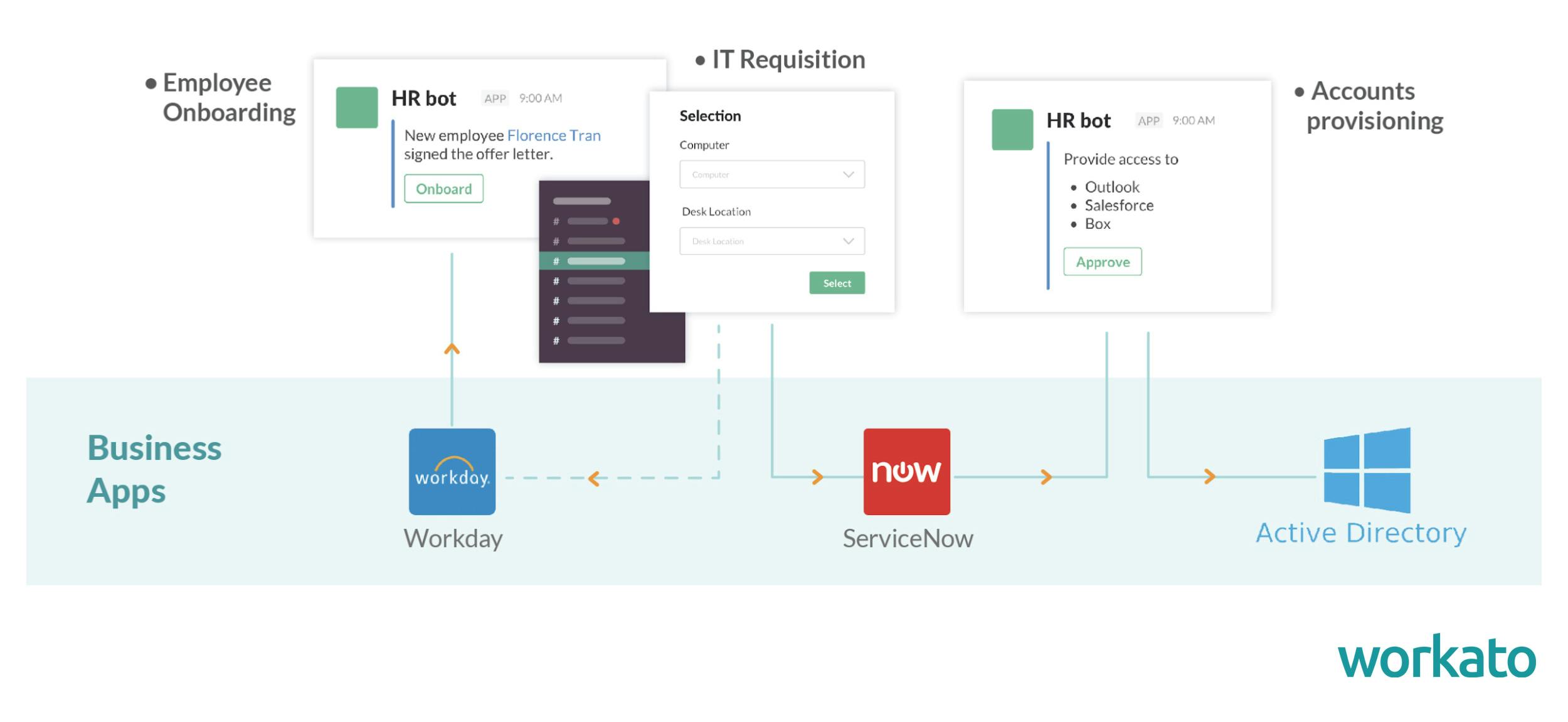
Source: Workato
Workato’s Workbot platform enables teams to perform tasks and access data directly from collaboration tools like Slack and Microsoft Teams. By embedding business workflows into chat interfaces, users can complete routine actions such as submitting expense reports, requesting time off, or approving app access without leaving their messaging environment. These interactions are personalized and designed to reduce context switching, improving productivity by allowing users to work where they already communicate.
Workbot is built with real-time security controls that verify user access before allowing changes to backend systems, ensuring compliance and data integrity. It supports automation across applications by linking form inputs to backend processes through Workato’s orchestration engine. The platform includes native integrations with a wide range of apps and uses natural language processing (NLP) to allow conversational interactions, simplifying adoption for non-technical users.
Additional features include multitasking support so Workbot can handle simultaneous user requests and tools for building custom, visually rich interfaces. Developers and business users can leverage no-code tools and prebuilt connectors to create workflows tailored to specific roles or processes. Resources like webinars, guides, and demo videos help teams quickly launch Workbot-based experiences within Slack or Teams environments.
Low-Code Apps
Source: Workato
Based on Workato’s product documentation, most of the work within the platform can be done by click and drag. The design, automation, and management process of projects, recipes, and connections can be done in a low-code / no-code experience. It also provides training and learning courses and designed certificates.
