Thesis
The volume of online data has been growing exponentially since the early days of the internet. In 2024 alone, an estimated 149 zettabytes of data were created worldwide, with global data creation projected to reach 394 zettabytes by 2028. The 120 zettabytes of data created in 2023 represents a nearly 60x increase from the data created in 2010.
Despite this massive influx of data, the efficacy of traditional search engines may be deteriorating, making it harder to find desired information. For example, a study published in 2024 by a team of German researchers after a year-long review of results for 7.4K product review queries on Google, Bing, and DuckDuckGo concluded that search engine query results have become increasingly populated with low-quality, highly optimized content that it characterized as “SEO spam”.
In addition to this, the average position of the top organic link on a Google search engine results page fell from 375 pixels down the page in 2013 to 615 pixels down the page in 2020. Studies indicate that these changes are more than just a minor inconvenience: over 50% of consumers reported in 2020 that they sometimes feel misled by search results, with 25% saying that they often end up somewhere unexpected by clicking on a search result. As a result of increasingly cluttered search experiences, some people have even started looking for answers in places like Reddit and TikTok instead of traditional search, with others touting that new advances in AI might put the future of search engines in peril.
During the same period as these changes in search, a pivotal shift occurred in natural language processing with the introduction of transformer architecture. Unlike previous recurrent neural networks and convolutional neural networks, transformers revolutionized the field by introducing self-attention mechanisms. This architectural innovation enabled models to process entire sequences of data in parallel rather than sequentially, leading to significantly faster training times and improved performance on complex language tasks.
This breakthrough, combined with enhanced processing power and the wealth of data available online, led to significant advancements in the size and scope of LLMs. With extensive training, these models become applicable to a wide variety of tasks. In November 2022, following its initial launch, ChatGPT crossed 1 million users in just five days. The product then became the fastest-growing consumer application in history, reaching 100 million users within two months of its launch. However, LLMs have their drawbacks, particularly in the realm of information retrieval. They are expensive to train on the most up-to-date knowledge and are susceptible to producing outputs that are occasionally factually wrong, a phenomenon known as hallucination, that stems from overfitting training data.
Perplexity, also known as Perplexity AI, is an AI-powered, conversational search engine that answers queries using natural language predictive text the draws on sources from around the internet. Perplexity performs real-time web searches to gather the most current information available across the Internet. It summarizes the information in a cited format, using LLMs to preprocess the questions and summarize search results, which is intended to deliver up-to-date and well-sourced information. Perplexity describes itself this way: “unlike traditional search engines that present a list of links, Perplexity delivers synthesized information in a natural language format, complete with citations and follow-up suggestions for more refined searches.” The company’s mission is to “serve the world’s curiosity”.
Founding Story

Source: Lenny’s Newsletter
Perplexity was founded in 2022 by Aravind Srinivas (CEO), Denis Yarats (CTO), Johnny Ho (Chief Strategy Officer), and Andy Konwinski.
Growing up, Srinivas was fascinated with computers and mathematics. After earning a Master’s in Engineering from the Indian Institute of Technology in 2017, he pursued a PhD in Computer Science at UC Berkeley, specializing in reinforcement learning and predictive coding. During his postdoc, Srinivas interned at DeepMind and OpenAI.
Srinivas has studied his biggest competitor, Google, for most of his life. Growing up in Chennai, India, he admired Sundar Pichai, who shared his hometown and would later become Google’s CEO. During his internship at DeepMind, Srinivas studied Google’s history and Larry Page’s vision to provide direct answers, not just links to them. 21 years later, with rapid improvements in foundational models, Srinivas launched Perplexity to disrupt Google Search.
Srinivas and fellow cofounder Denis Yarats first connected through email after the two published nearly identical research papers at UC Berkeley and NYU, respectively. They stayed in touch even as Yarats started working as an AI researcher at Facebook. In July 2022, Srinivas and Yarats joined together with former Quora engineer, Johnny Ho, and Databricks cofounder and fellow UC Berkeley alumnus, Andy Konwinski, to formally pursue a startup together.
Perplexity’s first product, Bird SQL, launched in December 2022. It used a tool from OpenAI called Codex to help turn everyday language into computer code and search through databases like Twitter. The tool turned natural language search queries into SQL, which would then return Twitter-specific results.
However, when Twitter announced it would stop allowing free access to its API in February 2023, the team decided to switch gears to focus on a core search product. By this time, ChatGPT was rapidly gaining popularity, having hit 100 million monthly active users within two months of launch, and the team saw an opportunity to create a product to address issues that some AI chatbots had, like serving up inaccurate information with unclear sources. Perplexity would also add citations for generated answers.
