Thesis
Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) are blockchain-verified digital objects. However, unlike other crypto tokens, NFTs are not mutually interchangeable and are either unique or have limited copies. The first NFT, Quantum, was minted in 2014. NFTs began to enter broader public awareness with the introduction of NFT collections hosted on the Ethereum blockchain in 2017.
In 2021 and 2022, the NFT market grew rapidly and entered mainstream relevance. Notable artists began using NFTs to create and sell fully digital artwork. For example, the artist known as Beeple sold an NFT art piece entitled “5000 days” for $69 million in March 2021. At the same time, NFT collections like CryptoPunks and Bored Ape Yacht Club (BAYC) also saw a dramatic rise in prices. One estimate of the total trading volume of NFTs being traded showed it going from ~$4.3 million weekly at the end of 2020 to an all-time high of $1.6 billion per week in February 2022.
Following the 2022 peak, NFTs in particular, and crypto in general, entered a bear market, with a large drop in both prices and trading volumes. NFT trading volumes, for example, saw a steady decline from the aforementioned $1.6 billion peak in February 2022 to $82.5 million by November 2023, although this was still far higher than pre-2021 volumes. NFT prices also declined relative to the rest of the crypto market, with top collections like CryptoPunks (worth 125 ETH at its ATH in late 2021) having declined 55% relative to Ethereum as of November 2023. Nevertheless, both prices and volumes in the market remained elevated relative to pre-2020 levels.
OpenSea describes itself as “the world’s first and largest digital marketplace for crypto collectibles and non-fungible tokens (NFTs).” It allows users to buy, sell, and create NFTs. Although it began with Ethereum, as of November 2023 it offered cross-blockchain compatibility across a variety of other blockchains including Solana, Polygon, Arbitrum, BNB, and others. OpenSea is a non-custodial platform where the platform doesn’t take custody of assets, instead enabling direct exchange between buyers and sellers.
Founding Story
OpenSea was founded in 2017. OpenSea founders Devin Finzer (CEO) and Alex Atallah (CTO) both studied computer science in college and founded startups at their respective colleges while still students. They were inspired to create OpenSea by CryptoKitties, an early NFT collection launched on the Ethereum blockchain that saw traction.
CryptoKitties charged a 3.5% commission on all sales after its launch and was able to generate $10 million in sales within months. Finzer and Atallah had the idea to create a marketplace that charged less than CryptoKitties (2.5%) and a broader selection of NFTs. As Finzer said in a 2019 interview:
“Initially, the idea for OpenSea stemmed from our interest in CryptoKitties. While marketplaces for digital goods have existed for quite some time, they tend to be self-contained ecosystems: individual marketplaces for specific games, marketplaces for domain names, marketplaces for tickets, etc. Scaling something like ‘eBay’ for digital assets would be difficult because there was little standardization around digital ownership. With the introduction of ERC721, it felt like such an idea was possible for the first time.”
ERC721 was a new Ethereum standard at the time that allowed for NFTs to be formed on the Ethereum blockchain. Finzer and Atallah validated their idea by joining various ERC721 projects that were emerging at the time, including CryptoCelebrities, Ether Tulips, and Mythereum. In doing so, they found that users of these projects didn’t have a way to trade their assets and OpenSea was therefore introduced as a solution. Users of these projects fueled OpenSea’s initial growth, which was further accelerated through cross-pollination with gaming communities on Discord.
The pair was able to build the first version of OpenSea “within a couple of months”, and it was used for testing by early adopters. OpenSea was then accepted into YC’s Winter 2018 cohort, where it was described as “the first (and largest) peer-to-peer marketplace for cryptogoods” and was explained as being “like eBay for crypto assets”. As of March 2018, YC claimed that OpenSea had seen “around half a million dollars in volume.”
