Thesis
Large language models (LLMs), a type of advanced AI trained on massive amounts of text, have shown rapid and consistent improvements. These include foundation models, which are general-purpose AIs that can be adapted for a wide range of tasks. One example is OpenAI’s o3-mini model. Released in January 2025, just four months after its predecessor, o1, o3-mini made significant performance gains. As of December 2024, on the ARC-AGI benchmark, which tests general reasoning skills, o3-mini scored 87.5% compared to o1’s 32%. It also performed better on the AIME 2024 mathematics benchmark, with a score of 87.3% versus 83.3% for o1, and on competitive coding tasks, it achieved a score of 2.1K compared to o1’s 1.9K.
Despite LLMs’ powerful capabilities, enterprises struggle to deploy them effectively for business functions due to production and ROI concerns. For example, business leaders cited inaccuracy and intellectual property infringement as the two most relevant risks as of May 2024. Additionally, inaccuracy was the only risk that business leaders were more focused on resolving in 2024 than in 2023, across areas like customer journeys, summarization, coding, and creative content. Other persistent risks include compliance and intellectual property infringement.
Concerns about productivity and ROI also persist: while LLMs excel at summarizing text, they fail at more sophisticated tasks, leading to 70% of generative AI initiatives stalling in pilot phases as of October 2024. Additionally, 92% of companies planned to increase AI spending in the next three years as of January 2025, yet only 1% considered their efforts mature. Meanwhile, implementing high-performing, scalable AI solutions becomes complex as costs encompass hardware, software licenses, and specialized personnel.
Some technology firms have introduced partial solutions to help enterprises develop and utilize generative AI applications. For instance, NVIDIA provides AI Foundry for building custom generative AI models, while Accenture helps clients accelerate access to enterprise data via a proprietary “switchboard” model. AWS’s Bedrock offers a platform for scalable generative AI, and OpenAI has a custom model program for enterprises. Cohere likewise supports enterprise-grade customization with flexible deployment options. However, many of these solutions require deep technical knowledge or rely on APIs that limit flexibility. They are also not always cost-effective, especially for companies without dedicated AI teams.
Writer is a generative AI platform that helps businesses use LLMs to generate accurate and compliant content and deploy generative AI applications across different departments, including operations, products, sales, and marketing. Its platform provides an integrated system of custom LLMs, graph-based RAG, AI guardrails, and development tools for organizations to deploy AI apps and workflows without the need for technical knowledge. With these offerings, Writer aims to make enterprise AI adoption simpler, more affordable, and more capable of meeting both worker and executive expectations.
Founding Story
Writer was founded in August 2020 by May Habib (CEO) and Waseem Alshikh (CTO).
Habib, who grew up in Lebanon, graduated from Harvard with a bachelor’s degree in Economics. She worked as an analyst at Lehman Brothers from June 2007 to February 2009, and later as Vice President at Mubadala from February 2009 to January 2013, where she focused on semiconductor investments and conducted research on NVIDIA. Alshikh studied computer science and semantics at Beirut Arab University and was ranked first nationally in Syria’s computer science competitions for two consecutive years, from 2003 to 2004.
While working at Mubadala in 2013, Habib became involved in a small Twitter community of computer scientists in Dubai. She met Alshikh after reaching out to him on Twitter about his work on statistical machine translation problems. Six months after their online connection, the pair met up and hit it off immediately with a shared interest in language barrier issues. In particular, Habib was motivated by the social inequities arising from language barriers, and Alshikh struggled with learning English while pursuing his computer science degree. In 2013, the pair co-founded a machine-learning translation company called Qordoba. Qordoba started by offering professional translations, including full-scale localization projects of academic textbooks, legal documents, entire mobile apps, and websites. By 2014, it began serving enterprise clients like Groupon, LinkedIn, HSBC, and SAP, taking content and preparing it for a new language and new international market.
Although Qordoba raised $23 million in total funding from investors like Aspect Ventures, reached 50 customers, and generated single-digit revenue, Habib and Alshikh saw a bigger opportunity with the introduction of the AI transformer architecture in June 2017. They believed that transformers presented a potential opportunity to go beyond mere translation, such as translating French to English, and instead, to translate off-brand content into on-brand content, which they said “felt like a very big, greenfield opportunity.”
In September 2020, Habib and Alshikh pivoted and transitioned Qordoba into Writer, which was built on Qordoba’s core principle — translating text from one “language” into another — and extended it to brand voice and messaging. Its AI content generation tool quickly transformed inconsistently branded content into text that conformed to a company’s established style. Determined to compete with established AI writing tools like Grammarly (valued at $13 billion in 2020), the founders secured a $5 million seed round that same year from investors like Aspect and Upfront Ventures, outlining a vision that would beat Grammarly at privacy, security, and enterprise readiness, as well as develop full AI-driven content creation.
However, Writer struggled to gain broad adoption before ChatGPT’s launch in November 2022. Despite the product’s capabilities, prospective enterprise clients were so hesitant to fully trust AI-driven content creation that Habib even removed a slide from pitch decks that laid out Writer’s future “AI writing” vision, fearing it would scare away prospective clients rather than inspire them. As a result, growth during Writer’s early days hinged on demonstrating tangible benefits — like brand consistency and saved editing time — without pushing too far into uncharted AI territory. Habib, who managed go-to-market, and Alshikh, who managed enterprise product development, won over clients by earning enterprise customers’ trust and onboarding them quickly.