Speaking on this topic, Srinivas noted that “citations are a great way to marry search and LLMs.” Perplexity developed a core vision “to become the best platform for answers and information” and launched an updated version of its Ask product in January 2023 focused on adding sources and follow-on questions to initial queries. The company described the launch as “the world’s first conversational search engine”, and it reached 2 million monthly active users within its first four months.
Product
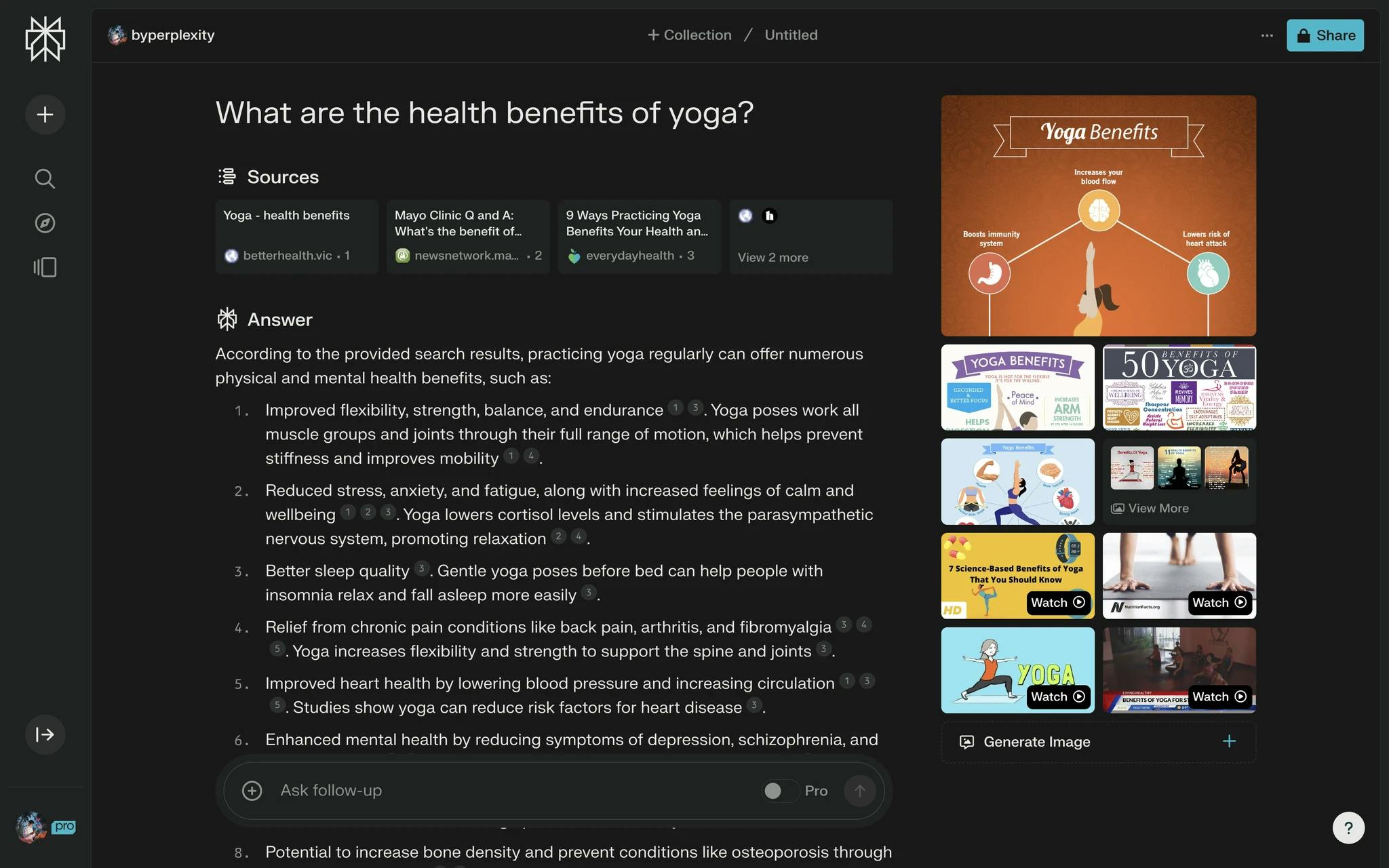
Perplexity’s core product is a conversational search engine that leverages advanced LLMs to provide direct, sourced responses to user queries in natural language. It offers a personalized and interactive search experience, with features like document importation for reference, image generation, and educational, professional, and content creation assistance.