Product
NFT Marketplace
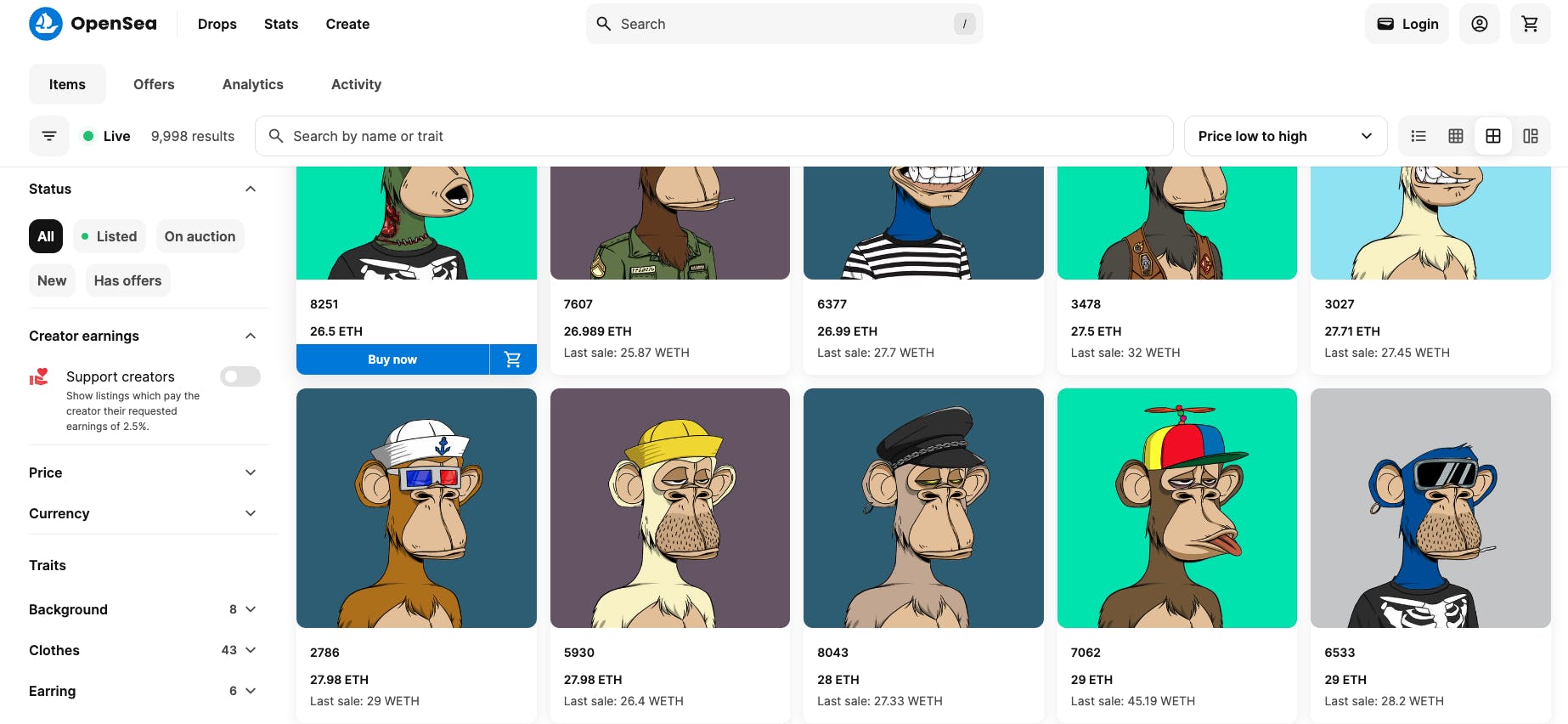
Source: OpenSea
OpenSea provides an NFT marketplace that allows users to create, buy, and sell NFTs. NFTs are unique digital assets stored on the blockchain. They can be jpegs, music files, animations, liquidity positions, game items, or any unit of storage. When created, they can be traded from one cryptocurrency wallet to another.
In addition to the Ethereum blockchain which it initially launched with, OpenSea is also compatible with a number of other blockchains including Solana, Polygon, Arbitrum, and BNB. OpenSea offers NFTs across a range of categories including art, gaming, memberships, profile pictures (PFPs), photography, and music.
Cryptocurrency users can log into OpenSea using their cryptocurrency wallets to view, buy, and sell NFTs. They are also able to create new NFTs using the OpenSea platform. Users can make accounts and generate an NFT for free. OpenSea supports the following wallets as of November 2023: MetaMask, Coinbase Wallet, WalletConnect, Ledger, Phantom, BitKeep, Kaikas, Core, Glow, Fortmatic, Bitski, Solflare, OperaTouch, and Trust.
NFT Collections

Source: OpenSea
On OpenSea, NFTs are typically organized into Collections of similar images by creators. Creators can market their collections using social media to build up excitement leading up to the launch of the collection. Once enough excitement is gathered, the collection can be sold (or “minted”) during events called “Mints” executed by the creators to raise funds for a project.
OpenSea uses the total amount of ETH trading volume to determine what NFT collections are most popular. As of November 2023, some of the most notable NFT collections on OpenSea were CryptoPunks (1 million+ ETH total trading volume), Bored Ape Yacht Club (1 million+ ETH), Mutant Apt Yacht Club (984K ETH total trading volume), Otherdeed for Otherside (613K ETH total trading volume), and Azuki (635K ETH total trading volume).