Before selling a product, the team developed solution maps by distilling insights from hundreds of conversations and experiments with various applications built on their platform. This process identifies high-impact use cases where generative AI can deliver real business value, while realistic ROI figures are emphasized to avoid overstated promises. It was by winning over customers individually that Habib and Alshikh were finally able to get over 50% of users actively using Writer daily rather than monthly in the first quarter of 2021.
After ChatGPT’s launch in November 2022, Habib felt that enterprise customers’ sentiments changed significantly and helped bring customers along. As a result, Writer grew rapidly from just $2 million ARR in 2022 to over $47 million ARR in 2024. Its strong traction also helped raise over $121 million across two funding rounds from November 2021 to September 2023 to help even more enterprises adopt generative AI.
As of April 2025, Habib remained CEO, and Alshikh continued as CTO of Writer. In 2023, Kevin Chung joined the company as Chief Strategy Officer, bringing experience as VP of Business Development at Miro and Head of Partnerships and Business Development at Dropbox. In July 2023, Andrew Racine was appointed Chief Marketing Officer. He previously held senior marketing roles at Fivetran (VP of Global Demand Generation), MongoDB (Director of Demand Generation), and Turbonomic, an IBM company, where he served as Senior Director of Demand Generation and Digital Marketing.
Product
Writer’s core product is the Palmyra LLM family. It provides large enterprises with AI writing generation tools designed to maintain consistent brand voice and content standards. While Writer initially focused on helping marketing and communications teams enforce style guidelines and brand compliance, it has expanded to the finance and healthcare sectors with its domain-specific Palmyra Med and Fin LLMs. In June 2024, Writer expanded its AI platform with the launch of its AI Studio, helping enterprise teams create custom AI applications.
Palmyra LLMs
Palmyra is a family of large language models developed by Writer which range in size from 128 million to 43 billion parameters as of July 2023 and January 2024, respectively. In AI, parameters are the internal values the model learns during training to understand language, recognize patterns, and generate accurate outputs. Typically, the more parameters, the more knowledge and nuance the model can capture.
However, despite having a relatively low number of parameters, compared to GPT-4o’s 200 billion and Claude 3.5 Sonnet’s 175 billion, Palmyra LLMs deliver precise, reliable performance across diverse tasks, demonstrated by their top rankings in Stanford HELM, PubMedQA, and BLEU for translations as of April 2025. Writer ensures user data is never used to train or modify models, adopting a zero data retention approach that stores information only as long as needed for platform usage. Within the Palmyra family, each model is further specialized for unique domain requirements.