Source: Perplexity
Answer Engine
Perplexity’s core offering is its answer engine is intended to bridge the gap between conventional search engines and AI-driven chat interfaces. As the CEO, Aravind Srinivas described it in a blog post in January 2024:
“With Perplexity’s search tools, users get instant, reliable answers to any question with complete sources and citations included. There is no need to click on different links, compare answers, or endlessly dig for information. In an era where misinformation and AI hallucinations are causing increasing concern, we’re built on the idea that accuracy and transparency are prerequisites to making AI-powered search ubiquitous. The times of sifting through SEO spam, sponsored links, and multiple web pages will be replaced by a much more efficient way to consume and share information, propelling our society into a new era of accelerated learning and research.”
In contrast to conventional search engines, which typically yield a list of hyperlinks, Perplexity’s core engine uses LLMs to summarize real-time search results into a succinct, text-based format with inline citations. The engine prioritizes more recently updated sources. Compared to traditional search, conversational AI provides an interactive search experience by enabling users to pose follow-up questions within the same conversational context.
Inline citations allow the product to confront two more significant challenges inherent in LLM-based approaches to information retrieval: outdated data and hallucinations. Perplexity’s answer engine conducts real-time web searches to fetch the most up-to-date information to combat stale data, ensuring that current data takes precedence. Additionally, the ask engine cross-references model output with contemporary sources to verify accuracy and reliability in tackling hallucinations.
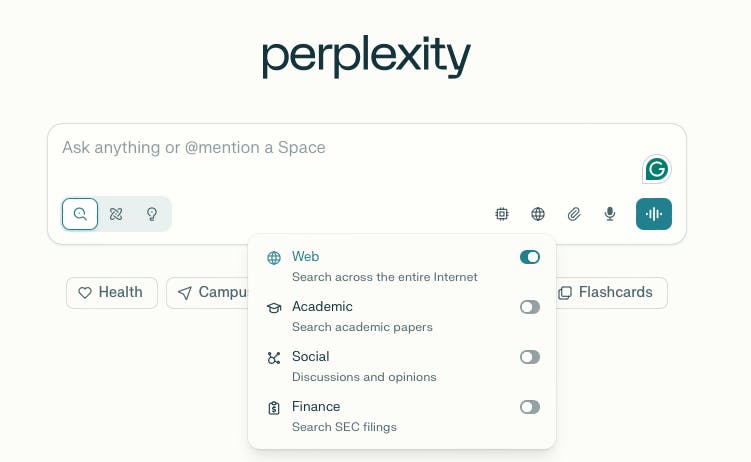
Perplexity offers several focus modes that tailor the answer engine’s behavior to specific content types or user intents. These include ‘Web’ for general-purpose search, ‘Academic’ for peer-reviewed academic papers, ‘Social’ for online discussions and opinions, and ‘Finance’ for searching SEC filings and earnings calls. Users can toggle between these modes directly in the interface, enabling more relevant results for queries ranging from scientific research to community opinions.
Source: Perplexity
For more complex questions, users can activate ‘Reasoning’ mode, which performs multi-step analytical reasoning. Research mode executes dozens of iterative searches to produce reports across domains like finance, technology, and healthcare. These modes are designed to scale from quick lookups to in-depth professional research.
LLM Backbone
Source: Perplexity
Perplexity's approach to its answer engine is characterized by a hybrid model strategy, which uses both internally developed models (based on open-source models) and third-party foundational models.
Sonar
Perplexity initially relied on OpenAI’s GPT‑3.5 for response generation and used Microsoft Bing to power its search results. Since then, the company has developed its own PPLX online LLMs built on open-source foundations, specifically Mistral‑7B (released by Mistral AI in September 2023) and LLaMA‑2 70B (released by Meta in July 2023). These online models are tightly integrated with Perplexity’s proprietary crawling and indexing infrastructure, allowing the models to respond using up-to-date web information without the cost and time of training fully original models from scratch.
In February 2025, Perplexity launched Sonar, its first productized in-house model built on top of LLaMA 3.3 70 B. Designed for high factual accuracy and clarity, the new Sonar model consistently outperformed peers like GPT-4o Mini and Claude 3.5 Haiku in A/B tests, while closely matching the performance of frontier models such as GPT-4o and Claude 3.5 Sonnet. As a result of its partnership with Cerebras for inference infrastructure, Sonar can deliver answers at over 1.2K tokens per second, enabling instant response times without sacrificing precision. As of October 2025, Sonar is also available via API, which includes advanced capabilities such as Sonar Pro, Sonar Reasoning (powered by DeepSeek R1), and Sonar Deep Research, enabling deeper analytical workflows for more demanding use cases.
