Thesis
The global supply chain has demonstrated a number of issues since the COVID-19 pandemic exposed how brittle global supply chain operations were, with 47% of companies having reported disruptions as of 2022. Post-COVID geopolitical tensions, like Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, indicate continued friction, such as global wheat prices, one of Ukraine’s primary exports, rising by 28%. These disruptions are no longer outliers; they’re the new baseline. Reshoring can de-risk geopolitical turmoil and shipping-related challenges in some cases. However, many critical manufacturing resources only exist in distant parts of the world, something reshoring cannot account for. As a result, 97% of enterprises reported plans in 2023 to “reconfigure their supply chains in some way”, signaling a significant shift in how businesses think about enterprise resource planning.
This shift is forcing companies to rethink their underlying systems. Despite global trade and manufacturing being valued at $33 trillion, over ~66% of firms still rely on Excel for enterprise resource planning as of 2025. SAP’s Advanced Planner and Optimizer (APO) product is one of the more dominant supply chain planning systems in the market, helping SAP support over $40 trillion of cash flows across its product lines, serving 99 of the world’s 100 largest companies. Despite SAP’s install base of APO, the company has been trying to sunset the product since 2017; currently expecting to do so in 2027. Some explanations have been that APO is built on legacy architecture and “designed for transactional consistency and not the kind of agile, scenario-based decision-making that gives modern planners the ability to navigate around the new volatilities of today’s supply chain.” Instead, SAP is pushing users towards its broader Integrated Business Planning (IBP) and S/4HANA platforms, though they’re much more expensive and complex.
o9 Solutions is positioning itself to take advantage of the industry’s forced shift away from legacy solutions by providing its own “Digital Brain” platform. The product offers a modular, AI-powered ERP platform built from the ground up for end-to-end planning. By emphasizing the ability to model “what-if?” scenarios, o9 enables clients to anticipate disruptions before they happen, rather than after the fact. The company emphasizes its offerings both as broad (across industries like consumer goods, manufacturing, retail) and deep (offering use case specific industry models).
Founding Story

Source: o9 Solutions
o9 Solutions was co-founded in 2009 by Sanjiv Sidhu (Chairman) and Chakri Gottemukkala (CEO) in Dallas, Texas.
