Thesis
In 2021, over half of technical leaders in one survey said their natural language processing (NLP) spending grew by 10% or more from 2020, and about a third of them said their NLP spending grew by at least 30%. This has only accelerated: in a December 2022 survey, 77% of businesses with active NLP projects said they planned to increase spending over the next 12-18 month period, with 38% of these businesses planning to increase spend by 11% or more. This growth accelerated after the release of OpenAI's product ChatGPT in late 2022, which served as an inflection point for the market.
However, companies still face formidable barriers to NLP adoption. Large language models used in NLP can cost well over $10 million to train and even more to actually use. Not only can NLP models themselves be expensive, but hiring the expertise to manage them can be difficult. A 2021 survey found AI talent acquisition to be a “significant” challenge for 19% of business leaders. As of 2022, 65% of companies surveyed found it either somewhat or extremely difficult to hire software engineers for AI-related roles, and 83% reported that it was either more difficult or equally difficult to hire for such roles looking back over the past three years.
Cohere provides NLP models for businesses. It allows companies to infuse NLP into applications without having to develop their own models in-house, which can be costly, time-consuming, and expensive. Cohere builds general-purpose language models and provides access to them via an API. Companies can use the models out of the box or fine-tune them to their particular use cases. As AI continues to see accelerated progress, the opportunity to access the latest models and components is likely to be of increasing importance.
Founding Story
Aidan Gomez (CEO), Nick Frosst, and Ivan Zhang founded Cohere in 2019. All three attended the University of Toronto as undergraduates. Gomez went on to complete a PhD in Computer Science at the University of Oxford. Gomez and Frosst later became AI researchers at Google Brain in Toronto. While working there, Gomez’s friend Zhang would regularly visit the office to study deep learning with Gomez. In June 2017, Gomez co-authored a paper called Attention Is All You Need which pioneered the transformer model, a neural network architecture that revolutionized NLP tasks.
Transformers use self-attention to weight the importance of different parts of the input. Compared to previous language models like recurrent neural networks, they were more parallelizable, enabling them to be trained on larger data sets. They underly top-performing language models, including Cohere's model and OpenAI models like GPT-4 (GPT stands for"generative pre-trained transformer"). In an August 2023 interview on Contrary Research Radio, Gomez described the company's origin as follows:
"Starting Cohere, Nick, Ivan, and I... the whole objective was to bring this tech, large language models [LLMS] to industry; bring it to the world, and facilitate adoption. Nobody really knew what large language models were, it was a research project, interesting tech, but no real commercial application. But I think we had conviction on the trajectory and the pace of progress and that computers would get increasingly good at manipulating language and we would quite soon arrive at a place where computers could speak our language... and that that would be increasingly valuable for the world."
Initially, the team did not have much clarity about what exact product they wanted to build for a commercial use case. However, not long after the company launched, OpenAI released GPT-3 which represented an inflection point for LLMs. As Gomez told Contrary Research:
"When we started up, initially we didn't really have an idea of what product we wanted to build... we just focused on building the infrastructure to train large language models on supercomputers using whatever compute we could get our hands on. Shortly after we started Cohere, GPT-3 came out, and that was a huge breakthrough moment that was very validating and gave us [an indication] that we were heading [down] the right path.”
The team was joined by Martin Kon (President and COO), previously CFO at YouTube, in early 2023.
Product
Cohere trains large language models (LLMs) for a variety of reading and writing tasks, such as summarization, content creation, and sentiment analysis. Its language models are optimized for three primary use cases: retrieving text, generating text, and classifying text.
Cohere provides API endpoints for enterprises to leverage its LLMs and a number of deployment options that allow companies to securely store their data with cloud partners like AWS or with Cohere’s managed cloud. To help make its LLMs more effective for customers, Cohere also offers custom model training services.
Cohere CEO Aidan Gomez described the product as follows in an August 2023 podcast episode with Contrary Research:
"We've tried building purpose-specific solutions. We have our summarize endpoint, we have classify. What we've found is that's more of a mature market product. For this technology, what people are most excited about is how general it is. Instead of us coming to them with a solution to their problem, we provide them with a general platform [Cohere's models]. It's like this generalist software that can just solve, within reason, any problem you're coming to it with.”
Retrieving Text
Three primary API endpoints focused on retrieving text for search, clustering, and recommendations are available as part of Cohere’s offerings.