Workato’s Workflow Apps platform allows users to build, deploy, and manage low-code/no-code applications for automating complex business processes. The platform is designed to turn manual workflows such as onboarding, helpdesk, and procurement into structured, interactive apps without requiring traditional software development. Users can create custom interfaces using a drag-and-drop visual editor and tie them to business rules, human approvals, and AI actions across connected systems.
Each app is backed by Workato’s built-in data storage, which lets users define and manage data models without writing code. This centralization ensures that data used across workflows is consistent and accessible. Security features include single sign-on (SSO) for authentication and role-based access controls, helping organizations maintain compliance and governance standards while scaling app usage across teams.
Workflow Apps also support task automation and user engagement through features like automatic task assignment, notifications, and a branded app portal for accessing enterprise apps. Integration with Workato’s broader ecosystem of prebuilt connectors allows these apps to operate across a wide range of tools and services, enabling organizations to streamline operations and deploy process automation rapidly.
B2B / EDI
Source: Workato
Workato’s B2B / EDI platform, developed in partnership with Orderful, offers an integrated solution for automating and managing partner electronic data interchange (EDI) across a broad subset of formats and systems. The platform is designed to streamline onboarding and ongoing integration with external partners by using customizable templates and prebuilt connectors. It supports a wide range of industry standards, including X12 ANSI, EDIFACT, HL7, GS1, and HIPAA, as well as transport protocols like AS2, FTP, SFTP, VAN, and email, allowing businesses to standardize communication across varied partner requirements.
The solution also emphasizes workflow orchestration and visibility, enabling organizations to automate complex multi-step business processes through Workato’s drag-and-drop interface. By connecting data across document types and business systems, teams can accelerate time-to-integration and reduce development workload. Real-time dashboards and custom Workflow Apps provide full visibility into transactions, allowing users to track dependencies, identify bottlenecks, and maintain compliance with service-level agreements (SLAs). This unified approach is aimed at improving partner experience, ensuring operational reliability, and scaling B2B data exchange efficiently.
Process Insights
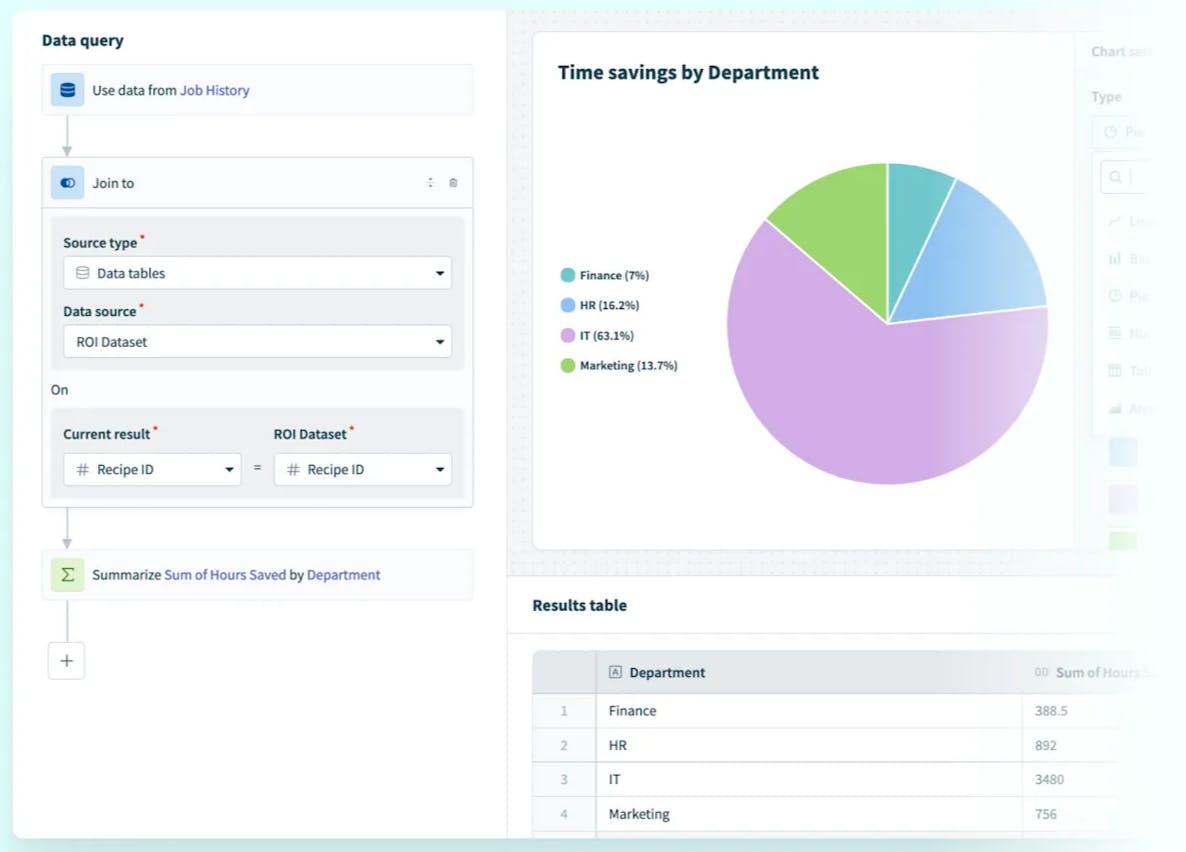
Source: Workato
Workato’s Process Insights platform provides tools to measure, visualize, and optimize the performance of automated workflows. The insights field provides insights and statistics on recipe executions ("jobs"), allowing users to view details and logs and re-run jobs as needed. It also displays plan usage information. Users can create custom dashboards and reports to monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) such as cost savings, time savings, and revenue impact. By leveraging job history and real-time data from automations, teams can analyze operational performance and track return on investment (ROI). The platform also supports custom metric definitions, enabling organizations to tailor insights to their specific business goals.