Sidhu and Gottemukkala previously worked together at i2 Technologies, also a supply chain optimization company. Sidhu was the founder, chairman, and CEO of i2, while Gottemukkala served as a Director. Under Sidhu’s leadership, i2 became a notable player in enterprise planning software before being acquired by JDA Software for $604 million in 2010. This experience gave both founders a unique vantage point into the limitations of legacy ERP systems and the emerging need for intelligent, integrated platforms.
After the acquisition, Sidhu and Gottemukkala identified three major issues plaguing enterprise planning: disconnected decision-making across departments, reliance on fragmented systems that forced users back into spreadsheets, and slow, unscalable legacy software. To solve these, the pair spent five years quietly building a new kind of enterprise system from scratch. The result was the o9 “Digital Brain”, a real-time, AI-powered planning platform that launched initially in US markets and gradually expanded globally.
Product
The o9 Digital Brain Platform
Source: o9 Solutions
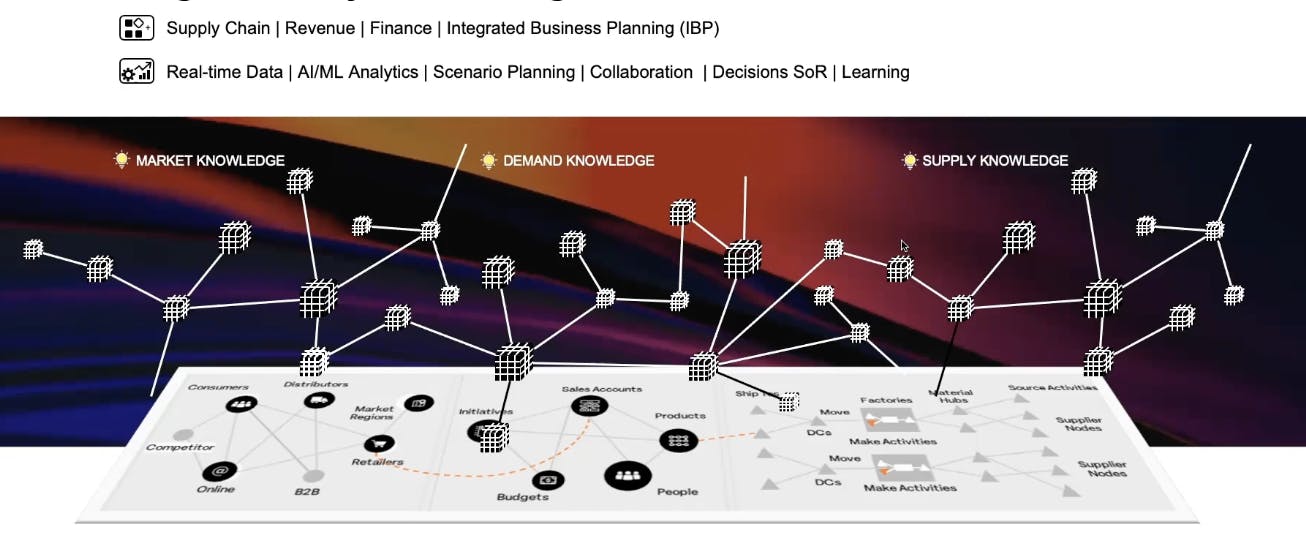
The o9 Digital Brain is the company’s primary product; a cloud-native platform for integrated planning and decision-making across an enterprise. It serves as a “digital brain” by connecting data from previously siloed functions within an organization (supply chain, demand, finance, etc.) into one knowledge graph, enabling better cross-functional insights. At its core is o9’s Enterprise Knowledge Graph (EKG), a graph-based model of the business that continually fuses internal and external data (e.g. ERP data, market signals) to create a real-time digital twin of the value chain. While the product is not verticalized, customers can choose to integrate industry-specific modifications, enabling the end product to serve niche requirements.
Through the platform, organizations can run real-time “what-if” scenario simulations to evaluate alternatives and see financial or operational impacts instantly. The platform’s integration capabilities allow it to ingest live data from multiple sources (internal systems, IoT feeds, external market data) and update plans dynamically, which enhances visibility and responsiveness.
This foundation allows the Digital Brain to provide a single source of truth and support advanced analytics, scenario planning, and collaboration. As Dr. Athina Kanioura, Chief Strategy and Transformation Officer at PepsiCo, explained:
“So with [o9], what we are achieving now is one single source of truth. Everyone aligns behind one number, with the ultimate accountability… being the general manager. So you take the power out of the functions and give it to the general manager to run the business as they see fit, which is unbelievable.”