Palmyra X 004 is a general-purpose model supporting text input and output with a 128K context window. The context window refers to the amount of text—measured in tokens—that the model can consider at once when generating responses. A token is typically a word or part of a word, so 128K tokens represent a substantial amount of information, allowing the model to understand long documents, maintain context over extended conversations, and make more informed decisions. Palmyra X 004 also includes advanced capabilities like tool-calling and retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), which let it pull in live data and trigger automated actions across connected systems.
As of April 2025, Palmyra X 004 was ranked among the top 10 on HELM Lite (86.1%) and HELM MMLU (81.3%). Palmyra X 004 also achieves an industry-leading structured call-planning (AST) score of 87.9% and a tool-call accuracy rate of 78.8% — nearly 20% higher than OpenAI’s 4-turbo-2024-04-09 (FC) model as of February 2025.
Palmyra Creative is built for creative and consumer-focused applications. Featuring a context length of 131K tokens and 122 billion parameters, it transforms basic prompts into impactful narratives for marketing, corporate communications, or technical content. This LLM helps retailers create personalized campaigns, finance teams build educational tools, and healthcare organizations produce targeted outreach, all with high-quality output.
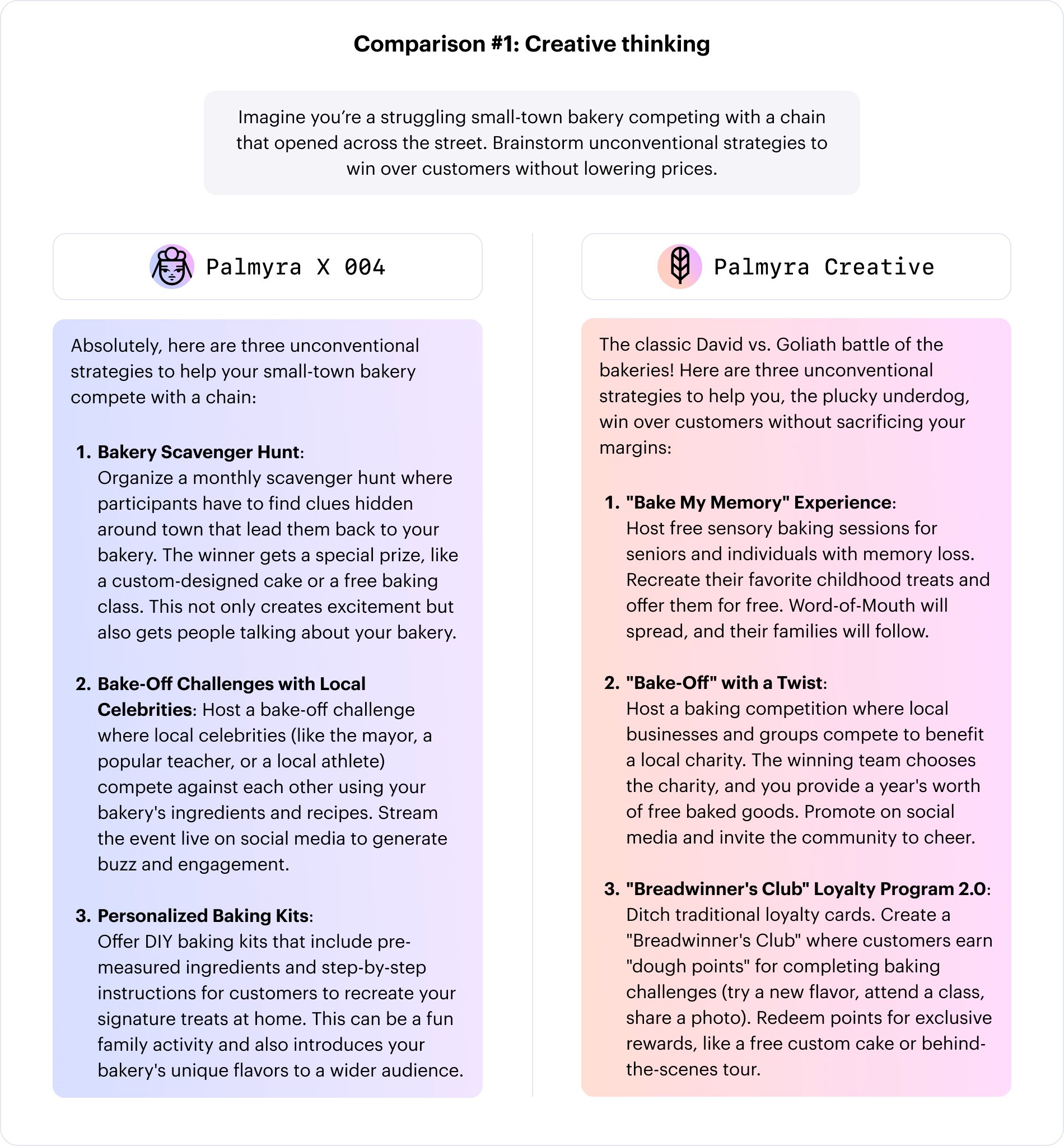
Source: Writer
Palmyra Fin caters specifically to the financial sector, providing expert-level analysis, reporting, and data processing. It passed the CFA Level III exam with a 73% score — a significant jump over the usual 60% passing threshold — and considerably outperformed GPT-4’s 33% as of April 2025. In real-world tasks like long-fin-eval, which test a model’s ability to handle complex, multi-step financial reasoning, Palmyra Fin also surpassed several leading models. Equipped with a 32K token window (approximately 33K tokens), it also achieved 100% accuracy on needle-in-haystack tasks, where the model must find a specific piece of information hidden in long financial documents, demonstrating strong retrieval capabilities.
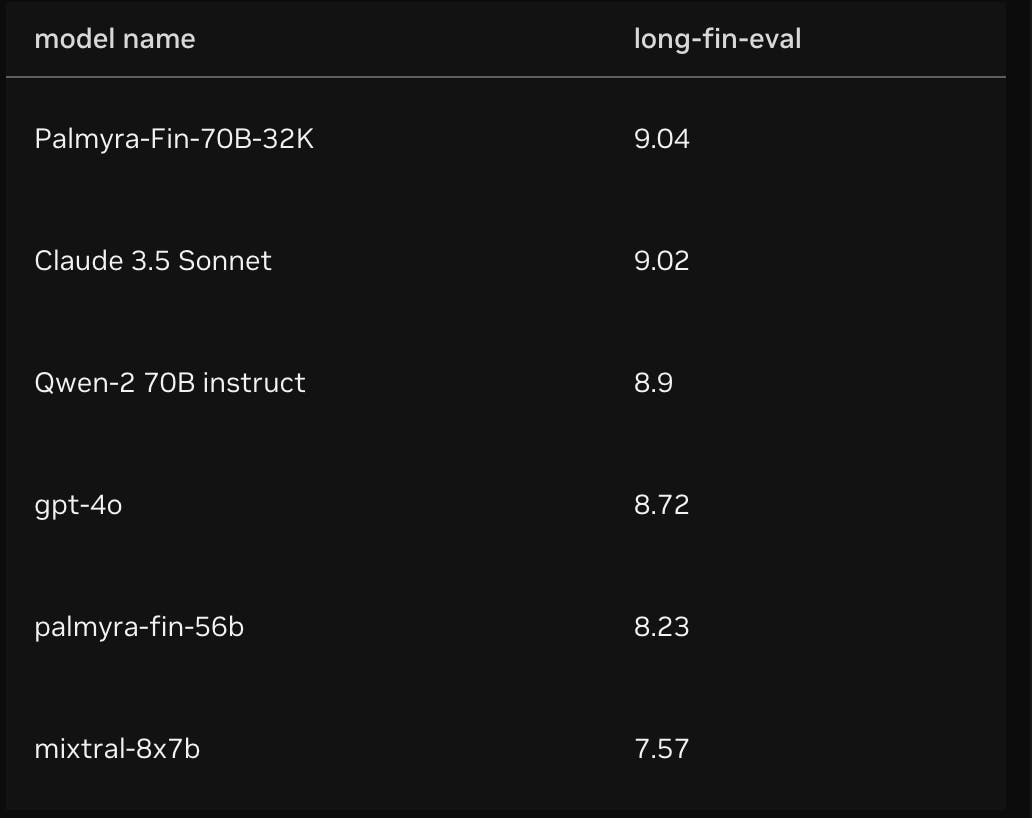
Source: NVIDIA
Palmyra Med excels in healthcare scenarios, ranking 85.9% on biomedical benchmarks despite having fewer parameters than typical language models as of April 2025. Supporting a 32K context length, the model excels at medical coding (ICD-10, SNOMED CT, RxNorm), clinical decision support, document summarization, and genetic data interpretation. Palmyra Med costs $10 per 1M output tokens, which undercuts GPT-4’s $60 for similar volume.