Embed: This endpoint offers accurate embeddings in English and 100+ languages, enabling users to uncover trends, compare languages, and build their own text analysis applications from their data.
Semantic Search: Provides users with semantic search capabilities that find text, documents, and articles based on meaning, not just keywords. It allows developers to build better search systems for any language.
Rerank: Rerank improves the search quality of keyword or vector search systems. It helps systems better understand context and the meaning of questions and queries while promising minimal overhaul of existing systems.
Source: Cohere
Generating Text
Cohere provides three API endpoints focused on text generation. Designed to generate contextually relevant and human-like text, this product offering consists of:
Summarize: Summarize provides text summarization capabilities at scale, enabling users to build applications that extract and summarize insights from long articles or documents.
Generate: This API endpoint produces unique content for various contexts, with examples including emails, landing pages, and product descriptions. By providing a topic and prompt, the Generate API endpoint can create relevant text content for users.
Command Model: As Cohere’s flagship text generation model, the Command Model is built to follow user commands for business applications. It can perform tasks like writing emails or answering questions about a document. Cohere allows the Command Model to be trained on customer data and language, providing a custom solution for unique business needs.
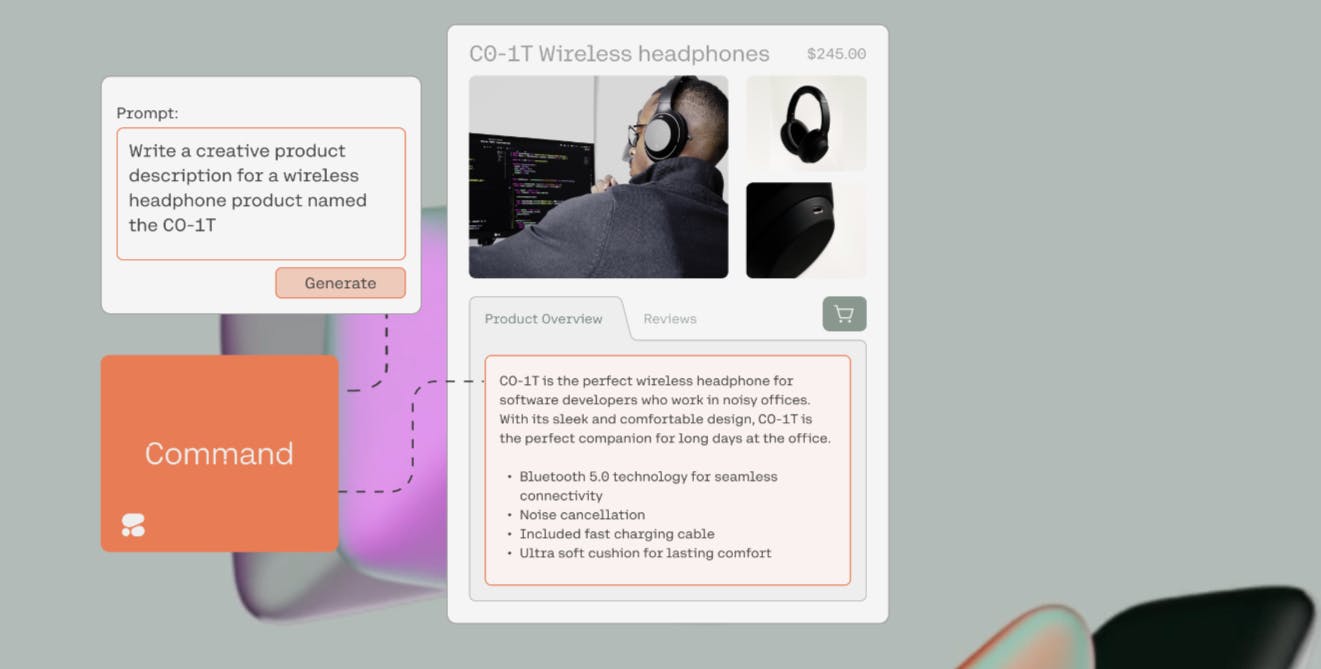
Source: Cohere
Classifying Text
Cohere's text classification endpoint is an API to Cohere’s LLMs focused on identifying meaning and insights from provided text. Example use cases of the Classify endpoint include content moderation and sentiment analysis for product reviews. Other potential applications of the Classify endpoint include chatbot experiences and customer support. Like Cohere’s other API endpoints and LLM offerings, customers can provide their data to Cohere to receive a customized model fine-tuned on their data.