Third-Party Models
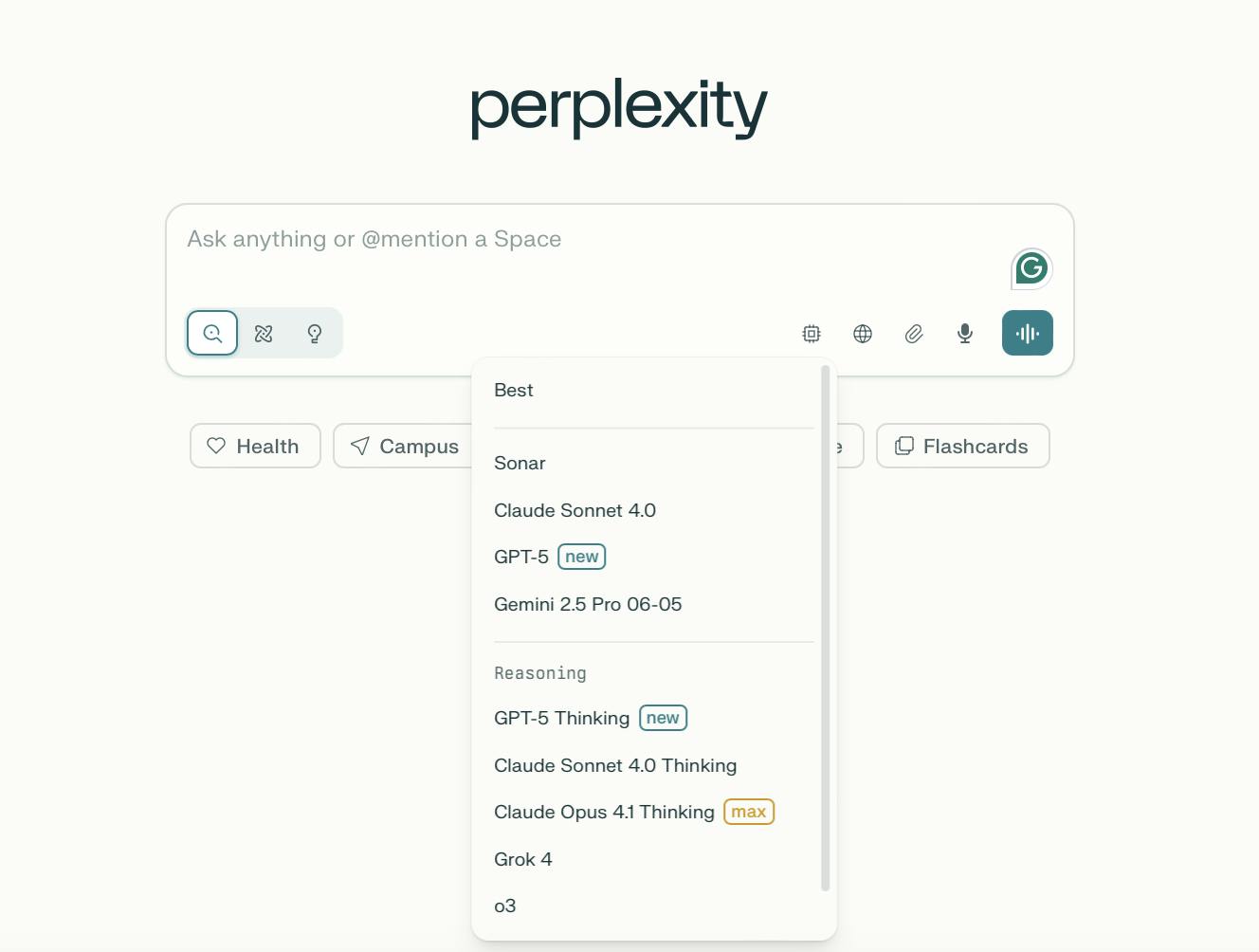
As of October 2025, Perplexity Pro users have the option to toggle between its default model and offerings from other providers, including OpenAI’s GPT series (e.g., GPT-5, GPT o3 Pro), Anthropic's Claude models, Google’s Gemini 2.5 Pro, and xAI’s Grok 4. This versatility allows users to select models that precisely align with their specific research objectives and preferences, including writing and image generation.
Platforms
Perplexity provides its application across a variety of different search and browsing experiences across different platforms, including mobile devices and web browsers.