The platform includes a no-code dashboard builder with configurable widgets and prebuilt templates, allowing users to quickly build visualizations without requiring technical expertise. Insights can be derived from automation logs and process data, helping teams identify bottlenecks and uncover optimization opportunities. Additionally, users can enhance reporting by adding custom columns to job data and aggregating them alongside other metrics, enabling deeper operational analysis and more informed decision-making.
Copilots
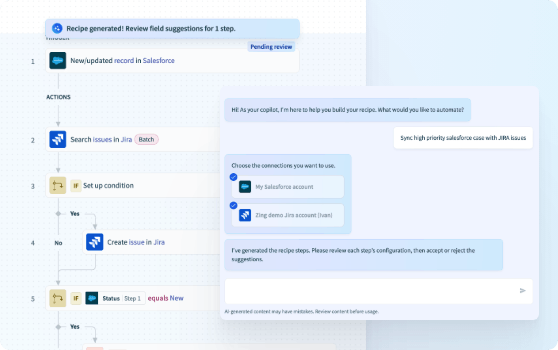
Source: Workato
Workato’s Copilots are AI-powered assistants designed to simplify the process of building, editing, and optimizing automation workflows, known as recipes, using natural language. Leveraging insights from millions of prior recipes, Copilots help users generate entire automations by describing a desired workflow in plain terms. For example, a user can request a recipe that sends high-priority tickets from Salesforce to JIRA, and the Recipe Copilot will build the corresponding automation, including triggers, actions, and data mappings. Additional Copilots assist with adding steps, mapping data fields, writing formulas, and generating recipe descriptions.
These tools aim to reduce manual effort and lower the technical barrier to automation by guiding users through complex tasks like data transformation, system integration, and connector development. Each Copilot is tailored to a specific part of the automation process for instance, Mapper Copilot assists with field matching, Formula Copilot helps with syntax and transformations, and Optimizer Copilot suggests performance improvements like batch processing or bulk actions. Connector Copilot further extends this functionality by guiding users through building custom connectors, including authentication and API actions, with minimal manual coding.
Together, Workato’s Copilots support faster automation development, improved recipe quality, and more efficient collaboration across technical and non-technical users. By embedding intelligent suggestions and automation best practices into each step, the Copilot suite helps teams scale their integration initiatives with greater speed and consistency. Workato incorporates AI and ML for decision-making and predictive automation, allowing workflows to be optimized based on data insights. It provides rebuilt Agentic Apps equipped with LLMs, RAG, and 1.2K+ apps.
AI Workflows
Source: Workato
Workato’s AI platform enables organizations to embed generative AI capabilities directly into business processes to increase efficiency and unlock new use cases. By supporting integrations with models from providers like OpenAI, Google Gemini, Amazon Bedrock, and Azure OpenAI, users can build AI-enhanced workflows for scenarios such as account-based marketing, recruiting, invoice processing, and customer support. Prebuilt connectors and built-in AI services allow users to access features like summarization, translation, classification, and automated content generation without relying on separate vendors.
The platform emphasizes security and control through role-based access management, real-time audit logs, and privacy safeguards that prevent exposure of sensitive data or personally identifiable information (PII). Users can manage who interacts with AI tools and ensure compliance across teams. These capabilities are designed to help businesses integrate AI rapidly while maintaining governance standards, allowing both technical and non-technical users to apply AI to a wide range of operational workflows.