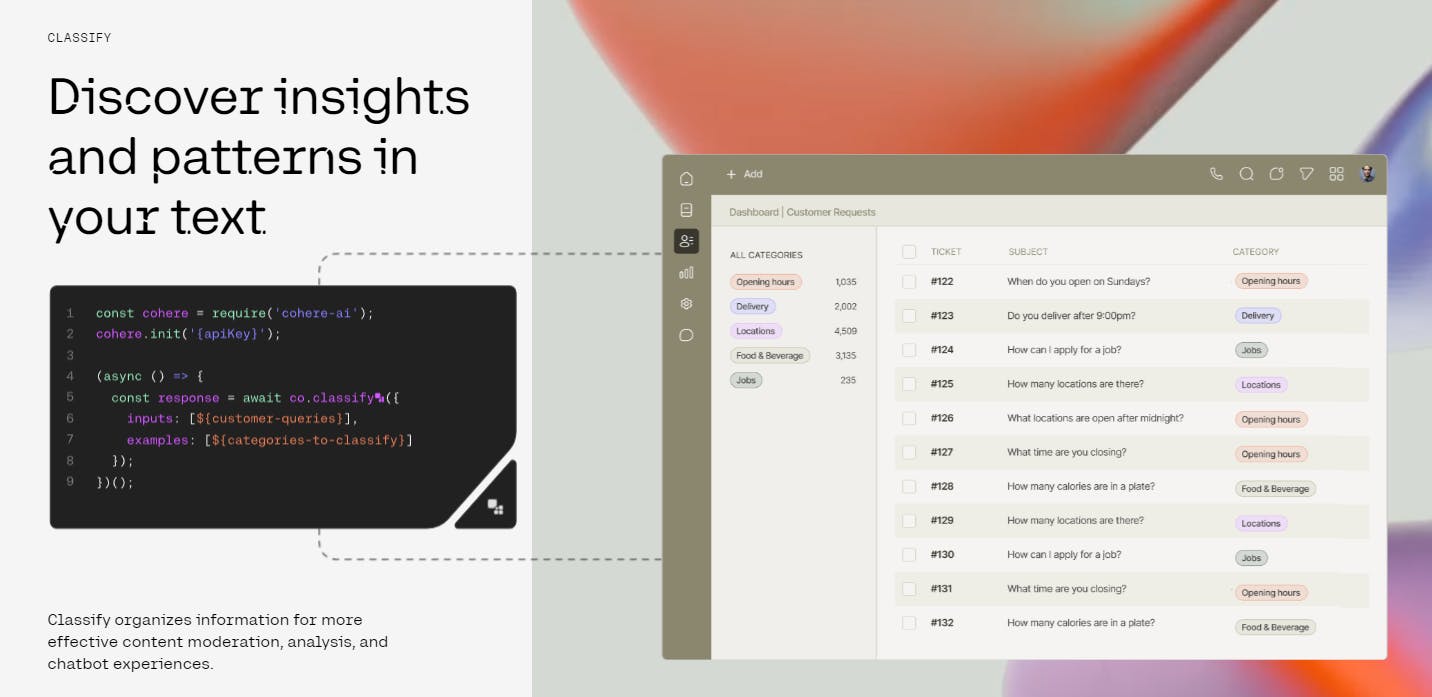
Source: Cohere
Market
Customer
As Cohere CEO Aidan Gomez described in an interview with Contrary Research, Cohere targets companies looking for an independent AI platform.
"We know the market will need an independent platform, not tied to any of the hyperscalers, to enable enterprises to adopt this technology in a way that is extremely data-private and secure."
Most businesses, aside from FAANG companies and competitors such as OpenAI with significant resources, lack the finances or engineering talent to train their own complex language models. The first hurdle for most potential customers of Cohere is the cost of running these models internally. For example, it was estimated that one training run of Google's PaLM model, released in 2022, on AWS would cost $25 million.
The second hurdle for companies that might otherwise look to build these models in-house is the lack of access to high-quality talent. Acquiring AI talent is a major challenge for companies in all stages of AI adoption. Even among more seasoned companies with relative sophistication in their AI deployments, almost 48% of them faced moderate, major, or extreme AI skills gaps as of 2020. As of 2022, 65% of companies in a McKinsey survey of 1.5K companies found it either somewhat or extremely difficult to hire software engineers for AI-related roles, and 83% reported that it was either more difficult or equally difficult to hire for such roles looking back over the past three years.