Desktop
Perplexity is accessible via a web app on desktop browsers, which is its most robust interface for long-form queries, research workflows, and content creation. In addition, Perplexity offers a dedicated macOS app that mirrors the browser experience while enabling deeper system-level integration, such as key shortcut support and faster performance for power users. In March 2025, Perplexity introduced its Windows app, available for users of Windows 10 or later versions.
Source: Apple
Mobile
Perplexity has developed a mobile application compatible with both iOS and Android. In September 2023, Perplexity acquired Spellwise, an “AI-powered keyboard writer,” whose team then helped further Perplexity’s mobile efforts. Perplexity’s mobile app offers various features designed to facilitate easier and more effective information retrieval, with an emphasis on voice search. The iOS app can be downloaded from the Apple App Store, and the Android version is available on Google Play. Both versions are free to download and use. An iOS update in April 2025 added support for voice commands, enabling users to perform tasks like writing emails, setting reminders, and booking dinner reservations. On Android, Perplexity supports more advanced interactions, including background conversations and on-screen context sharing.
To expand reach and default usage, Perplexity is actively pursuing OEM integrations with mobile manufacturers as of October 2025. In March 2025, the company became the lead assistant partner for Deutsche Telekom’s AI Phone, offering voice-activated help for everyday tasks directly from the lock screen or power button. The assistant is also embedded in the carrier’s MeinMagenta app, bringing AI functionality to existing devices. In April 2025, Perplexity announced a global partnership with Motorola to pre-install its assistant on new smartphones, including the Razr and Edge lines. The integration includes deep system hooks, such as external display support, direct access via Moto AI, and free trials of Perplexity Pro.
Source: Testing Catalog
As of October 2025, Perplexity remains in discussions with Samsung to embed its AI-search capabilities into the upcoming Galaxy S26 series. This could include the Perplexity app pre-loaded on Samsung devices, Perplexity search features within Samsung's web browser, and possibly integrating Perplexity with Samsung's Bixby virtual assistant. So far, Galaxy has largely relied on Google’s Gemini model for AI-powered features. A deal with Perplexity would decrease Samsung’s AI reliance on Google.
Browser
In July 2025, Perplexity launched Comet, an AI-powered browser built on Chromium and supported by the company’s acquisition of productivity-focused browser startup Sidekick in May 2025. Comet is designed to move beyond the clutter of tabs and hyperlinks, offering a conversational interface where users can issue broad instructions, such as “book a restaurant” or “find a train ticket,” and watch the browser execute multi-step workflows across sites while maintaining context. The company describes Comet as a shift “from browsing to thinking,” where research becomes conversation and the internet acts as an extension of the user’s mind. Early reviewers noted impressive performance on automating tasks like booking travel or drafting emails, though outcomes were sometimes inconsistent, and questioned whether differentiation is enough to disrupt the traditional browsing experience.
Srinivas has positioned Comet as both a strategic product and a foundation for building AI agents, suggesting it could already replace certain office roles such as recruiters or administrative assistants. He has also emphasized the browser’s ability to capture richer behavioural data beyond search, spanning purchases, site visits, and time spent on content, creating new pathways for monetization. With Comet, Perplexity has officially entered the AI browser race against industry leaders like Microsoft and OpenAI. In July 2025, Microsoft announced Copilot mode in Edge with task automations and multi-tab intelligence. In the same month, OpenAI also announced that it is building and will soon release its own browser to compete with traditional players like Chrome. As of October 2025, the base version of Comet is available to the general public, and is available to Perplexity Pro users ($20 per month) and Perplexity Max ($200 per month) at higher rate limits.
Perplexity also offers a Chrome extension that integrates into the user’s browser. This extension can provide instant page summaries, enable queries directly from the toolbar, and offer a contextual understanding of the content being viewed. The Browser Company partnered with Perplexity in January 2024, integrating Perplexity into the Arc Browser as a default search engine option. In November 2024, Perplexity also released its default search extension on the Chrome Web Store.
Source: Testing Catalog
API
Perplexity offers an API platform that allows developers to embed its AI capabilities into their own applications. The API is used across industries, from sales enablement to clinical decision support, and is built to support scale, speed, and customization. At the core of the API suite is Sonar, Perplexity’s in-house model optimized for fast answers. For more advanced tasks, developers can use Sonar Pro, which supports complex queries with deeper context retrieval. The platform also includes Sonar Reasoning, powered by DeepSeek R1, for multi-step analytical tasks like market analysis or investment theses, and Sonar Deep Research, which generates report-style outputs on broad or technical topics, sometimes taking over 30 minutes for processing.