In 2024, o9 began augmenting the Digital Brain platform with generative AI capabilities, introducing “composite agents” that can handle complex cross-functional queries and tasks by orchestrating the knowledge graph. These AI agents can, for example, automatically gather and analyze data across sales, supply chain, and finance to answer a question or perform a root-cause analysis, further speeding up decision-making.
As of August 2025, o9 reported that over 30 industry verticals (from consumer goods and retail to automotive, tech, telecom, and industrial manufacturing) rely on the Digital Brain as a mission-critical planning solution. Function-specific “Modules” can be purchased as add-ons to enhance the functionality of the Digital Brain platform.
Demand Planning
Source: o9 Solutions
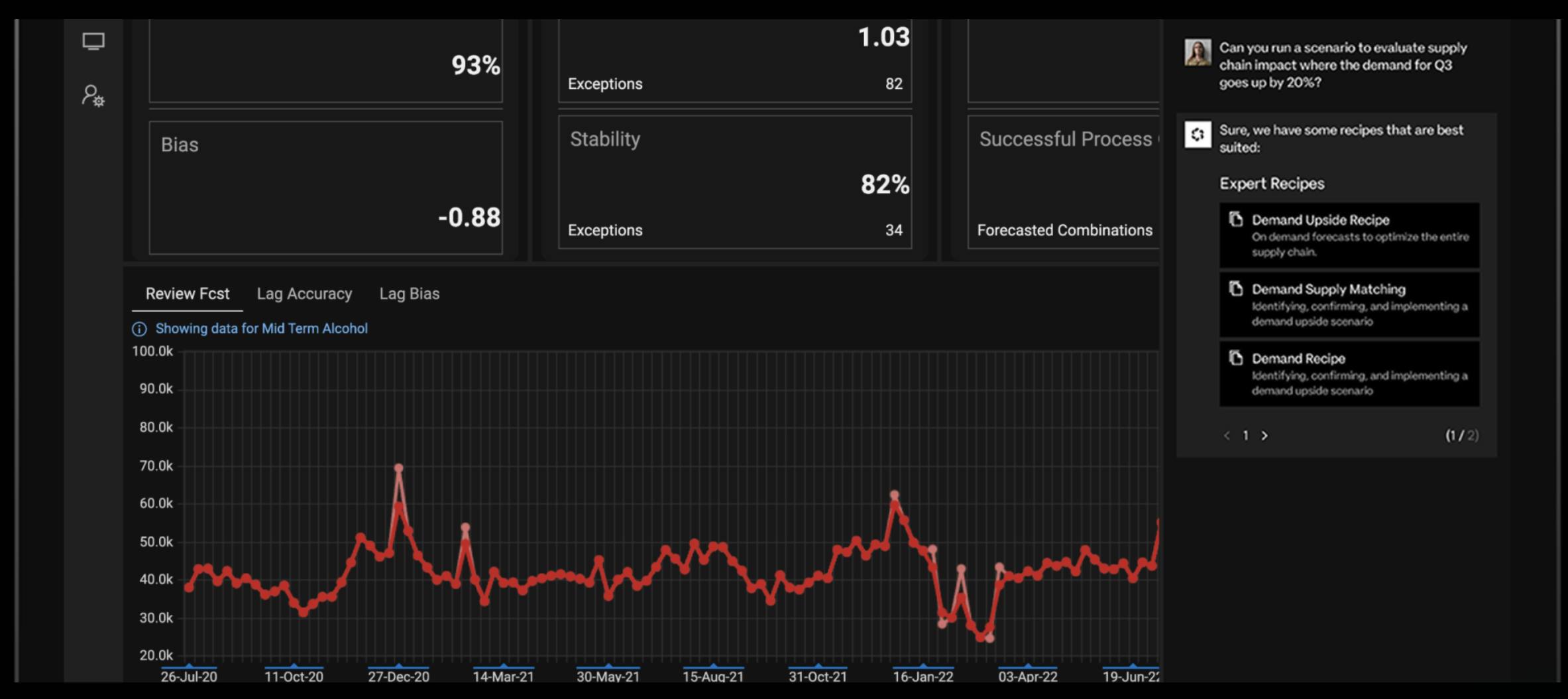
o9’s Demand Planning module is a forecasting solution focused on predicting consumer or enterprise demand using machine learning algorithms that learn from historical sales, seasonality, promotions, and other drivers. Planners can then enrich this forecast with market intelligence from integrations into external signals like macroeconomic indicators or even event data through partners like PredictHQ to sense demand shifts in real time. Users can input adjustments, add commentary, and reconcile a consensus plan, eliminating the need for disconnected spreadsheets. The module supports granular forecasting across customer segments and regions. As a result, planners can drill down to SKU-level or aggregate up to product family or brand level, with changes propagating through the hierarchy intelligently.
Supply Chain Planning & Analytics
Source: o9 Solutions
The Supply Chain Planning & Analytics module covers the process of balancing demand and supply through constraint-aware supply plans, inventory optimization, and detailed production scheduling. Unlike Demand Planning where users produce potential demand outcomes, the Supply Chain Planning module enables users to act on those insights and plan accordingly. Planners can conduct multilevel materials and distribution planning to ensure the right raw materials and finished goods are available where and when needed to meet demand. The platform takes into account production capacities, supplier lead times, inventory policies, and other constraints to generate feasible, optimized plans.
Supplier Relationship Management
Source: o9 Solutions
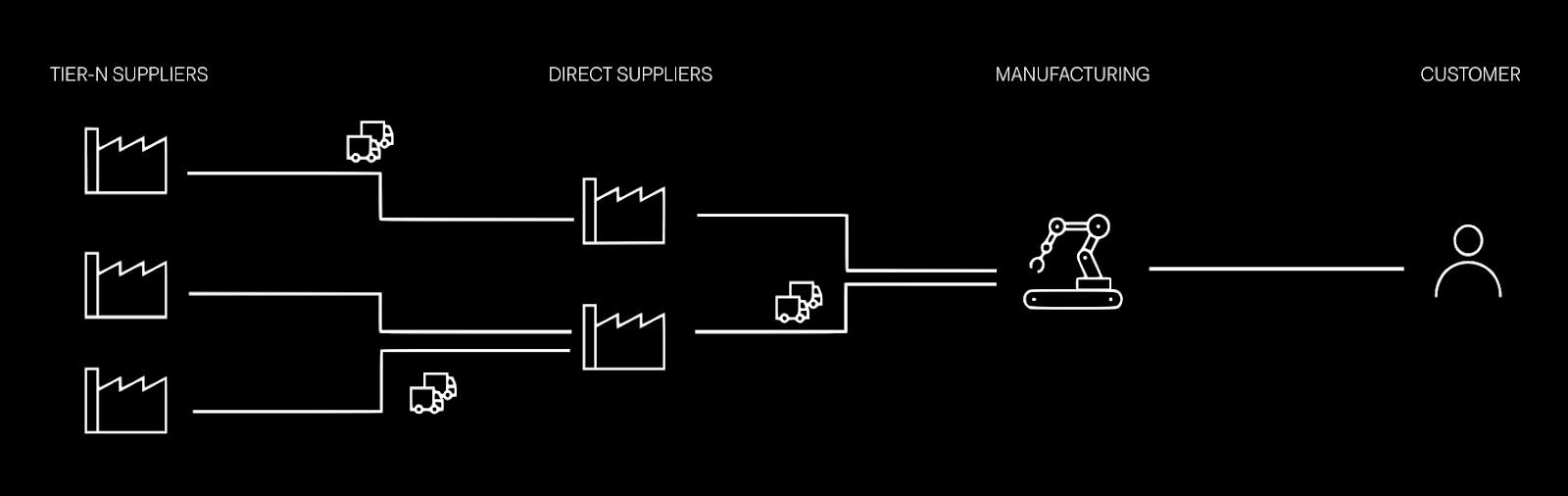
o9’s Supplier Relationship Management (SRM) enables real-time, multi-tier collaboration across suppliers in the supply chain.