Palmyra Vision extends the Palmyra suite to image and video inputs. The model is designed to interpret and generate text from images, providing robust visual analysis capabilities for enterprise needs. From extracting handwritten text to interpreting complex charts and graphs, Palmyra Vision enables businesses to transform visual content into actionable insights. The model achieved an 84.4% accuracy score on the VQAv2 benchmark as of April 2025, surpassing popular models like GPT-4V and Gemini 1.0 Ultra. It also excels at reading handwriting, extracting insights from charts, and quickly identifying elements in visual media.
All Palmyra LLMs are multilingual, supporting over 30 languages, including Spanish, French, Chinese, Hindi, Arabic, and Russian as of January 2024. They also integrate into enterprise workflows through platforms like Slack, where teams can use “Ask Writer” for powerful chat-based assistance or deploy custom AI apps developed with Writer. The Palmyra family provides domain-specific models with strong data protections, offering advanced language capabilities while meeting enterprise needs for security, flexibility, and cost-efficiency.
AI Studio
Writer’s AI Studio is a suite of development tools that empowers users to build AI applications and workflows fully integrated with Writer’s generative AI platform. It offers a spectrum of solutions tailored to various skill levels, from a no-code tool that allows non-technical employees to automate repetitive tasks or generate assets without writing code, to a robust open-source Python package called the Writer Framework.
With this framework, developers can create visual applications, customize them using Python on the backend, and deploy everything with a single command — while connecting to enterprise data and using Writer’s powerful LLMs. For organizations looking to incorporate generative AI into existing software, the Writer API provides endpoints that enable tool-calling, graph-based RAG, and access to Palmyra LLMs. This makes it possible to integrate complex data sets, structured or unstructured, into advanced applications that operate within a user’s technology stack.
Beyond these core components, AI Studio supports building sophisticated custom applications that can take a wide range of actions across connected systems, data sources, and tools. It provides SDKs in popular languages like Python and TypeScript, as of April 2025, with more to come, helping developers speed up time-to-market and enable deep customization of feature-rich AI solutions. In short, AI Studio accelerates the deployment of generative AI initiatives while ensuring that applications remain closely tied to enterprise data.
Source: Writer
Knowledge Graph
Writer’s Knowledge Graph is a graph-based retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) system that stores data in an easily updatable structure while preserving its semantic relationships. Central to this approach is a specialized LLM that processes information at scale, linking data points through contextual connections rather than merely embedding them into vectors. This leads to more accurate retrieval, evidenced by the system’s 86% accuracy on RobustQA, outperforming seven well-known vector-based RAG methods.
Once relevant data is identified, it flows into Writer’s Palmyra LLMs, which have been trained on 1 trillion tokens to minimize hallucinations and maintain high-fidelity answers. In practice, this integrated Knowledge Graph empowers enterprises to create expert digital assistants anchored in their proprietary knowledge, delivering results that are both reliable and contextually sound while reducing costs by 67% compared to leading alternatives as of April 2025.
In contrast, the traditional, vector-based retrieval method converts data into numerical embeddings that capture semantic meaning in purely mathematical form. When a user query arrives, the system generates an embedding for that query and compares it with existing embeddings to gauge similarity. Although this method can be effective, it has notable drawbacks. Data must typically be split into chunks, which can lose essential context, and similarity is defined strictly by the distance between vectors. Moreover, maintaining and updating a vector database can be expensive, and retrieval accuracy often depends heavily on the tuning of KNN or ANN algorithms. If suboptimal chunks are retrieved, even a strong LLM may produce hallucinations or incorrect answers.
Source: Writer
Writer’s Knowledge Graph retains the nuanced relationships between data points through a graph structure, rather than relying solely on existing embeddings. Sophisticated compression and indexing techniques supply rich metadata, thereby improving both accuracy and relevance during retrieval. Once the Knowledge Graph locates the most pertinent data, Palmyra LLMs, trained with advanced methods on massive collections of high-quality text, take over to generate final outputs. The result is a faster, more cost-effective, and more accurate retrieval system that maintains strict security and compliance while enabling deep customization for each enterprise’s unique needs.
AI HQ
In April 2025, Writer launched AI HQ, a platform where IT and business teams can build and manage custom AI agents together. Users can design agent logic, adjust prompts, connect to internal systems, and define how each agent works. Business users handle setup through no-code tools, while developers can add more complex features when needed.
AI HQ also gives users access to over 100 prebuilt agents for tasks across support, sales, HR, and more. These agents are built for real workflows, connected to company data, and ready to use across industries like healthcare, finance, retail, and tech. Agents can be accessed through desktop apps or browser extensions for Chrome, Mac, and Windows.
Each team can customize its workspace to show the most useful agents. The platform also includes Ask Writer, a chat agent that can answer questions, search data, and generate content. As of April 2025, the agent builder tool within AI HQ was available only as a beta feature, accessible through a waitlist.