Workato Agentic
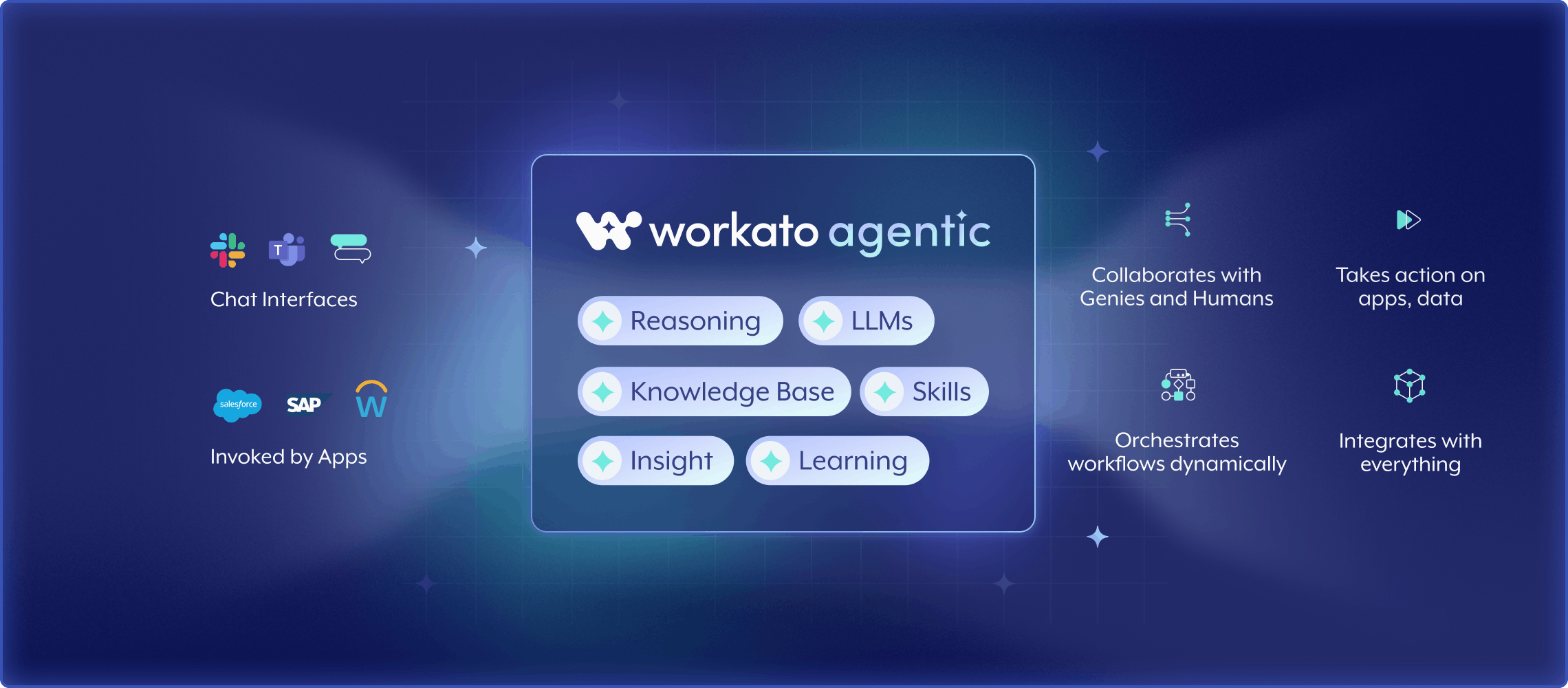
Source: Workato
Workato’s Agentic platform enables enterprises to rapidly build and deploy AI agents, called Genies, that automate business workflows across applications and teams. Unlike standalone large language models (LLMs), Genies are designed to operate with enterprise context and can take actions across connected systems. These agents are built using low-code tools in Agent Studio and can interact through interfaces like Slack or Microsoft Teams.
Genies are customizable, skill-based agents that dynamically orchestrate processes and adapt as business needs evolve. Each Genie can be extended with skills, including modular automation capabilities that use Workato recipes or external integrations and can collaborate with both humans and other agents. The platform includes built-in support for over 1.2K cloud and on-prem apps, enabling flexible deployment across diverse tech stacks. Governance features include role-based access control (RBAC), audit logs, runtime authentication, and encryption, ensuring compliance and secure execution. Workato positions the Agentic platform as a fast and controlled pathway to enterprise-grade AI automation.
AgentX
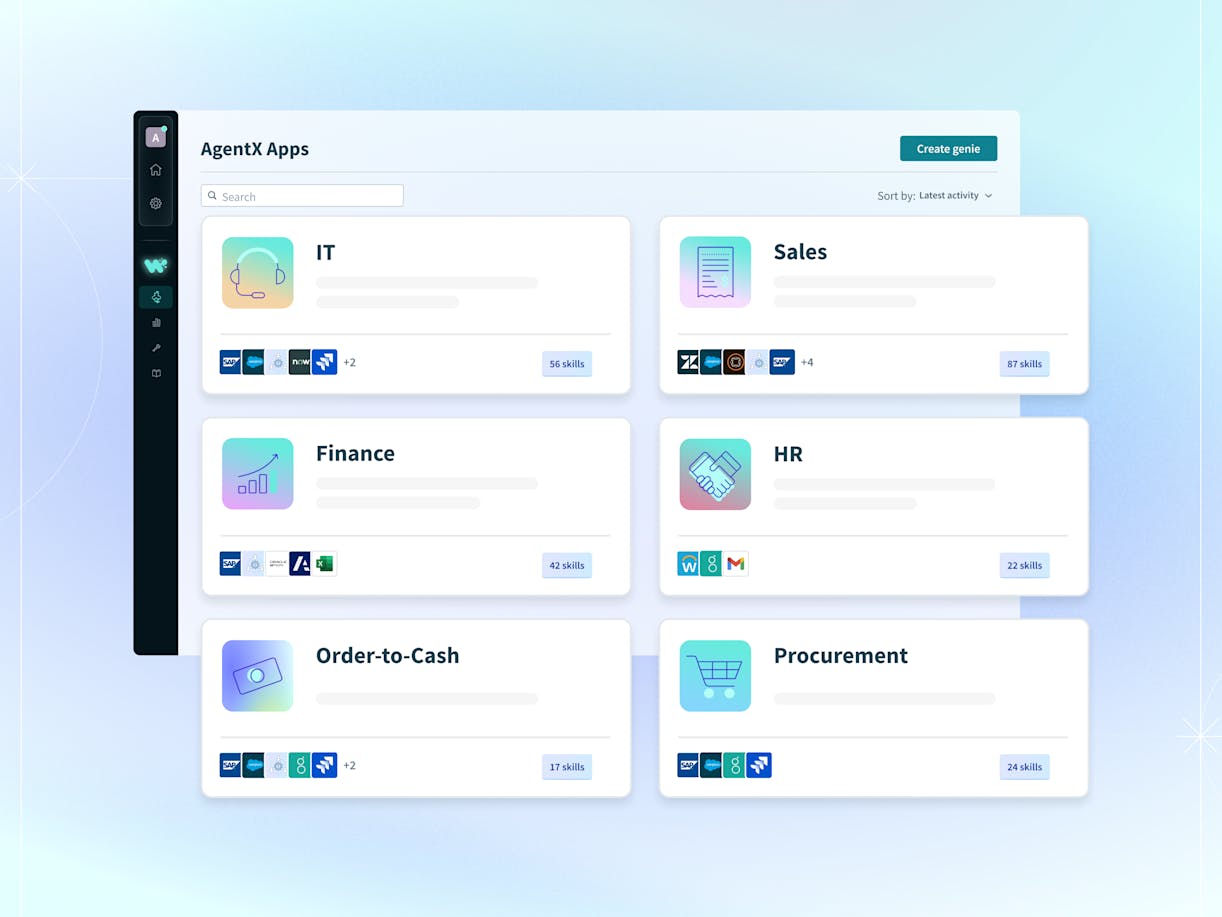
Source: Workato
Pre-built AgentX apps cover common business domains—such as IT, HR, and sales—helping organizations accelerate time to value while improving response time, resolution rates, and productivity.
AgentX IT: Workato’s AI-powered helpdesk agent is designed to automate and streamline IT support processes. Built on the Workato Agentic platform, it handles tasks such as ticket management, software access provisioning, endpoint monitoring, and account management using AI-driven workflows. It also offers enterprise-grade governance, including role-based access controls, runtime user authentication, hourly encryption key rotation, and detailed operational logging to ensure data security, compliance, and auditability.
AgentX Sales: An AI-powered agent from Workato designed to streamline and automate key sales processes. It supports functions such as inbound lead management, outbound prospecting, customer research, quote creation, and real-time coaching. The agent provides sales teams with AI-generated insights, personalized outreach sequences, and automated follow-ups, helping to prioritize opportunities, shorten sales cycles, and reduce manual effort. AgentX Sales is customizable through no-code skill development and includes enterprise-grade governance features like role-based access control, encrypted data handling, and full auditability.