Multi-tier collaboration enables organizations to share forecasts and production schedules across their supply chain, as opposed to vendor-by-vendor analysis. Through o9’s supplier portal, suppliers can confirm order commitments, flag constraints, or negotiate changes in real time. This advanced visibility into upstream supply tiers helps planners respond to disruptions before they impact operations.
Integrated Procurement Planning lets purchase orders from the supply plan flow directly into SRM, creating a seamless feedback loop where suppliers can provide constraint data or changes, making the overall plan more realistic, creating a workflow that replaces error-prone email and spreadsheet-based communication. Additionally, SRM acts as a launchpad for ESG and Cost Management, tracking supplier sustainability certifications and feeding cost data into o9’s analytics engine to support responsible sourcing and cost optimization.
Revenue Growth Management
o9’s Revenue Growth Management (RGM) suite helps businesses drive profitable top-line growth through smarter pricing, promotions, and product mix strategies. Introduced in 2024 and tailored for CPG and retail verticals, RGM connects with demand and supply planning, aligning commercial and operational plans on one platform.
With the RGM module, planners can see how competitor actions or promotions influence demand in real time and adjust strategies accordingly. It also helps align bottom-up product / channel / customer revenue plans with top-down financial targets, recommending promotional or pricing adjustments to close performance gaps. The module forecasts new product sales based on early data, helps set launch targets, and advises on marketing and inventory allocation.
Post-execution, commercial analytics dashboards evaluate what worked and why. The system quantifies underperformance (e.g., low promotion lift or supply shortfalls), recommends changes, and highlights untapped opportunities, like unmet demand in specific regions.
ESG & Sustainability Solutions
o9 launched its ESG & Sustainability suite in 2022. Rather than offering it as a separate module, o9 integrated sustainability directly into the Digital Brain Platform, enabling organizations to prioritize ESG without having to purchase a separate module. This launch came as companies faced growing pressure to address carbon emissions and supplier-level ESG risks outside their direct control. o9’s ESG suite helps customers predict emerging environmental and social risks before they escalate, ranging from extreme weather patterns to geopolitical events that may influence tariffs. These predictive capabilities empower planners to respond proactively to changing risk levels and maintain business continuity. According to Chris Fink, Global Supply Chain Manager at Caterpillar:
"We are seeing about a 50% scrap reduction. And that is driven by the fact that we have a line of sight now to our customer forecasts, and we’re making decisions to avoid bringing in excess inventory or inventory we don’t need.”
Traditional disruption management focuses heavily on short-term cost mitigation which can be ineffective in the long-term. o9 enhances disruption management by factoring in both ESG risks and sustainability goals, helping supply chain professionals make more balanced, sustainability-aware decisions. This dual focus enables businesses to respond to disruptions with a long-term, responsible perspective, rather than reflexively cost-cutting. o9 also enables customers to make more aware assessments of supplier sustainability ratings. Unlike traditional methods that are based on financial data and supplier assessments, which are often outdated and inaccurate, o9 provides a composite ESG risk score on suppliers, based on “strikes, imposed sanctions, human rights violations, or fires, etc” associated with the supplier.
Partner Program & Ecosystem

Source: o9 Solutions
o9’s Partner Program is targeted at improving the onboarding process of its Digital Brain platform for customers. It consists of two main arms: consulting partners and technology partners. Partners include consulting firms Deloitte, KPMG, PwC, and Accenture that co-deliver implementations and configure o9 modules for industry-specific needs. This partnership network had expanded rapidly since 2020, with over 1K consultants certified as “o9 implementers”.