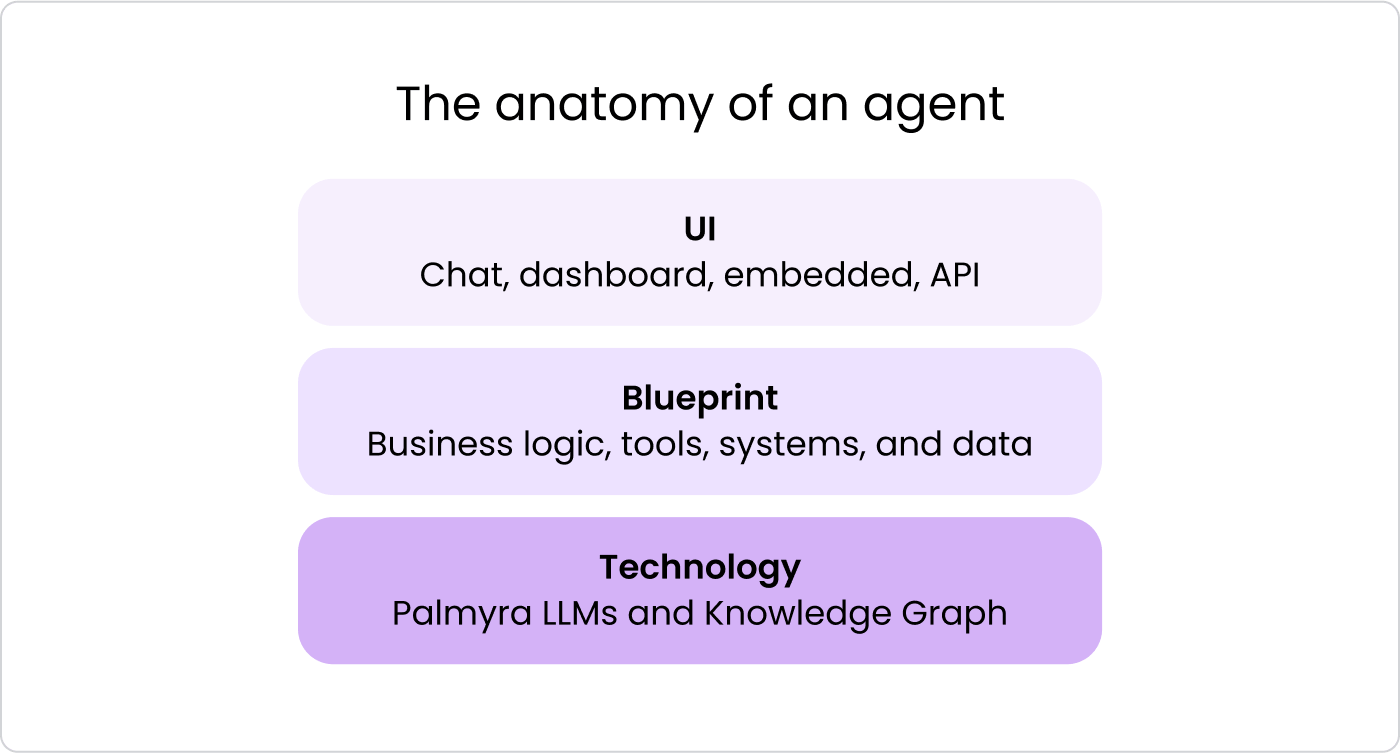
Source: Writer
Market
Customer
Writer caters to large enterprises in diverse industries, including apparel, consulting, finance, technology, real estate, legal, hospitality, and more. Some notable customers as of April 2025 include Accenture, Hilton, Vanguard, Uber, Lennar, and American Eagle.
By serving large enterprises across different industries, Writer can integrate its customers’ data, compliance rules, and sophisticated workflows across departments into its custom LLMs to improve productivity. Although individual developers and small teams can also use Writer’s products, the immediate ROI may not be as clear for them as for an enterprise, since smaller teams may operate with less complexity.
Market Size
In 2024, the global market for AI and Natural Language Processing (NLP) was valued at $214.6 billion and was projected to reach $1.3 trillion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 35.7% from 2024 to 2030 as of May 2024. If growth continues at this projected rate, the AI market could surpass $3 trillion by 2035. Key catalysts for this growth include a rise in the adoption of big data, analytics, and the increasing potential of R&D in developing AI systems. Political changes may also further catalyze growth in the AI and NLP sectors.
President Trump’s second term — beginning in January 2025 — has focused on deregulation and expanded private-sector involvement. By April 2025, his administration had repealed President Biden’s 2023 AI Executive Order, which emphasized safety and risk mitigation. It also announced a $500 billion “Stargate” fund the day after inauguration, backed by major tech and finance firms such as OpenAI and SoftBank. Enabled by emergency declarations that streamline permitting for infrastructure projects, the initiative seeks to position the US as the global leader in AI by reducing regulatory barriers and accelerating development.
Within the broader AI and NLP landscape, Writer is focused on the emerging LLM tools segment, which, as of January 2025, was forecasted to grow at a 48.8% CAGR from 2024 to 2030. By 2030, the market for LLM-powered tools may reach $22 billion, up from roughly $1.4 billion in 2023. Key drivers for the LLM tools segment are the increasing demand for advanced AI capabilities, advancements in model training techniques and computational power, and the availability of LLM APIs.
Competition
Full-Stack Enterprise AI Platforms
Anthropic: Founded in 2021, Anthropic has developed the Claude family of large language models (LLMs). Its latest version, Claude 3, exhibits strong improvements in cognitive tasks and is available in three variants — Haiku, Sonnet, and Opus — each offering different levels of capability. Anthropic also offers Claude Enterprise, an AI chatbot that supports business use cases such as brainstorming, coding, and content creation. Early adopters like GitLab and Midjourney used it in beta mode to upload documents for AI-driven, detailed guidance.