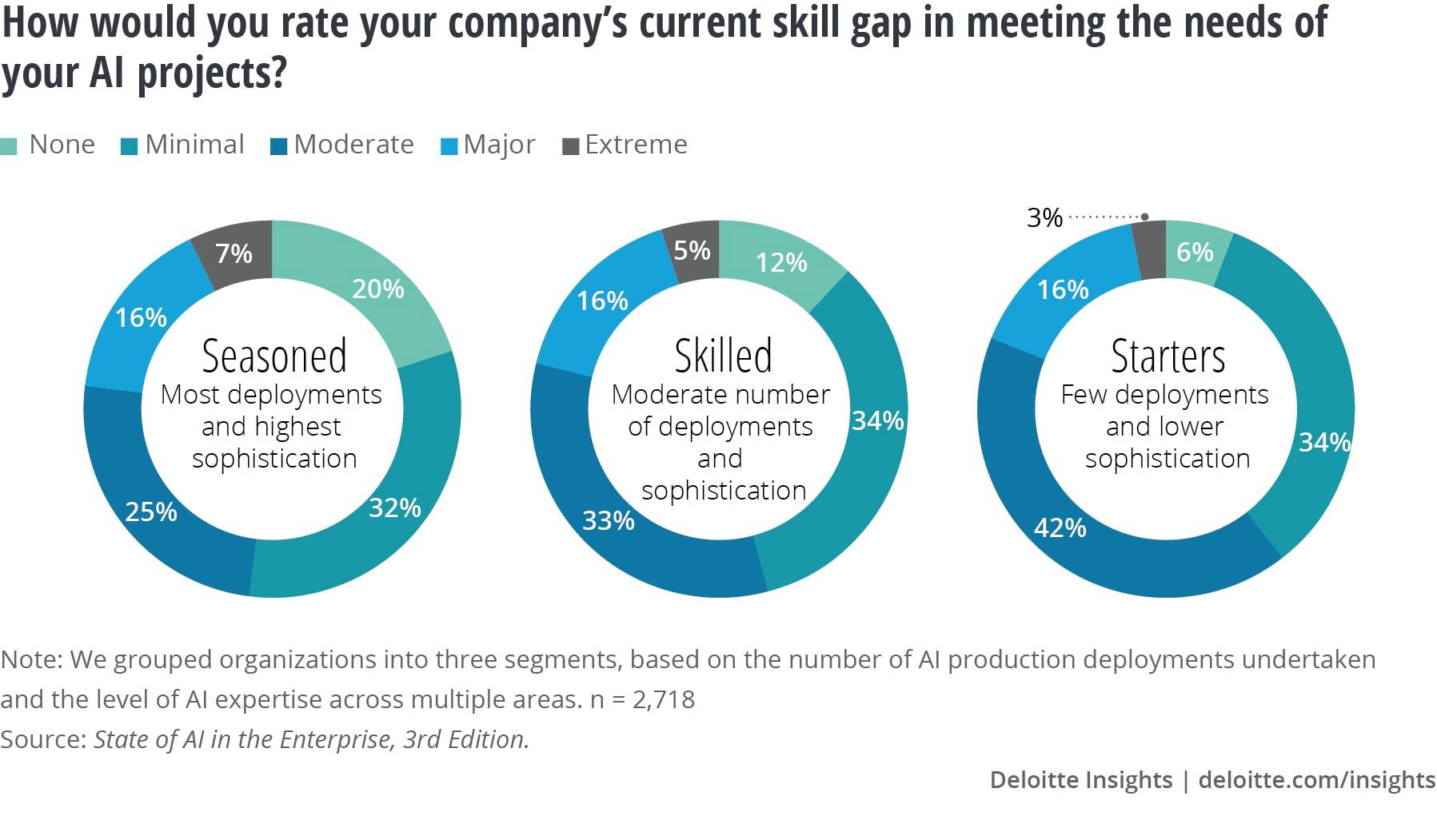
Source: Deloitte
Cohere's customers as of September 2023 include Oracle, Notion, Jasper, Spotify, HyperWrite, and Glean.
Market Size
The NLP market was valued at $27.8 billion in 2022, with an estimated market size of $41 billion in 2023. The market is projected to reach $440 billion by 2030, growing at an estimated CAGR of 40.4% from 2023 to 2030. Another report from June 2023 predicted that generative AI could reach a size as large as $1.3 trillion by 2032 with an up to 42% CAGR, with its growth being driven by use cases such as AI copilots to increase the speed of coding, specialized AI assistants, and new infrastructure products.