On the technology side, o9 collaborates with Microsoft Azure, its primary cloud partner, as well as Google Cloud, AWS, and data providers like PredictHQ. These partnerships enhance o9’s capabilities in areas like event-based demand sensing, external data ingestion, and cloud-native scalability.
As a result of the Partner Program, o9 is trying to ensure that clients experience a much smoother onboarding process, circumventing the initial challenges of integrating an entirely new resource planning software.
Market
Customer
o9 Solutions primarily targets large global enterprises that operate complex supply chains. Its ideal customer profile includes Fortune 500–scale companies, typically with greater than 10K employees and upwards of $1 billion in annual revenue. These companies span a range of industries, including automotive, CPGs, manufacturing, industrials, energy, and retail. Each customer typically has at least one unifying trait: they manage substantial physical operations and require tightly coordinated planning across demand, supply, production, and finance.
o9’s product is often seen as a replacement or augmentation of legacy systems, like SAP APO or Excel-based planning workflows. For many prospects, this represents a full ERP-adjacent digital transformation, which introduces friction. Implementation can be high-stakes, resource-intensive, and initially disruptive to internal workflows. As a result, customers are often hard to sell to, requiring not just proof of ROI but also strong stakeholder buy-in across multiple layers of leadership. To some extent, o9’s Partner Program mitigates this friction to some degree.
o9 Solutions’ clients include firms such as Nestlé, AB InBev, General Electric, Bridgestone, Estée Lauder, Caterpillar, and Walmart.
Market Size
There are roughly 9.9K global companies with over $1 billion in annual revenue as of 2025, a rough estimate of the total number of firms that fall within the typical financial positioning of o9’s customers. However, not all of these companies necessarily benefit from supply chain management services, especially if they operate in professional services industries or software for example. Extrapolating data from the 2024 Fortune 1000 companies report, estimates can be made that around 40-50% of the 9K+ global companies exist in industries that contain complex supply chains. This leaves o9 with a total customer universe of around 4K to 5K customers.
More generally, o9 Solutions operates across three overlapping software markets: Enterprise Resource Planning, Supply Chain Planning, and ESG / sustainability planning tools. The enterprise resource planning market is approximately valued at $64.8 billion as of 2024 and is estimated to grow to $125 billion by 2030. The supply chain planning market is estimated to be a $30 billion opportunity as of 2025. This figure is projected to grow to $72.7 billion by 2033. In parallel, o9 is also competing in the emerging ESG and sustainability software market, particularly with its Scope 3 emissions tracking and supply chain risk modules. This market is estimated at $900 million as of 2025, with projections reaching $2.1 billion by 2029, fueled by regulatory pressure and corporate sustainability mandates.