Exploration Tools
In addition to its core search capabilities, Perplexity has developed a suite of user-facing interfaces designed to help users explore, organize, and share information. These tools sit above the search layer and are tailored for different levels of engagement, from passive discovery to active research and publishing.
Labs
Launched in May 2025, Perplexity Labs is a workplace for executing larger projects that go beyond single queries. Labs can generate outputs such as reports, spreadsheets, dashboards, and simple web applications by combining Perplexity’s research capabilities with tools for web browsing, code execution, and chart or image creation. Unlike Deep Research, which typically delivers comprehensive answers in a few minutes, Labs is designed to run for longer periods, often ten minutes or more, and leverages additional tools like file generation and mini-app creation. The product reflects Perplexity’s effort to expand from delivering answers to supporting end-to-end project workflows. As of October 2025, Labs is available to Perplexity Pro subscribers.
Pages
Perplexity Pages, launched in May 2024, is a tool that helps turn research into content that is intended to be visually engaging and comprehensive. It allows users to create, organize, and share information by generating formatted articles on any topic. With features like customization for different audiences, adaptable article structures, and enhanced visuals, Pages is intended for a wide range of creators, including educators, researchers, and hobbyists. The tool aims to simplify the content creation process, enabling users to focus on effectively sharing their knowledge and publishing their work in Perplexity's expanding library of user-generated content.
Discover
Discover functions as Perplexity’s curated feed of trending queries, topics, and user-generated content. It offers a snapshot of what other users are exploring across the platform and surfaces Pages worth reading. In addition to passive browsing, Discover may evolve into a personalized recommendation layer and advertising surface as the company expands its monetization efforts. Discover Daily is a short-form AI-generated podcast launched by Perplexity in February 2024. Powered by ElevenLabs, it curates top stories from the Discover feed into 5-10 minute episodes. As of October 2025, the podcast seems to have been discontinued, as the last episode was released in March 2025.
Source: Perplexity
Spaces
Spaces is Perplexity’s collaborative layer, providing a shared workspace where multiple users can contribute queries, answers, and follow-up prompts in a single interface. It’s designed for teams or classrooms that want to explore a topic together without switching between tools. Spaces bring version control and context persistence to multi-user exploration.
Modules