In January 2025, Anthropic raised a $2 billion venture round led by Lightspeed Venture Partners at a $60 billion post-money valuation. This brought its total funding to $15.8 billion as of April 2025. Like Writer, Anthropic targets enterprise customers, but has placed a particular emphasis on coding with the launch of Claude Code in February 2025. As of February 2025, Claude ranked first on most major coding benchmarks.
Cohere: Founded in 2019, Cohere is an enterprise AI platform that claims to offer secure, scalable solutions for improving workflows and customer experiences. It provides multiple deployment paths, including SaaS, cloud service providers, and virtual private cloud (VPC) to meet data sovereignty and compliance needs.
Unlike companies that rely on general-purpose models, Cohere uses its own customized AI models called Command to power domain-specific tools such as North, its AI work platform, and Compass, its context-aware search. This approach emphasizes cost-efficiency and targeted performance over broad versatility. In July 2024, Cohere raised a $500 million Series D round at a $5.5 billion valuation led by Alumni Ventures and PSP Ventures, bringing its total amount raised to $1.1 billion as of April 2025.
Compared to Writer AI, which is built to work closely with a company’s internal data and tools, Cohere focuses more on offering flexible ways to run its AI, like on different cloud platforms or private servers. Writer is designed for companies that want to connect AI directly to their data and build highly customized models. Cohere, on the other hand, provides ready-made tools for specific tasks like workplace productivity and search, with an emphasis on easy deployment and control over where the AI runs.
OpenAI: Founded in 2015, OpenAI is well-known for GPT-4, a leading-edge model recognized for its advanced reasoning and capacity to handle complex tasks. It offers a broad spectrum of applications, from text generation to code assistance, making it a strong contender in enterprise AI. GPT-4’s adaptability caters to various organizational needs, although much of OpenAI’s focus remains on the core model rather than full-stack workflow solutions.
In October 2024, OpenAI raised $4 billion in debt financing, and in March 2025, OpenAI raised $40 billion at a $300 billion post-money valuation, bringing its total funding to $61.9 billion as of April 2025. As of April 2025, OpenAI had more than 20 million paid subscribers and was used by more than 500 million people on a weekly basis. Like Writer and Anthropic, OpenAI appears to also be targeting enterprise customers, reporting one million paying business users across ChatGPT Enterprise, Team, and Edu.
Specialized AI Content Platforms
Jasper: Founded in 2015, Jasper specializes in generative AI for creative text and visuals, supporting tasks such as marketing content, social media posts, and more. Tools like Jasper Studio and a marketing toolkit enable quick content generation even for non-technical users, and RAG integrations extend their capabilities. Despite this breadth, Jasper typically concentrates on creative use cases rather than deep enterprise workflows and compliance. In October 2022, Jasper raised a $125 million Series A round led by Insight Partners, bringing its total funding to $131 million as of April 2025.
Typeface: Founded in 2022, Typeface provides AI-driven text-generation tools that streamline marketing and creative processes. The platform is designed primarily for content creators who need swift, high-quality outputs, making it a popular choice for marketing teams. Similar to Jasper, Typeface focuses on creativity and user-friendliness, with less emphasis on large-scale, compliance-driven enterprise needs. In June 2023, Typeface raised a $100 million Series B funding round led by Salesforce Ventures. It has raised $165 million in total funding and is valued at $1 billion as of February 2025.
Enterprise Search and Knowledge Platforms
Glean: Founded in 2019, Glean offers an AI-powered platform designed to unify data from various tools and databases, boosting productivity and knowledge management. It uses conversational AI and large language models to deliver personalized responses rooted in a company’s internal data. While Glean overlaps with Writer’s retrieval-based use cases, it centers largely on search rather than broader AI-driven workflow automation. In September 2024, Glean raised a $260 million Series E round led by Altimeter and DST Global. It had raised $600 million in total funding as of April 2025.
Hebbia: Founded in 2020, Hebbia delivers AI solutions to improve enterprise operations, deploying large language models across more than 1K production use cases. Its AI tools offer versatile business integrations, but similar to Glean, Hebbia’s core strengths lie in retrieval-based technologies. Although there is some overlap with Writer’s capabilities, Hebbia remains primarily focused on enhancing search and information retrieval rather than creating comprehensive enterprise AI workflows. In July 2024, Hebbia raised $130 million in Series B funding led by Andreessen Horowitz. It had raised $161.1 million in total funding as of April 2025.
Business Model
Writer operates on a subscription-based SaaS model, generating revenue through a combination of seat licenses and usage-based billing. This flexible structure supports a wide range of organization sizes and levels of AI adoption.
Prior to April 2025, Writer offered three main pricing tiers: a no-cost Developer Plan, a Team Plan, and a customizable Enterprise Plan. The Developer Plan served as an entry point for teams to explore Writer’s platform with no upfront investment. The Developer Plan provided free credits, low-code tooling, and access to Writer’s development framework, including AI app templates and a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) system for data connectivity.
The Team Plan, previously available at $18 per user/month (or $162 annually per user to save 25%), catered to growing teams. It supported up to five users and included access to 35+ prebuilt AI apps, productivity tools like Recaps and Ask Writer, style enforcement features, and browser and Word extensions for in-workflow AI assistance.
For large organizations, the Enterprise Plan offered a tailored solution with custom pricing. In addition to all Team Plan features, it allowed for the development of custom AI applications, deeper integration through the Knowledge Graph, and the ability to manage multiple teams with unique style guides and configurations. Enterprise users also benefited from advanced security, flexible deployment options, and dedicated onboarding and support.