Competition
Competitive Landscape
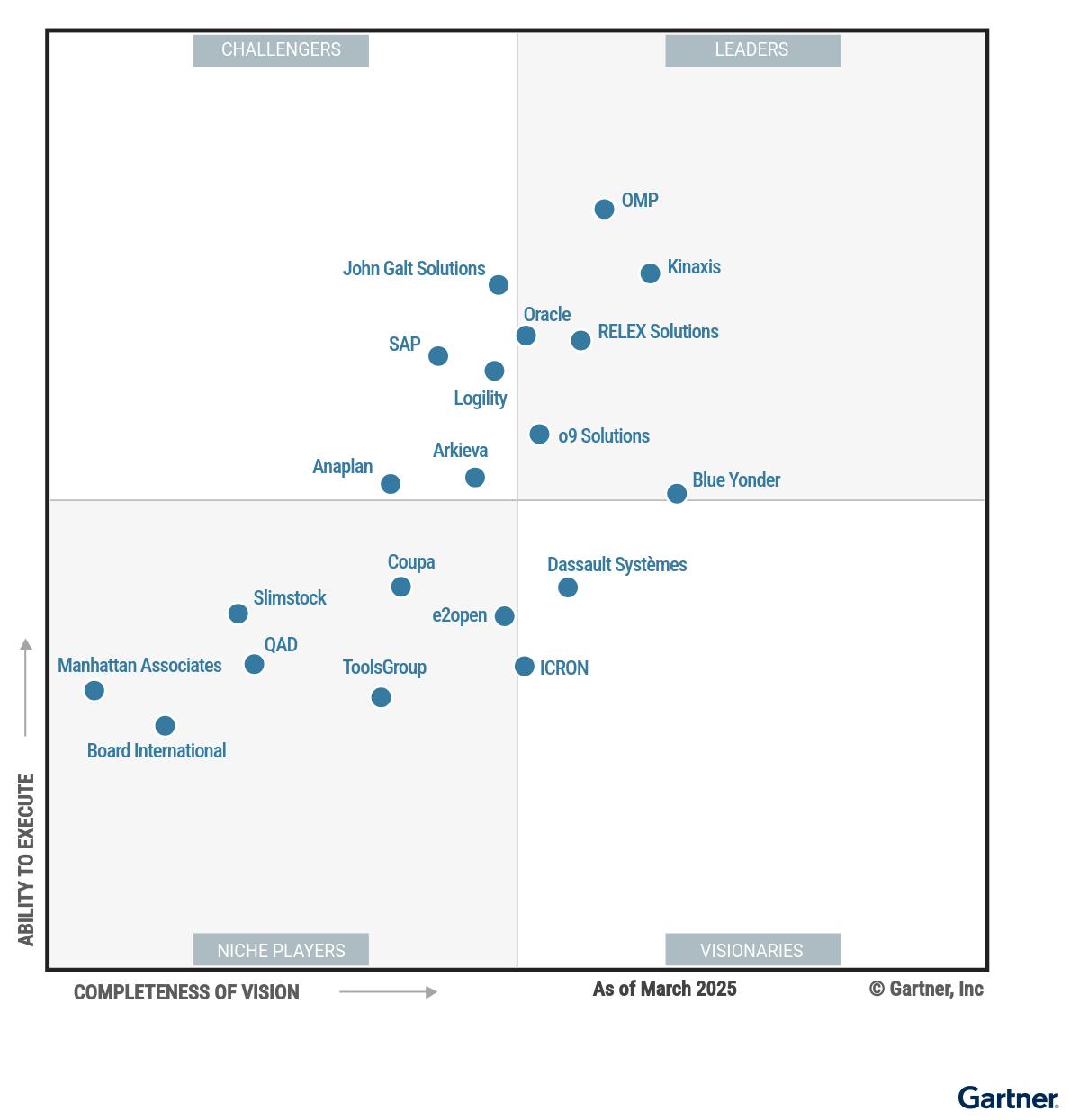
The enterprise planning and supply chain software market is fragmented, with a mix of legacy ERP providers, specialized supply chain vendors, financial planning platforms, and data platform alternatives. Legacy ERP giants like SAP and Oracle hold the largest market share as of 2025, offering comprehensive suites that encompass various business functions. However, specialized players such as Kinaxis and Blue Yonder have carved out significant niches in supply chain-specific applications. While SAP offers the product closest to a complete solution, no single vendor currently offers a solution that seamlessly integrates all these features, presenting opportunities for companies like o9 Solutions to disrupt the market.
Source: Gartner
Competitors
SAP: SAP SE, founded in 1972, is a public German multinational software corporation known for its enterprise resource planning (ERP) software. It offers the most extensive product suite out of all its competitors, including modules for finance, human resources, supply chain, and customer relationship management. SAP’s flagship product, the S/4HANA platform, offers real-time data processing and analytics, catering to large enterprises worldwide. In 2024, SAP reported revenues of €34.2 billion ($38.9 billion), establishing its position as Europe's most valuable tech company with a market capitalization of $342.4 billion. SAP's strength lies in its comprehensive, integrated solutions, though its complexity and cost can be a barrier for some organizations.
Kinaxis: Founded in 1984, Kinaxis is a public Canadian software company that specializes in supply chain management. Its flagship product, RapidResponse, provides real-time analytics and scenario planning to help businesses respond swiftly to supply chain disruptions. Kinaxis went public in June 2014, raising approximately $92.3 million. As of 2024, the company reported revenues of $483 million and had a market capitalization of around $3.5 billion. Kinaxis differentiates by providing a highly specialized service, honing in on supply chain management, catering to industries that don’t require significant focus on other aspects of ERP like aerospace, automotive, and pharmaceuticals.
Blue Yonder: Originally established as JDA Software in 1985, Blue Yonder rebranded in 2020 to emphasize its transition from an old-age software firm to be, instead, “embracing a future full of endless innovation, continuous improvement and outstanding customer experience.” The company offers end-to-end solutions that leverage machine learning, typically at flexible prices, making them appealing to a wide range of clients. In 2021, Panasonic acquired Blue Yonder for $7.1 billion, integrating it as a subsidiary to enhance its digital supply chain offerings. In 2024, Blue Yonder reported an annual revenue of $1.4 billion.