The rapid growth of the generative AI market was fueled by the release of OpenAI's product ChatGPT. After its release in late 2022, ChatGPT acquired 100 million active users within two months, which made it the fastest-growing consumer app in history and served as an inflection point for the generative AI market. One survey in late 2022 found that 77% of companies using NLP solutions were planning to increase investment going forward.
Competition
OpenAI: Founded in 2015, OpenAI is a leading AI research lab that has developed several iterations of the GPT model, an LLM similar to Cohere's offerings. OpenAI's GPT-3, released in June 2020, has been widely adopted for various applications, from content generation to customer service automation. But OpenAI’s watershed moment that has ushered in an “AI boom” was the release of ChatGPT, a conversation-optimized LLM in November 2022. As of February 2023, ChatGPT reached 100 million MAUs just two months after launch, making it one of the fastest-growing consumer apps in history. OpenAI's reputation, extensive research capabilities, and the widespread adoption of its models pose a significant competitive threat to Cohere. OpenAI raised $300 million in April 2023 in a venture round that valued the company between $27-29 billion.
Meta: Meta, formerly known as Facebook, is a tech conglomerate with significant investments in AI research and development. Its AI research division, FAIR (Fundamental AI Research), has developed various AI models and tools, some of which compete directly with Cohere's offerings. In July 2023, Meta released Llama 2, an LLM free for research and commercial use pretrained on 2 trillion tokens. Shown to be comparable to OpenAI’s GPT-3.5 (similar to ChatGPT) in reasoning tasks, the release of Llama 2 as a publicly available LLM represents a significant threat to Cohere.
Google: In April 2023, Google merged DeepMind, a world-leading AI research lab known for its work in reinforcement learning and neural networks, with its existing Google Brain team. Since the rapid adoption of ChatGPT, Google has made significant strides in integrating LLM capabilities into its existing products. In March 2023, Google released Bard, an AI chatbot directly competing with conversational AI offerings like Cohere’s Command Model. Google’s position as a leading AI research company as well as its vast resources and distribution make it a significant competitor to Cohere, with Google continually growing the use of LLMs in offerings like its Workspace products.
Anthropic: Anthropic is an AI research company focused on building reliable, interpretable, and steerable AI models. Founded in 2021, Anthropic aims to make large language models more understandable and controllable. Anthropic's focus on interpretability and safety could appeal to customers seeking transparency and customization in their AI models, posing a competitive threat to Cohere. In May 2023, Anthropic raised a $450 million Series C, with a leaked pitch deck targeting a $4.1 billion valuation.
Stability AI: Stability AI is an AI company that develops open-source models. Its Stable Diffusion text-to-image model, released in August 2022, was a runaway success, gathering over 27K stars on Github and inspiring over 3.5K forks as of July 2023. While not reaching Stable Diffusion’s level of success, the company released Stable LM, an open-source LLM in April 2023. As an LLM, Stable LM directly competes with Cohere’s product offerings and its position as an open-source model puts pressure on Cohere’s offerings to differentiate themselves. Stability AI raised up to $25 million as a convertible note and was previously valued at $1 billion after its October 2022 seed round.
Business Model
Cohere bears large upfront costs to build each model and ongoing costs for inference. It recoups costs with usage-based pricing and offers three different pricing tiers:
Free: Access to all Cohere API endpoints with rate-limited usage intended for learning and prototyping.
Production: Increased rate-limit access to all of Coheres API endpoints, elevated customer support, and the ability to train custom models on provided data. Cohere charges based on number of tokens (a token is basically a number, letter, or symbol) for all its API endpoints, with varying prices for endpoints ranging from $0.0000004 (Embed) to $0.001 (Rerank) per token.
Enterprise: Dedicated model instances, highest levels of support, and custom deployment options. Pricing for the Enterprise tier is not publicly available.