In April 2025, Writer restructured its pricing model, consolidating the Developer and Team Plans into a single Starter Plan. Priced at $29 per user/month (billed annually) or $39 per user/month (billed monthly), the Starter Plan includes a 14-day free trial and supports up to 20 users. It provides access to 100+ prebuilt agents, full AI Studio capabilities to build up to five custom agents, one knowledge graph, and basic agent governance.
The Enterprise Plan remains custom-priced and includes everything in Starter, plus support for unlimited custom agents at scale, higher API limits, unlimited knowledge graphs, advanced security, reporting, governance, and dedicated implementation support.
This pricing shift likely coincided with the launch of AI HQ in April 2025, a major platform update that enables users to build custom agents and access a significantly expanded library of prebuilt agents. This move reflects both an industry-wide trend toward agent-based AI development and Writer’s strategic pivot to support that shift.
To drive adoption, Writer likely employs a land-and-expand strategy. The platform often enters organizations through a single department solving a targeted use case, then expands across other teams as the value becomes clear. Rather than offering just API access, Writer delivers a complete AI ecosystem—including knowledge graphs, compliance guardrails, and workflow tools—helping enterprises operationalize AI in secure, scalable, and practical ways. By solving the “last mile” of enterprise AI adoption, Writer justifies its premium pricing and supports sustained customer growth.
Traction
Writer was founded in 2020 and began generating early traction quickly. By 2022, the company had reached $2 million in ARR. That figure grew to $15.7 million in 2023 and then to $47 million by November 2024 — a 194% year-over-year increase. This rapid growth reflected strong enterprise demand for specialized AI solutions and Writer’s focus on building a vertically integrated platform tailored to business use cases.
In 2023, Writer launched its own family of large language models, Palmyra, purpose-built for enterprise applications. The company also introduced capabilities for connecting customer data sources to its models and enabled self-hosting — key differentiators for organizations with strict data security and compliance requirements. These product milestones positioned Writer as a full-stack provider rather than just an API or model vendor.
By mid-2024, Writer was serving 250 enterprise customers, including global brands such as Uber, Spotify, L’Oréal, and Accenture. This customer growth was supported by continued product innovation. In October 2024, Writer released Palmyra X 004, a new model trained primarily on synthetic data. The model cost only $700K to develop — far less than the estimated $4.6M it takes to train a comparably sized model from OpenAI.
In March 2025, Writer announced a major international expansion to support growing global demand. New hubs were opened in Singapore, Dublin, Chicago, and Austin, along with expanded offices in San Francisco, New York, and London. To deepen its presence in EMEA, Writer launched an advisory board led by former Salesforce President Gavin Patterson, and appointed regional leadership to support market entry and customer growth across Europe and Asia-Pacific Japan (APJ). This international footprint was expected to play a critical role in sustaining ARR growth and enabling localized support for large-scale enterprise deployments.
In April 2025, Writer launched AI HQ, a strategic move into agentic AI that built on its model foundation. AI HQ includes Agent Builder (a collaborative environment for teams to develop agents), Writer Home (a library of 100+ prebuilt agents for key workflows), and observability tools for governance and monitoring. While Writer Home is live, Agent Builder and observability features are in beta with general availability expected later in 2025.
The company’s land-and-expand motion continues to drive strong customer expansion, with a reported 160% net revenue retention rate. Many customers grow from initial contracts of $200K–$300K to more than $1 million annually. According to a Forrester TEI study, a composite enterprise using Writer saw a 333% ROI over three years and a six-month payback period.
Valuation
As of April 2025, Writer had raised a total of $326 million. The company reached a $1.9 billion valuation after closing its $200 million Series C round in November 2024. The round was led by ICONIQ Growth, PremjiInvest, and Radical Ventures, following a $100 million Series B led by ICONIQ Growth in September 2023 at a $500 million valuation. Much of Writer’s appeal lies in its specialized AI models, which can be adapted for verticals such as the healthcare and finance sectors with especially high compliance and security requirements.
Beyond prominent venture investors like Insight Partners and ICONIQ Growth, Writer has also attracted investments from the corporate venture arms of major enterprise clients, including Salesforce Ventures, Citi Ventures, and Workday Ventures. Their participation reflects the long-term partnership Writer has built with its customer base, as these organizations commit not only to using Writer’s platform but also to supporting its ongoing growth.
As of April 2025, Writer’s valuation was estimated at a 40x multiple of ARR, positioning it competitively within the broader AI landscape. By comparison, OpenAI traded at a 39.2x multiple on its $4 billion ARR (as of September 2024), while Anthropic’s $18.4 billion valuation and $800 million revenue translate to a 23x multiple. Jasper’s last private valuation of $1.5 billion represented a 20x multiple, whereas Hebbia’s $700 million valuation at $13 million ARR reached 54x. Writer’s 40x multiple positions it near the top end of industry comparables, indicating strong market confidence and willingness among investors to pay a premium for its specialized enterprise AI offerings.
Key Opportunities
Expansion Through Vertical-Specific LLMs
Writer already excels at delivering domain-tailored AI models, exemplified by its Palmyra Fin and Palmyra Med offerings for finance and healthcare. Both have demonstrated remarkable effectiveness. As of July 2024, Palmyra Fin was capable of passing the CFA Level III exam, while Palmyra Med outperformed competitive benchmarks in biomedical tasks. These specialized successes have fueled Writer’s revenue, helping the company scale to an ARR of $47 million and achieve a $1.9 billion valuation as of 2024. Looking ahead, Writer can leverage this expertise to create additional vertical-specific LLMs for highly regulated or knowledge-intensive sectors such as legal, insurance, and manufacturing. In these environments, stringent compliance requirements and a need for advanced domain knowledge create significant barriers to entry, positioning Writer’s specialized AI solutions as uniquely valuable.