NFT Discovery
Collections are also how users discover and search for NFTs. When a user puts in the name of a collection on OpenSea’s search bar, it’ll show every single NFT from that collection. The search will show the collection’s corresponding name, image, last sold price, and some other filters users may find interesting (like clothing type, eye color, etc.). NFTs are often discovered either on social media platforms or through the exploration tabs on OpenSea.
OpenSea Pro
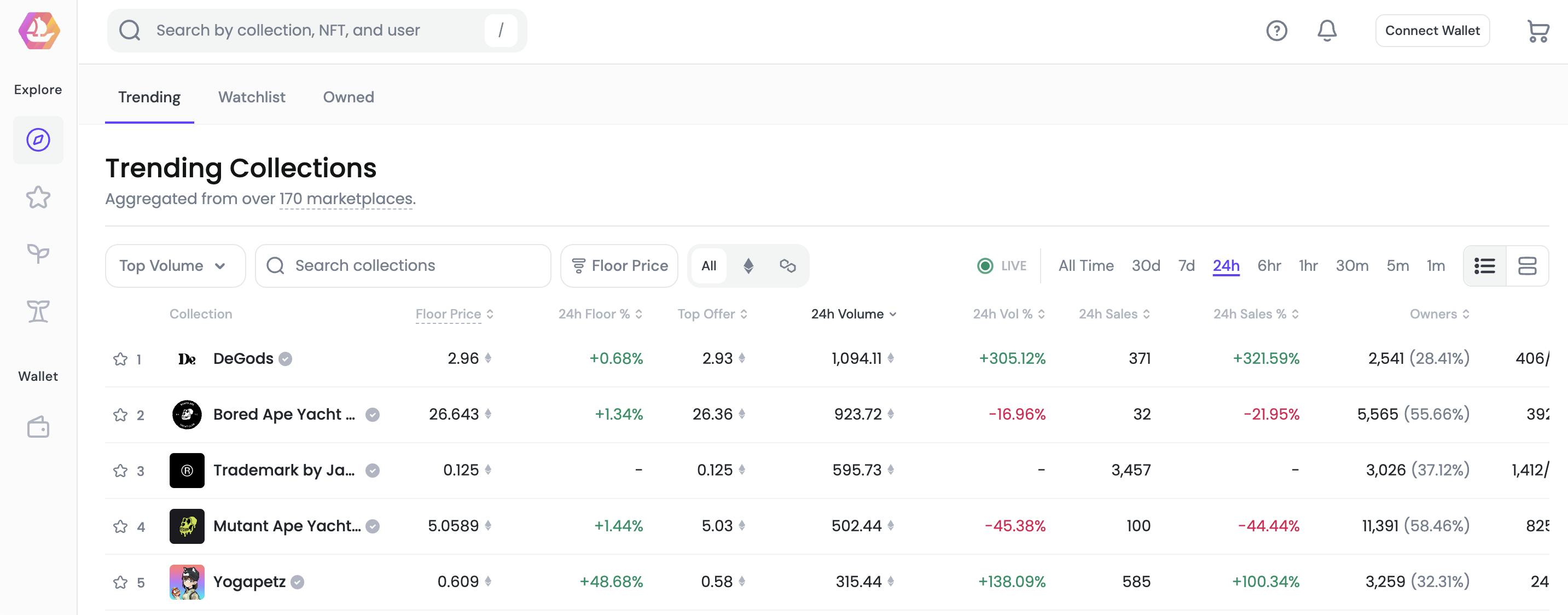
Source: OpenSea Pro
OpenSea Pro is described by OpenSea as “the most powerful NFT marketplace aggregator with over 170 marketplaces.” It was designed for high-volume NFT buyers and sellers, and the company claims that it ‘features the most optimized gas fees of any NFT aggregator”. It allows other marketplaces to list NFTs on OpenSea for a 0.5% fee and offers inventory management tools so that users can list and buy items in bulk.
Market
Customer
NFTs are digital collectibles that creators can use to monetize their fans, and so the target customer profile for OpenSea includes creators (including artists, musicians, and developers) who wish to create and sell NFTs on the supply side and fans or audience members of those creators on the demand side.
According to one source, as of December 2022, OpenSea had over 2.5 million registered users who had made at least one transaction, which represented a 61x increase from March 2020. Another source has estimated that the company had 1.5 million active users as of April 2023.