AgentX Support: An AI-powered customer service solution from Workato designed to improve resolution times, reduce operational costs, and enhance the customer experience. It combines AI-driven search, automated triage, and no-code workflow automation to enable self-service, streamline live agent support, and handle multi-step processes across support channels. Features include cognitive search, automated email handling, integrated live chat, agent co-pilot tools, and analytics for monitoring performance. It supports skill-based customization and includes enterprise-grade security controls such as role-based access, audit logs, and hourly key rotation for data encryption.
Agent Studio is Workato’s low-code / no-code development environment for building, deploying, and managing AI agents, or Genies, that can take actions across enterprise applications and orchestrate complex workflows. The platform allows users to define and modify “Enterprise Skills,” which determine how Genies operate across systems, and supports collaboration between multiple Genies and human users. Genies can access business-specific knowledge bases, integrate into tools like Slack and Microsoft Teams, and be launched using pre-built templates such as AgentX for IT, sales, or customer support scenarios.
Workato’s Agent Studio offers extensive customization options for actions, approvals, and workflow logic, while maintaining enterprise-grade security and governance. Features include runtime authentication, hourly rotating encryption keys, role-based access controls, and full operational observability via logs and dashboards. This combination of automation, integration, and oversight enables organizations to scale AI agents while maintaining compliance and control.
Market
Customer
Workato's focus on the enterprise means that top-down sales are a big part of their business model, likely targeting Chief Information Officers (CIOs), Directors of IT, heads of Digital Transformation, Chief Technology Officers (CTOs), and others responsible for organization-wide purchases of tools for streamlining operations and improving connectivity between tools.
Workato sells to IT, Marketing, HR, Finance, Sales, Success/Support, and Product functions across Manufacturing, Retail, Logistics, Healthcare, Media, BPO, and Non-profit industries. As of June 2025, customers include Atlassian, Autodesk, Box, Broadcom, Canva, GitLab, MGM, Monday.com, Nextdoor, Nokia, Nutanix, Toast, etc.
Based on one unverified source, Workato’s operations are predominantly in North America, Europe, and parts of Asia/Pacific, and the platform is often utilized by major corporations with over 10K employees. In addition, a significant portion of Workato's customers are mid-sized organizations. Specifically, Workato has around 170 customers with between 1K to 5K employees and 124 customers with between 500 to 999 employees in 2025.