Strategic Acquisitions To Strengthen Workflows
With the acquisition of Streamsync, a company building an open-source framework to build AI apps, in June 2024 for an undisclosed amount, Writer launched the Writer Framework as an open-source framework that allows developers to create feature-rich AI apps fully integrated with the Writer platform. As of February 2025, Writer’s platform also includes capabilities like a No-Code Tool and a graph-based Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) framework. These tools enable more complex, end-to-end automation of workflows, ranging from real-time data updates to compliance checks. With Palmyra X 004’s ability to call external tools and interact with enterprise systems, Writer is already facilitating tasks that go well beyond simple content creation. Notably, the adoption of these advanced features by clients such as Uber, Spotify, and L’Oreal underscores how integral the company’s solutions can become in broader enterprise ecosystems. As corporations seek to streamline operations further, Writer has an opportunity to position itself as the go-to AI platform for mission-critical workflow automation by strategically acquiring companies that focus on building AI frameworks.
For instance, the platform can integrate with internal ticketing systems to automatically categorize, triage, and respond to incoming support requests, reducing manual effort and response times. In finance, real-time analysis and reporting pipelines could be automated by connecting Writer to company data stores and enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, allowing for automated quarterly summaries, risk assessments, or compliance checks. In HR, Writer can streamline employee onboarding by generating policy documents tailored to specific roles, collecting e-signatures, and updating relevant databases without requiring human intervention. All these examples highlight how the platform’s core strength of combining retrieval-augmented generation with advanced tool-calling can automate entire processes and workflows, moving Writer’s role from a text generator to a pivotal orchestrator of mission-critical operations.
Deeper Integration and Upselling
Writer follows a “land-and-expand” strategy in which it is first deployed for specific departmental use cases and then rolled out organization-wide once the benefits become evident. This approach has proven successful, with Writer serving over 250 customers as of mid-2024, many of whom have invested in the company through their corporate venture arms—Salesforce Ventures, Citi Ventures, and Workday Ventures, among others. Such investments reflect a deep commitment to Writer’s long-term roadmap, signaling the potential for substantial upselling opportunities. By embedding Writer’s domain-specific LLMs, workflow automation tools, and compliance guardrails across multiple teams and departments, companies can realize more comprehensive value, in turn generating additional revenue for Writer and solidifying the platform’s role as a linchpin in their AI strategy.
One avenue is customized compliance modules, where organizations can purchase additional guardrails and policy-enforcement capabilities tailored to industry-specific regulations (e.g., HIPAA compliance for healthcare or FINRA for finance). Another offering could be advanced analytics dashboards that provide insights into how AI-driven workflows are performing across multiple teams—pinpointing bottlenecks, measuring content quality, or forecasting demand for human review. Writer could also roll out vertical-specific expansions of its Palmyra LLMs, bundling these model enhancements with consulting or training packages. Finally, enterprise license agreements that consolidate all of Writer’s offerings — including the Knowledge Graph, AI Studio, and any specialized domain models — would give large clients a single, unified toolkit for AI-driven transformation.
Key Risks
Intensifying Competition from Larger AI Players
Writer operates in an increasingly crowded space dominated by well-funded competitors such as OpenAI, Anthropic, Cohere, and even tech giants like Microsoft and Google. These players have broader ecosystems, extensive developer communities, numerous enterprise customers, and massive R&D budgets. While Writer differentiates itself through specialized models and end-to-end workflow tools, competitors may replicate these capabilities or undercut Writer on pricing. Maintaining a clear strategic focus, rapidly innovating, and demonstrating tangible ROI to enterprise clients will be critical for Writer to preserve its market position.
Evolving Regulatory and Compliance Landscape
With AI rapidly scaling into sensitive enterprise environments — finance, healthcare, and beyond — government regulations and data protection requirements are in flux. As policies shift (e.g., Trump’s recent deregulation, followed by potential new legislation in other jurisdictions), enterprises will demand transparent compliance frameworks. While Writer’s guardrails and secure data handling offer an advantage, any misstep in data governance, privacy, or compliance could erode trust. Additionally, maintaining compliance across multiple regions and verticals will require ongoing investment in legal and regulatory expertise.
Reliance on Large Enterprise Contracts for Growth
Writer’s success depends on landing and expanding within large enterprise accounts, a strategy that can accelerate growth and boost revenue multiples. However, such customers typically have lengthy procurement cycles and may reduce or stall AI investments if economic conditions change. Should a major client decide to cut back or switch to another provider, Writer could face significant revenue swings. Diversifying its customer base, both in terms of industry segments and deal sizes, will help mitigate the impact of potential churn or budget freezes among larger clients.
Summary
Writer is a specialized enterprise AI platform that delivers industry-specific language models, advanced workflow automation, custom AI agent development, and deep enterprise integrations through a tiered SaaS pricing model. Its product suite includes domain-focused models like Palmyra Fin and Palmyra Med, along with a comprehensive development framework for building custom AI applications and agents. As of April 2025, Writer serves 250 enterprise customers, including Uber, Spotify, L’Oréal, and Accenture.
The company’s growth opportunities lie in expanding its vertical-specific models into new industries, automating a wider range of enterprise workflows beyond content generation, and upselling premium features such as compliance tooling and data integration capabilities. However, it faces risks from increasing competition with larger AI players, emerging regulatory pressures such as the EU AI Act, and a reliance on large enterprise contracts that may be sensitive to macroeconomic fluctuations.