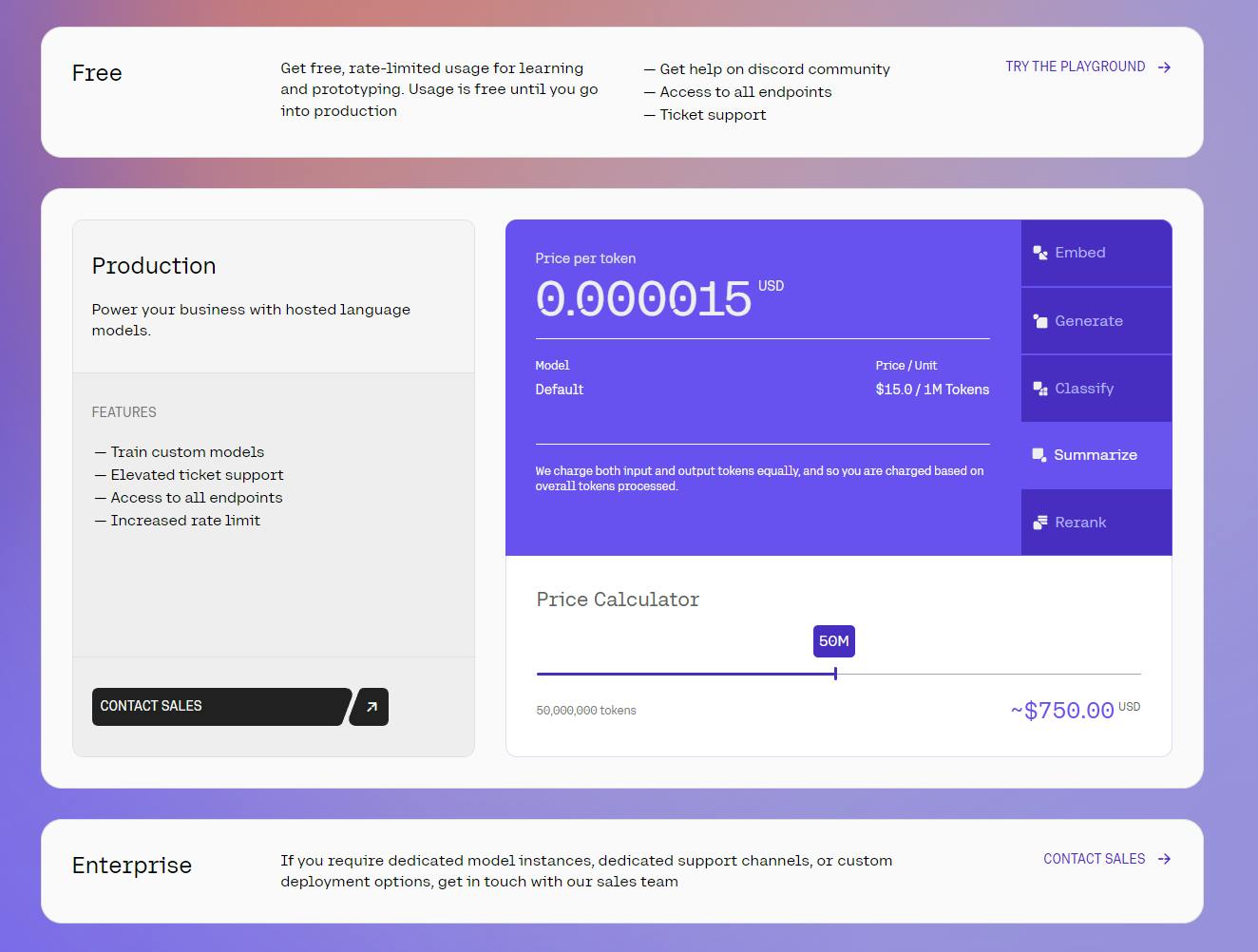
Source: Cohere
Traction
Cohere launched its API in November 2021 and saw an 800% increase in usage between its Series A round announced in September 2021 and its Series B round announced in February 2022. In November 2021, the company announced a partnership with Google Cloud for access to the cloud computing infrastructure needed to build and deploy its products. That partnership includes Google’s Cloud Tensor Processing Units (TPUs), which are "supercomputers that are optimized for large-scale ML". The following year, Cohere announced a partnership in June 2023 with Oracle to leverage Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) to train, build, and deploy its LLMs. Cohere’s biggest strides have come in the enterprise market, with Cohere and McKinsey announcing a strategic collaboration in July 2023 for McKinsey to offer Cohere’s generative AI services to its clients.