Market Size
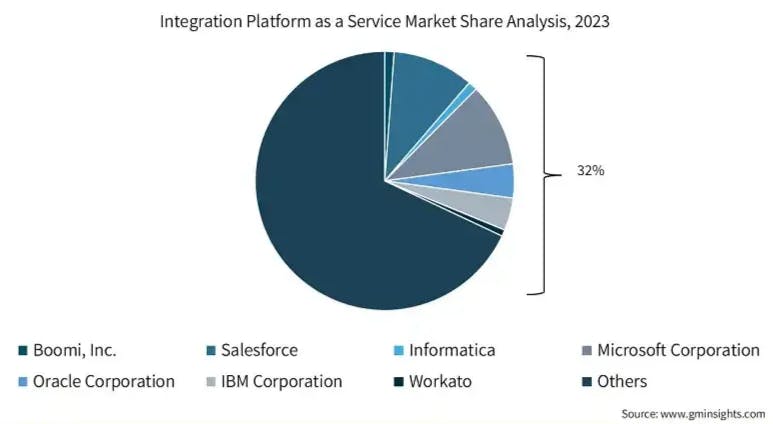
Source: Global Market Insights
The integration platform as a service (iPaaS) market grew by 30.7% to $7.7 billion in 2023 from $5.9 billion in 2022. The global iPaaS market is estimated to increase by $10.3 billion from 2022 to 2027. The market's growth momentum will progress at a CAGR of 26%. By geography, North America is estimated to account for 38% of the global market during the forecast period.
The vendors, Salesforce (MuleSoft), Oracle, Informatica, SAP, and Boomi, accounted for a 57.7% share in 2023, contributing approximately 66% to the net dollar inflow of the overall iPaaS segment.
Competition
Workato competes in a dynamic automation and integration landscape with enterprise incumbents and emerging players in the iPaaS market, as well as an adjacent competitive ecosystem with SaaS platforms that provide similar integration and automation systems combined with software, workflow automation, and robotic process automation (RPA).
Direct iPaaS Competitors
MuleSoft: MuleSoft was founded in 2006 and acquired by Salesforce in 2018 for $6.5 billion, becoming the core of Salesforce’s integration strategy. Its Anypoint Platform offers enterprise-scale API design, management, and monitoring and is deeply embedded within the Salesforce ecosystem.
Boomi: Boomi is a Dell Technologies spinout that offers a cloud-native iPaaS that facilitates quick integration across various applications and data sources and automation with a vast array of connectors and low-code tools. Its platform includes Boomi Integration, Boomi Flow, and Boomi Event Streams. Boomi introduced new AI-powered services and event-driven features in 2023 to stay competitive in a modern integration environment.
Informatica: Founded in 1993, Informatica went public again in 2021 after a period of private ownership. It provides a comprehensive data and application integration suite through its Intelligent Data Management Cloud (IDMC), powered by the AI engine CLAIRE. As of June 2025, Informatica serves approximately 5.4K customers across nearly 100 countries. In May 2025, Salesforce announced plans to acquire Informatica for $8 billion.
SnapLogic: Founded in 2006, SnapLogic offers a visual, no-code platform for building integrations and automating data workflows. The platform supports cloud and on-prem deployments, with compatibility across AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud. SnapLogic raised a funding round at a $1 billion valuation and, as of June 2025, had raised $371.3 million to date.
Tray.ai: Tray.ai (formerly known as Tray.io) offers the Universal Automation Cloud, an AI-enhanced, low-code iPaaS that allows both technical and non-technical teams to automate processes across apps. Founded in 2012, Tray is a VC-backed player that has raised $149.1 million by June 2025 and positions itself as a flexible tool for high-growth teams and startups.
Paragon: Paragon takes a different approach by offering embedded iPaaS, allowing SaaS companies to build native integrations for their users directly into their product. Paragon targets developer teams and is increasingly popular among B2B SaaS platforms. As of June 2025, Paragon has raised $21.2 million.
Workflow Automation & RPA Competitors
Not all integration problems require APIs. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) solves automation by mimicking user actions like clicks and keystrokes, especially in legacy systems without APIs.
UiPath: UiPath started from RPA and expanded to a broader automation platform that integrates AI-driven decision-making and business process orchestration. With over 10K customers, UiPath integrates with cloud providers like AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft. As of June 2025, UiPath had a $6.8 billion market cap.
Zapier: Zapier is a prosumer-focused automation platform that enables non-technical users to connect over 7K+ apps via triggers and actions. Zapier focuses more on SMB and solo user markets with its no-code simplicity.
Enterprise SaaS Ecosystem Platforms
Major enterprise software vendors offer native integration tools as part of their broader suites, which pose a threat to Workato through vendor lock-in and bundled pricing.
Oracle Integration Cloud: Oracle Integration runs on OCI and provides robust prebuilt adapters for Oracle’s own ERP, HR, and analytics tools. This makes Oracle’s iPaaS highly appealing to enterprises already embedded in the Oracle stack.