Beyond search, Perplexity has added interactive modules that let users take action within the platform, such as shopping, analyzing financial data, booking travel, or tracking live events. These features are often powered by third-party integrations with providers such as Shopify, PayPal, Kalshi, and Selfbook, enabling Perplexity to combine conversational AI with structured data and basic transactions.
Perplexity Finance
In October 2024, Perplexity introduced Perplexity Finance, a tool designed to give users a range of resources for analyzing company financials, tracking stock performance, and comparing industry peers. The platform includes real-time stock data, historical earnings reports, industry benchmarks, and in-depth financial analysis.
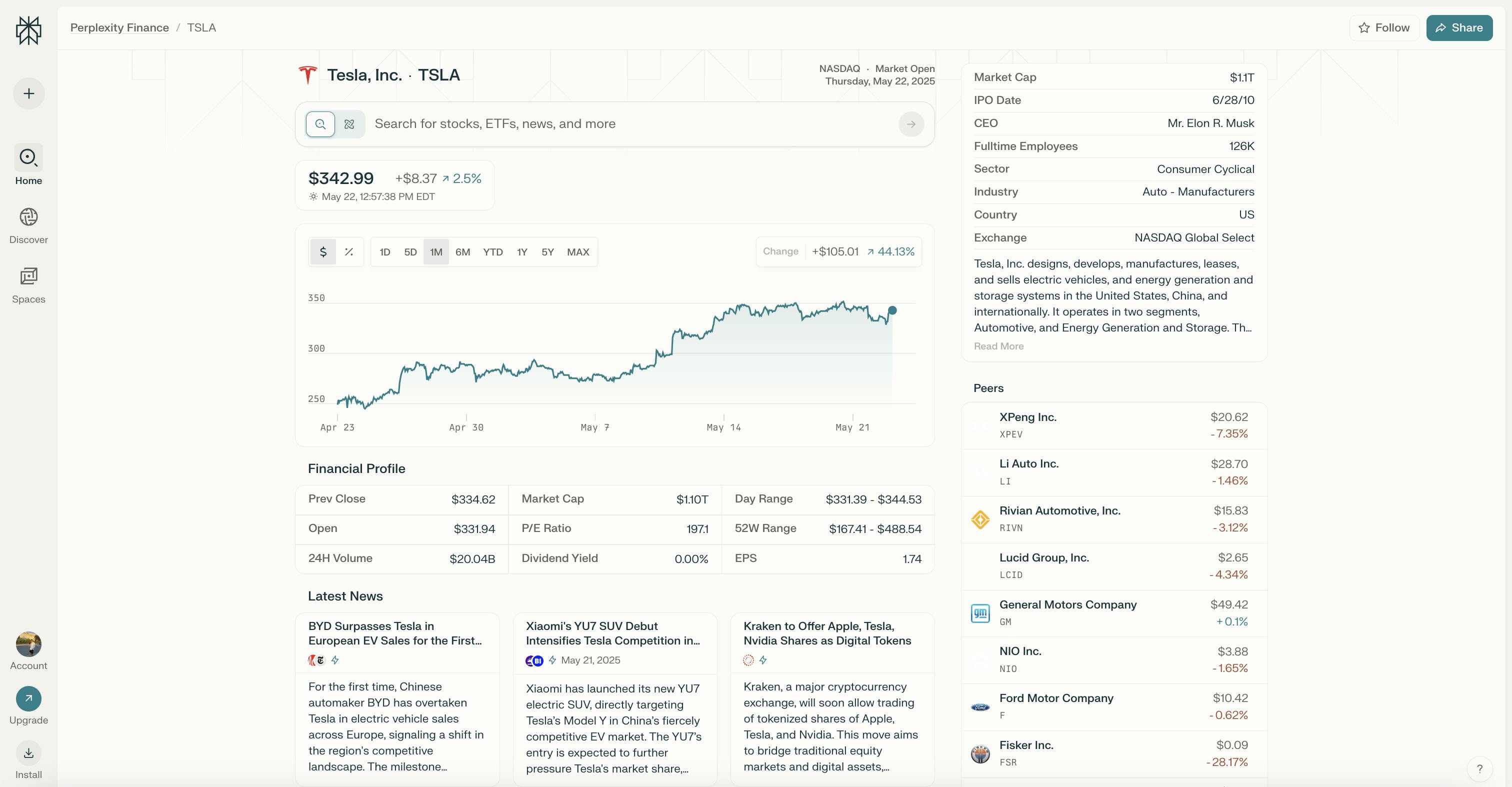
Source: Perplexity
Although Perplexity has provided limited details about how the new product works, an unverified source discovered that the data for Perplexity Finance is not from an LLM, but from Financial Modelling Prep, which claimed to be “the most accurate financial data available on the market.” Additionally, live company earnings call transcripts are powered by the Quartr API.
The tool is available to Perplexity Pro account holders, requiring a subscription of $20 per month. Users can access stock data by searching for a company name alongside the word "stock." The results feature a graph of recent stock prices and a detailed breakdown of financial information with a link to learn more about the company.
In addition to basic stock data, Perplexity Finance has formed partnerships with Crunchbase and FactSet, enabling access to proprietary data for deeper analysis. Crunchbase offers private company information, such as firmographics and financials, through an API for Enterprise Pro users. FactSet provides financial data to mutual clients through this partnership, further enhancing Perplexity’s data offerings for businesses and individual users. To access these advanced features, users need an Enterprise Pro account, which costs $40 per month per seat for smaller companies, with customized pricing for larger enterprises.
By incorporating this array of financial data, Perplexity Finance positions itself as a competitor to traditional financial data platforms, leveraging AI to streamline how users interact with and retrieve financial insights.
Shopping Hub
In November 2024, Perplexity announced the launch of an integrated shopping hub as part of the core Perplexity product. The product will reportedly “give users product cards showing relevant items in response to questions related to shopping.” The product will include integration with e-commerce platforms such as Shopify. In addition, Perplexity is planning a Merchant Program that will enable retailers to provide product information through Perplexity to enrich the context that the platform is able to provide around shopping-related questions.