Market Size
The volatility of the crypto market in particular, and NFTs in particular, complicates the process of estimating the value of OpenSea’s addressable market. Nevertheless, the NFT market has seen both significant growth and decline in the early 2020s. One estimate of the total trading volume of NFTs being traded showed it going from ~$4.3 million weekly at the end of 2020 to an all-time high of $1.6 billion per week in February 2022.
Following the 2022 peak, NFTs in particular, and crypto in general, entered a bear market, with a large drop in both prices and trading volumes. NFT trading volumes, for example, saw a steady decline from the aforementioned $1.6 billion peak in February 2022 to $82.5 million by November 2023, although this was still far higher than pre-2021 volumes.
NFT prices also declined relative to the rest of the crypto market, with top collections like CryptoPunks (worth 125 ETH at its ATH in late 2021) having declined 55% relative to Ethereum as of November 2023. Nevertheless, both prices and volumes remained elevated relative to pre-2020 levels. The NFT market was valued at $20.4 billion in 2022 by one estimate and was projected to be growing at a CAGR of 34.2% until 2030.
Competition
Other NFT Marketplaces
Blur: Blur, which describes itself as the “NFT marketplace for Pro Traders”, was founded in 2019. It raised an $11 million seed round in March 2022 led by Paradigm, which is its total funding raised as of November 2023. Blur’s trading volume overtook OpenSea in May 2023, when it had $442 million in sales vs. $183 million by OpenSea — accounting for 65% of the total NFT market share. Blur listed more than 1 million NFTs as of March 2023, features advanced trading tools for its users, and has no mandatory loyalties. It also offers NFT sniping because it updates its listings’ prices 15 times a minute.
Magic Eden: Magic Eden describes itself as the “community-centric marketplace”. It was founded in 2021 and has raised a total of $170 million in funding as of November 2023. It raised a $130 million Series B in June 2022 which valued the company at $1.6 billion, which was co-led by Electric Capital and Greylock. It listed more than 1 million NFTs as of March 2023, and has been described as the ‘go-to NFT marketplace on the Solana blockchain”. It doesn’t charge listing fees, and charges 2% transaction fees, compared to the 2.5% charged by OpenSea.
LooksRare: LooksRare was founded in 2021. It is an Ethereum-based NFT marketplace that launched a vampire attack on OpenSea in January 2022, which involved indexing all of the NFTs on Ethereum and offering incentives in the form of its LOOKS token, which allowed it to produce $307 million in protocol revenue that month (vs. OpenSea’s $110 million).
However, most of the volume on LooksRare turned out to actually be “wash trading” of the LOOKS token (a practice to manipulate the market by simultaneously selling and buying the same asset to simulate activity). Sites like The Block track what percentage of LooksRare’s volume was not wash trading and how much volume there is after filtering out wash trades.
For the first couple of months since its launch, the average real volume, according to The Block, has consistently hovered at <40% of its total, reaching around ~$45 million monthly. While this was significantly less than OpenSea’s $650 million, it’s not negligible. It listed more than 1 million NFTs as of March 2023 and offered a lower 2% fee on sales (vs. OpenSea’s 2.5% fee). It also allows users to earn rewards in the form of LOOKS tokens for staking, trading, and NFT listing on its platform.
Other Crypto Exchanges
Other crypto exchanges like Kraken, Binance, and Coinbase now also offer NFTs. As of March 2023, Binance had over 1K NFT collections on its NFT marketplace, Kraken listed 110 NFT collections., and Coinbase had over 10K NFTs listed on its marketplace.
Business Model
OpenSea’s marketplace primarily makes money on its 2.5% take rate on the price of all transactions on OpenSea. For OpenSea Pro, the company charges a lower 0.5% fee. It takes these payments for exchanges of ERC721 or ERC1155 NFTs. When someone creates an NFT, they can set a “creator earnings %“ that determines how much money they make each time an NFT they create is traded. OpenSea advises creators to set the creator earnings to 2.5%.
To drive more transactions, OpenSea shares statistics, leaderboards, and other features supporting the launch and gathering momentum behind an NFT collection. Its platform attempts to increase the number of people interested in buying NFTs and the total number of transactions.
Traction
After its founding, OpenSea’s monthly trading volume hovered around $500K until October 2019. In January 2021, its volume climbed to $8 million before its first 10x spike to $96 million in February 2021. OpenSea volume grew 10x again in August 2021 from ~$300 million to ~$3 billion. Volume remained above $2 billion monthly for the following five months before collapsing ~73% from $2.6 billion to $695 million in June 2022.