Valuation
In May 2023, Cohere announced a $270 million Series C led by Inovia Capital which valued the company at over $2.1 billion. Two months later, consulting company SAP invested an undisclosed amount in Cohere in July 2023 as part of a broader investment in generative AI startups that also saw it investing in Anthropic and Aleph Alpha. In August 2023, Tiger Global sold a 2.1% stake it had in Cohere for $63 million, implying that Cohere’s valuation had grown to $3 billion. Tiger Global retained a 5% stake in the company even after the sale.
As of July 2023, Cohere has raised over $445 million from investors including Tiger, Index Ventures, Radical Ventures, and Section 32. Notable people in the AI world such as Geoffrey Hinton (known as the "Godfather of AI", Stanford computer scientist Fei-Fei Li, Berkeley's Pieter Abbeel, and University of Toronto's Raquel Urtasun have also invested in Cohere.
Key Opportunities
Growing Use Cases For LLMs
Although AI has seen rapid consumer adoption in 2023, there is still considerable room for growth in the business adoption of LLMs. In an interview with Contrary Research, Cohere CEO Aidan Gomez stated that:
"We're still early... the world looks very different two years from now and this technology is a feature of every single product that we interact with. It just becomes day-to-day, it just becomes an expectation. You expect to talk to an agent that is automated and as smart as a human."
If such a world materializes, demand for Cohere's product will be extremely high. Cohere is well positioned to capitalize on that growing demand.
Human-Agent Interaction
Cohere’s optimal scenario is one where its language models advance far enough that human-computer interaction becomes seamless. Google Cloud CEO, Thomas Kurian, put it like this: "language is the next big phase of evolution of the way that people interact with systems.” If AI agents using generative AI for either specific or general use cases become indistinguishably intelligent from a human, it would continue to fuel the adoption of LLMs.
Understanding Unstructured Data
Analyst estimates suggest that 80-90% of data is unstructured. However, unstructured data (e.g. text, images, audio files, etc.) lacks a consistent data model, making it difficult to analyze. Structured data, often stored in an easy-to-process table format, is relatively easy for companies to analyze and search. Only 18% of organizations have capitalized on unstructured data, 3x less than the number of organizations that have taken advantage of structured data.
Unstructured data will only become more prevalent with an annual growth rate of around 60% compared to 12% for structured data. NLP is necessary to unlock the insights of the enormous volume of unstructured data. Industries including finance, shipping, legal, and healthcare already employ NLP to extract structure from text. NLP can also enable improved searchability, including semantic search (search by meaning).
Computer Vision
Aidan Gomez, the founder and CEO of Cohere, describes multimodal language models incorporating a “visual grounding system for language” as “really promising.” Not only could computer vision improve Cohere’s language models, but it could also provide additional standalone products for Cohere. Expanding into computer vision from NLP would double Cohere’s addressable market size, as estimates indicate the computer vision market is expected to grow from $9.5 billion in 2020 to $41 billion in 2030.
Key Risks
LLM Commoditization
The release of open-source large language models like Stable LM and Llama 2 poses a significant risk to Cohere's business model. These open-source models democratize access to advanced language processing capabilities, potentially eroding Cohere's competitive advantage. If more developers and organizations adopt these free alternatives, Cohere could face challenges in attracting and retaining customers who might opt for these cost-effective solutions.
While Cohere's models could offer unique features and capabilities, the value proposition might not be compelling enough for some customers given the availability of free, high-quality alternatives. Increased adoption of open-source LLMs could commoditize commercial LLMs, impacting their profitability and sustainability. In the face of these challenges, Cohere will need to continually innovate and differentiate its offerings to maintain its market position.
Potential Biases
Language models sometimes exhibit bias and produce inappropriate language, raising ethical and legal concerns. In 2021, the Federal Trade Commission banned companies from using biased algorithms to make decisions impacting consumers. Biases arise because language models reflect the characteristics of their training data. Large language models like Cohere’s are generally trained on large volumes of Internet data that contain biased language. Although Cohere invests in addressing its models’ safety concerns, Gomez believes the company will never fully solve them.
Summary
Through its API, Cohere provides its customers with access to language models for generating text, classifying text, or producing text. The speed of progress in NLP continues to accelerate, and companies like Cohere will have to stay at the cutting edge in terms of the models they’re providing to their customers. Obstacles include product differentiation among their competitors and dealing with the continued biases and weakness within existing language models. Cohere has the ability to help customers overcome the obstacles of high cost in running these models, and talent shortages to effectively manage them. That ability creates an opportunity to satisfy the growing demand for access to these types of models.