SAP Integration Suite: SAP Integration Suite enables end-to-end integration across SAP and non-SAP applications. It includes access to SAP’s Business Accelerator Hub, allowing customers to rapidly deploy prebuilt integration flows aligned to key business processes.
IBM App Connect: IBM App Connect, part of the Cloud Pak for Integration, supports both hybrid and multi-cloud integration environments. It appeals to large enterprises with existing IBM infrastructure and offers advanced transformation and mapping tools.
Business Model
Workato monetizes its automation platform through a two-part pricing structure introduced in February 2024, consisting of a fixed platform fee and a variable usage-based fee.
The fixed fee includes three tiers: Standard, Business, and Enterprise, each designed for distinct customer segments based on scale, support needs, and compliance requirements.
The usage-based fee is calculated on tasks executed within customer workflows ("recipes"), such as individual actions or API requests. Workato also provides an option for organizations handling large-scale workflows through High-Volume Recipes (HVRs). Recipes converted into HVRs are billed at a fixed rate per recipe instead of per task, providing predictable and cost-efficient billing for customers managing high task volumes.
Workato employs a quote-based pricing strategy and does not publicly disclose specific prices on its website as of Mar 2025.
Traction
Workato's revenue reportedly increased by 484% from the fiscal year 2020 to 2023. According to one unverified source, the company’s ARR reached $150 million in 2023, a 36% increase from $110 million in 2022. Workato expanded from 3.5K customers in December 2018 to more than 6K by November 2019, reflecting a 71% increase within one year. By November 2021, Workato served approximately 11K businesses.
Valuation
In late 2021, Workato announced the acquisition of RailsData and the closing of Series E of $200 million at a $5.7 billion valuation. As of the Series E, the company had raised $421 million in total funding across nine rounds from key investors including Altimeter Capital, Battery Ventures, Redpoint Ventures, Fabrica Ventures, etc. As of June 2025, secondary markets indicated that Workato’s valuation may have fallen significantly and may be closer to $1.7 billion.
In January 2021, Workato raised $110 million in Series D, which valued the company at $1.7 billion. In November 2019, Workato raised $70 million in Series C funding, led by Redpoint Ventures with participation from Norwest Venture Partners, Geodesic Capital, and existing investors Battery Ventures and Storm Ventures. In December 2018, Workato announced a $25 million Series B funding round from Battery Ventures, Storm Ventures, ServiceNow, and Workday Ventures. In July 2017, Workato announced a $10 million Series A led by Storm Ventures with participation from strategic investors.
Key Opportunities
Digital Transformation Boom
The shift toward digitized operations across industries is accelerating, and integration sits at the heart of it. Worldwide spending on digital transformation reached $1.9 trillion in 2022, and is estimated to nearly double to $3.9 trillion in 2027, reflecting a CAGR of 16.2%. With hybrid work models becoming the norm, cloud infrastructure becoming the default, and teams operating in increasingly app-heavy environments, the demand for seamless, automated system connectivity is greater than ever.
As a platform purpose-built to orchestrate data and workflows across fragmented systems, Workato is well-positioned to capture value from this macro trend. Whether enabling internal teams to connect legacy systems or helping businesses integrate new AI services into customer-facing tools, Workato's integration and automation capabilities provide the glue that holds digital transformation together.
AI & Workforce Automation
The future of work is autonomous, and that requires orchestration. The adoption of emerging technologies such as cloud computing, AI, and generative AI is fundamentally changing how enterprises operate. One 2023 study found that 40% of organizations increased their AI adoption due to generative AI breakthroughs, and 75% expect it to significantly disrupt their industries in the next three years.
Workato has an opportunity to serve as a key orchestration layer, enabling companies to plug AI services into operational workflows, automate decision-making across departments, and trigger actions across apps in real time. As AI proliferates, it’s not enough to generate insights; businesses need tools to act on them. That’s where platforms like Workato come in.
Meanwhile, digital labor is becoming a reality. According to one report, 23% of jobs will undergo structural change in the next five years. From bots and digital agents to fully autonomous workflows, enterprise interest in workforce automation is growing. Another report found that 70% of business leaders expect to use AI to replace or augment jobs, especially those with repetitive, rules-based tasks. Workato’s low-code approach could lower the barrier to automation adoption and become the platform of choice for distributed teams seeking to scale productivity without scaling headcount.
SaaS Explosion & App Sprawl
The average enterprise today uses 342 SaaS applications, and knowledge workers now rely on an average of 11 tools to do their jobs, up from six in 2019. As software ecosystems expand, so does data fragmentation, system redundancy, and the risk of human error.
With app sprawl showing no signs of slowing, integration and automation are moving from “nice to have” to “must have.” 47% of digital workers now say they struggle to find the information needed to do their jobs effectively. Platforms like Workato, which offer prebuilt connectors, no-code builders, and embedded governance tools, are well-suited to help businesses simplify internal operations, eliminate silos, and reduce manual touch points.
The proliferation of SaaS also creates room for more verticalized automation: industry-specific workflows, compliance automations, and AI/ML-enabled business rules tailored to each function. This unlocks the potential for Workato to expand its marketplace of prebuilt recipes and connectors to serve more targeted use cases across finance, HR, sales, and IT.