Anaplan: Anaplan, founded in 2006, is a cloud-based business planning software provider that enables organizations to model and analyze various business scenarios. Its proprietary Hyperblock technology, similar to o9’s EKG technology, allows for real-time, collaborative planning across finance, sales, and supply chain functions. In 2022, private equity firm Thoma Bravo acquired Anaplan for approximately $10.7 billion.
Business Model
o9 Solutions operates a SaaS subscription model, selling multi-year enterprise licenses that scale based on the number of modules deployed, user seats, company size, and data volume. Pricing is not publicly listed, however, and likely varies significantly based on a client's needs and parameters. The company’s revenue is predominantly recurring, with ARR growing 37% year-over-year in 2024, according to company disclosures.
Given that o9 is a cloud-native SaaS platform, it does not incur heavy infrastructure costs, and by outsourcing implementation services to partners, it avoids the headcount and delivery costs that typically drag on margins in more complex services-heavy enterprise software. This structure supports high gross margins and scalability, particularly as o9 moves further upmarket with larger contracts.
Traction
According to one estimate, o9 Solutions crossed $200 million in revenue as of early 2023, placing it among the top five global supply chain software vendors by revenue. o9 has consistently posted mid-double-digit growth in ARR between the years 2022 to 2025, with continued acceleration in new customer acquisition (+60% YoY in Q1 2025). o9 has scaled its internal operations in parallel with customer adoption. Headcount increased from 300 in 2019 to over 3K by 2024, a result of both a growing client base and increasing product complexity.
As of 2025, o9 services some of the largest clients in their respective industries, including Walmart, Nike, Estee Lauder, Starbucks, Nestlé, Google, Sony, Samsung, Caterpillar, and Bridgestone, among many others. Beyond direct customer traction, o9 has cultivated a notable ecosystem of system integrators and technology partners. Accenture, o9’s largest system integrator partner, has implemented over 30 enterprise deployments and named o9 its 2024 Partner of the Year. o9 also maintains active partnerships with Deloitte, EY, KPMG, and other major consulting firms.
Valuation
o9 Solutions was bootstrapped for over a decade before taking its first external investment from KKR in 2020 when the company raised $100 million at a $1 billion valuation. Later, in January 2022, General Atlantic, KKR, and Generation Investment Management invested $295 million at a $2.7 billion valuation. In July 2023, o9 raised $116 million led by General Atlantic’s BeyondNetZero fund, with participation from existing investors KKR and Generation Investment Management. General Atlantic categorized o9 solutions as a “climate” sector investment and deployed capital from their BeyondNetZero fund. The round valued the company at a post-money valuation of $3.7 billion. In total, as of August 2025, o9 had raised $533 million across several rounds.
While o9 remains private, public and acquired competitors offer valuation benchmarks in the adjacent supply chain and planning software space. Kinaxis reported $360 million ARR in Q4 2024 with a market cap of $3.5 billion, implying a ~9.7x revenue multiple. Blue Yonder was acquired by Panasonic in 2021 for $7.1 billion. At the time of acquisition, Blue Yonder was reportedly generating $475 million in ARR, implying a ~15x ARR multiple, though the premium reflected strategic synergies with Panasonic’s IoT and logistics operations. These comps suggest that o9’s 2023 valuation ($3.7 billion) likely implies a forward revenue multiple in the 15–18x range, assuming ~$200 million in ARR as of 2023.
Key Opportunities
Displacement Tailwinds
One of the most immediate opportunities for o9 Solutions is the retirement of SAP Advanced Planning & Optimization (APO), a legacy system still widely used across large enterprises. SAP has formally announced the sunset of APO by 2027, urging customers to migrate to its newer solution, SAP Integrated Business Planning (IBP). However, the transition from APO to IBP has drawn criticism for being costly, slow, and functionally limited, creating dissatisfaction among customers.
This presents a rare displacement opportunity in a market that is traditionally incredibly sticky. o9 is well-positioned to capitalize given that it is offering an AI-driven alternative. In practice, this gives o9 a chance to capture market share from incumbents, not through greenfield expansion, but through replacement cycles in companies already primed for change. For a category with high switching costs and inertia, that’s a notable unlock.
Regulatory Pressure
With a wave of regulatory requirements rolling out globally, ESG compliance is no longer optional for large enterprises. Notable among these are the EU Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive which required over 50K companies to report ESG performance beginning in 2024 and the Germany Supply Chain Due Diligence Act which mandates oversight of supplier labor and environmental practices.
These developments create a demand-side pull for integrated ESG tracking and reporting tools, particularly ones that connect directly to supply chain operations. o9 is one of the only platforms in the market that enables customers to view real-time, holistic supplier ESG scores, enabling users to comply with these regulatory shifts.