The following months saw a steady decline in volume as a result of the onset of the crypto bear market in 2022. Monthly trading volume on OpenSea had fallen to $286.8 million by December 2022, and by October 2023 it was at $49.1 million, which represented a ~100x decline from its peak monthly trading volume of $4.9 billion in January 2022. However, volume is still much higher than it was before the COVID-19 pandemic.
The number of OpenSea’s monthly active traders, which peaked at 511K in February 2022 after growing from just 6K at the beginning of 2021, had declined to 76K as of October 2023. In November 2023, after the long decline in active users and trading activity on OpenSea, the company announced that it was reducing its staff by 50%. It said that it was doing so as part of an initiative to relaunch as “OpenSea 2.0”.
Valuation
OpenSea raised a $300 million Series C in January 2022 which valued the company at $13.3 billion and brought its total funding to $427.2 million. The round was led by Paradigm and Coatue. Its Series C valuation represented an 8x increase from its previous funding round less than six months earlier in July 2021, which was a $100 million Series B at a $1.5 billion valuation, led by a16z. However, in November 2023, following a long bear market in NFTs, there was a report that Series C investor Coatue had marked down its stake in OpenSea by 90%, implying that OpenSea’s valuation had fallen to $1.4 billion or less from $13.3 billion less than two years prior.
Key Opportunities
Recapturing Market Share
In May 2023, OpenSea competitor Blur captured 65% of the NFT trading market and overtook OpenSea in terms of volume. This was just one month after OpenSea introduced OpenSea Pro, which was aimed at a similar target customer as Blur (i.e. “pro” traders). OpenSea Pro offers an even lower 0.5% fee and similar bulk trading tools but wasn’t able to prevent Blur from capturing market share from OpenSea.
Moving forward, however, OpenSea could continue to capitalize on its consumer-oriented differentiation from Blur to appeal to everyday consumers. Because of the cyclical nature of crypto markets, many of these consumers, which formed the bulk of OpenSea’s monthly active users, have been dormant during the bear market; they could return in force if the NFT market sees another bull market, and OpenSea could position itself to benefit from this and recapture market share.
Authenticity and Fraud Detection
From April to August 2022, 33% of OpenSea’s blog posts focused on fraud prevention, verification, security, and other safety-related announcements. NFT trading is fraught with scams, plagiarism, fraud, and other risks that have significantly curbed public appeal. OpenSea’s efforts to steer the NFT industry into more secure waters could build trust in using NFTs for skeptics who have been hesitant in the past. Bringing down fraud would also significantly increase the trading volume of existing users, reducing the risk of each transaction.
Key Risks
Competition
New entrants to the NFT market like Blur and Magic Eden have taken market share from OpenSea amidst the bear market, while large centralized crypto exchanges like Coinbase and Binance entered the NFT market in 2022 and began offering the ability to buy and sell NFTs. With other competitors in some cases undercutting OpenSea’s fees, and in others conducting vampire attacks to siphon off OpenSea users, OpenSea must work to fortify its defensibility even as it seeks to regain market share that it has lost.
Market Volatility
Cryptocurrency markets are notoriously fickle. Macroeconomic turmoil in 2022 impacted general interest in buying NFTs. Monthly trading volume on OpenSea had fallen to $286.8 million by December 2022, and by October 2023 it was at $49.1 million, which represented a ~100x decline from its peak monthly trading volume of $4.9 billion in January 2022. As a result, the company was forced to lay off 50% of its staff in November 2023 and had its valuation reduced by over 90%. If the NFT market does not recover at some point, it would be a serious problem for OpenSea.
Summary
OpenSea, founded in 2017 by Devin Finzer and Alex Atallah, is a prominent NFT marketplace that gained traction in the wake of the 2021 NFT boom. Initially inspired by CryptoKitties, OpenSea differentiated itself by offering lower fees (2.5%) and a broader selection of NFTs. The platform allows users to create, buy, and sell NFTs, with cross-blockchain compatibility, including Ethereum, Solana, Polygon, Arbitrum, and BNB. Notable NFT collections on OpenSea include CryptoPunks and Bored Ape Yacht Club. However, the platform faced challenges in the crypto bear market, experiencing a decline in trading volumes and a drop in the value of top collections by November 2023. OpenSea raised a significant Series C funding round in January 2022, valuing the company at $13.3 billion, but faced a subsequent markdown in valuation to around $1.4 billion by November 2023. The platform's key opportunities include recapturing market share and addressing authenticity and fraud concerns.