Untapped Industries
While enterprise tech adoption is strongest in North America, major opportunities lie in automating less digitized industries and expanding into under-penetrated regions. One estimate indicates that the US accounts for 35.8% of global digital transformation spending, with Europe and Asia-Pacific rapidly catching up. Asia-Pacific, in particular, is expected to see the fastest growth, fueled by urbanization, government support, and a growing digital workforce.
As of 2023, only 30% of organizations in the Asia-Pacific region have adopted AI, compared to 40% in North America. This adoption gap signals greenfield opportunities for automation platforms like Workato. Industries like healthcare, financial services, logistics, and government continue to face pressure to modernize while navigating compliance-heavy environments. With its focus on security, scalability, and flexibility, Workato could position itself as the integration backbone for industries historically underserved by modern tools.
As enterprise IT budgets shift from monolithic platforms to composable ecosystems, Workato can tap into a massive, growing TAM by serving as the connective tissue that helps companies move faster, reduce error, and unlock the full value of their tech stack.
Key Risks
Intensifying Competition
Workato operates in a hyper-competitive space where consolidation and commoditization are accelerating. On one end, enterprise software incumbents like Microsoft, Oracle, SAP, and IBM have embedded native integration and automation tools into their platforms, often bundled at discounted rates. These offerings create strong customer lock-in and reduce the incentive to adopt independent tools like Workato.
On the other end of the spectrum, Workato faces competition from established iPaaS leaders like MuleSoft and Informatica (Salesforce-owned), as well as Boomi (a Dell spinout). In addition, Workato faces additional competition from a wave of newer low-code and developer-focused entrants such as Tray.io, Paragon, and Make. These challengers are targeting mid-market companies and developers with more flexible pricing and rapid deployment cycles. As Gartner warns, up to two-thirds of iPaaS vendors may not survive, Workato’s long-term position will depend on sustaining product differentiation and proving ROI at scale.
Platform Risk
As a horizontal platform, Workato’s value is largely dependent on the breadth and depth of its integrations with third-party applications such as Salesforce, Slack, NetSuite, and ServiceNow. Changes to APIs, pricing models, or ecosystem policies by these partners could disrupt Workato’s integration quality or increase costs to maintain compatibility. Additionally, if these platforms expand their native automation offerings, for example, as Salesforce has with MuleSoft, it could reduce demand for Workato as an external layer.
This dependency introduces a strategic vulnerability, especially if Workato cannot keep pace with rapidly evolving partner roadmaps or if key partners develop incentives to limit or compete with external integration tools.
Disintermediation via AI Agents
The rise of autonomous AI agents capable of orchestrating workflows, calling APIs, and performing reasoning-based task automation may eventually shift how businesses approach integration. Platforms like OpenAI’s AutoGPT and enterprise-grade agents in development by companies like Microsoft, Google, and Cognition Labs, creators of Devin, suggest a future where AI systems could replace many of the logic-based workflows built within iPaaS platforms.
While Workato is actively integrating AI into its platform, it may still face existential risk if businesses increasingly prefer autonomous agents that generate and manage workflows dynamically, reducing the need for static, human-designed automation paths.
Pricing Pressure & Procurement Complexity
As the core capabilities of iPaaS solutions (such as connectors, workflow builders, and APIs) become commoditized, customers are becoming more price-sensitive. Gartner's 2023 Magic Quadrant for iPaaS emphasized that buyers are increasingly evaluating platforms based on cost, ease of implementation, and integration with their existing ecosystems.
Workato’s pricing model, which often scales with the number of automations, users, or volume, can become expensive for large enterprise deployments. In contrast, vendors that bundle iPaaS functionality into existing software suites (e.g., Microsoft Power Platform or SAP BTP) often offer it at a lower marginal cost. In emerging markets and among mid-market buyers, this could steer decision-makers toward lower-cost alternatives or even open-source options that offer “good enough” functionality at a fraction of the cost.
Summary
As enterprises accelerate digital transformation, AI adoption, and SaaS proliferation, the demand for unified automation and integration platforms is rising. Workato is positioning itself to meet this need with its cloud-native, low-code iPaaS that combines consumer-grade usability with enterprise-grade scalability. The rise of generative AI and agentic AI is driving demand for orchestration layers that bridge AI and enterprise systems. As digital labor and workflow automation become central to operations, Workato offers a compelling solution for companies navigating SaaS sprawl and operational complexity.
The iPaaS space is becoming increasingly crowded. Workato faces pressure from incumbents bundling integration tools into larger platforms (e.g., Microsoft, Oracle) and from agile challengers offering faster, cheaper alternatives. Differentiation is narrowing, pricing pressure is rising, and the emergence of autonomous AI agents could shift how workflows are built altogether. To win in the next chapter, Workato must extend beyond integration to become a true business automation layer. The goal for Workato is to provide a solution that is AI-native, cost-effective, and scalable across industries. If successful, it could become a core pillar of enterprise tech stacks in a world where automation is no longer optional.