Regionalized Supply Chains
In response to geopolitical risk and supply chain resilience concerns, global manufacturers are increasingly shifting operations to emerging markets like Vietnam, India, and Mexico; a process commonly referred to as “China+1.” This creates new complexity in planning for global supply chains and opens geographic whitespace for software vendors able to support these fast-evolving ecosystems.
If o9 can establish an early presence in these regions, particularly by partnering with local integrators or offering lightweight deployments tailored to mid-market enterprises, it stands to lock in local market share before competitors scale globally. Moreover, customers expanding into these regions will need planning tools that can quickly adapt to new suppliers, logistics routes, and regulatory regimes, which could play to o9’s capabilities in configurability and scenario-based modeling.
Key Risks
Partner-Led Implementation
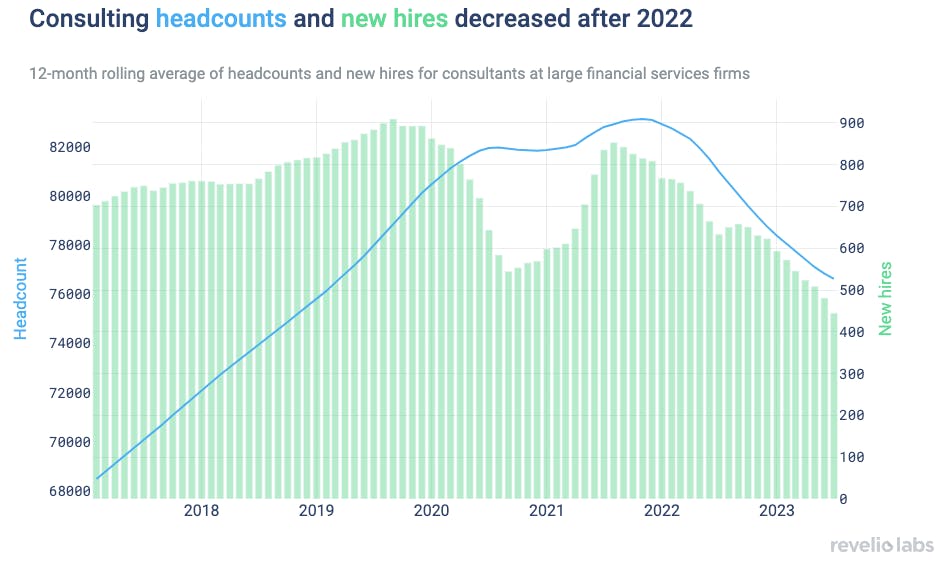
While o9’s asset-light model allows for scalability, it also introduces dependency risk on third-party consultants for implementation. The company outsources the majority of its deployment and configuration work to global systems integrators like Accenture, Deloitte, and EY. This limits o9’s direct control over customer onboarding timelines, solution quality, and long-term satisfaction.
If a consulting partner mismanages a high-profile deployment it could damage o9’s brand and reduce renewal rates. Moreover, a slowdown in the broader consulting market or a strategic shift away from o9 by one of its key partners could bottleneck growth or disrupt planned go-lives.
Source: Revelio Labs
Incumbent Vendors
Although SAP has announced the sunset of its legacy APO solution, the sunset date has been extended several times since it was originally announced in 2017, with support expected to end in 2027. The extension in the sunset deadline occurred to elongate the transition window between SAP APO and SAP IBP. For risk-averse enterprise clients, this gradual timeline reduces the urgency to migrate to a new platform, particularly one from a non-incumbent.
In addition, SAP benefits from deep entrenchment and brand loyalty. For customers who see IBP as “good enough,” o9’s technical superiority may not be enough to justify a costly switch. This status quo bias, especially in industries where IT turnover cycles are long and budgets are locked well in advance, could slow o9’s pace of customer acquisition in its core enterprise segment.
Summary
o9 Solutions sits at the convergence of aging enterprise infrastructure, rising regulatory complexity, and growing demand for integrated, AI-driven supply chain planning tools. Its modular platform positions it as a modern alternative to legacy systems like SAP APO, enabling it to service a broad range of clients with depth.
o9 has shown strong momentum over the last decade it has been in the market, growing to $200 million in ARR across rapid customer expansion. However, its reliance on third-party consultants for implementation and ongoing pressure from incumbent vendors like SAP and Oracle introduce friction to scaling. The key question is whether o9 can maintain product differentiation and implementation quality as it moves deeper into regulated and risk-averse enterprise environments.