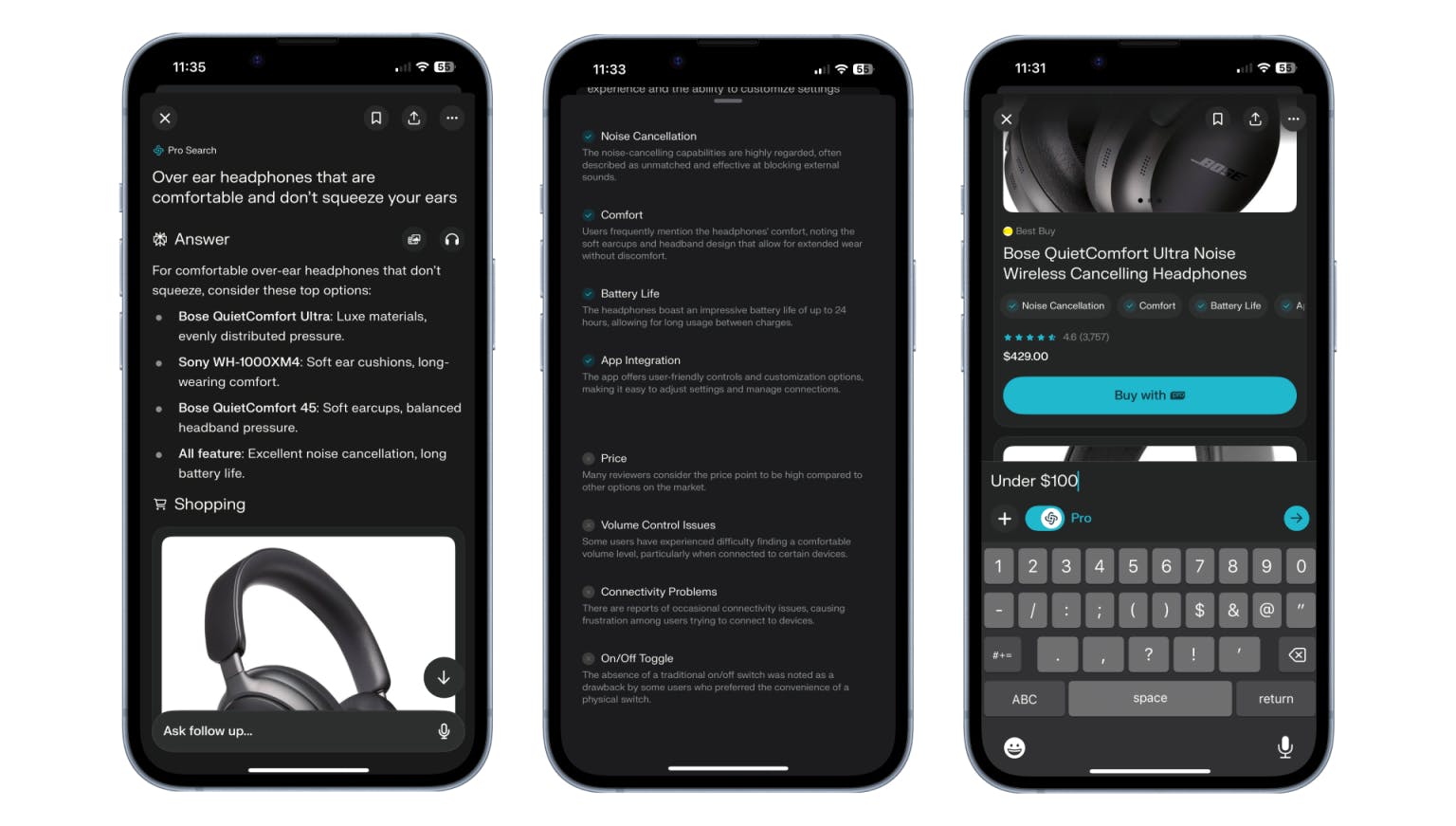
Source: TechCrunch
Beyond natural language requests for shopping information, users can also utilize Perplexity’s Snap-to-Shop feature, where users can take a picture of an item and automatically receive results on information about the product, as well as ways to purchase it. These types of features will enable Perplexity to more effectively compete with Google, whose search dominance is heavily supported by shopping use cases.
In regard to how different products are recommended by Perplexity, Srinivas gave a somewhat quizzical answer, saying, “all these things are yet to be fully understood, to be very honest with you, in terms of how the ranking works [and why] the AI is preferring to rank one over the other.” However, he did emphasize that merchants who provide data as part of Perplexity’s Merchant Program will have an “increased chance of being a recommended product.”
In May 2025, Perplexity announced a partnership with PayPal to power its in-platform checkout capabilities. Users will be able to make purchases directly within Perplexity’s interface using PayPal or Venmo. The integration is designed to make checkout seamless, with payments, shipping, and order tracking handled in the background. PayPal’s infrastructure and authentication will support these transactions, aiming to simplify commerce to a single query.
Travel
In January 2025, Perplexity launched a dedicated Travel module, allowing users to search for destinations, read reviews, compare hotel options, and book stays directly within the platform. The product is powered by integrations with Tripadvisor and Selfbook, combining travel content with booking capabilities.
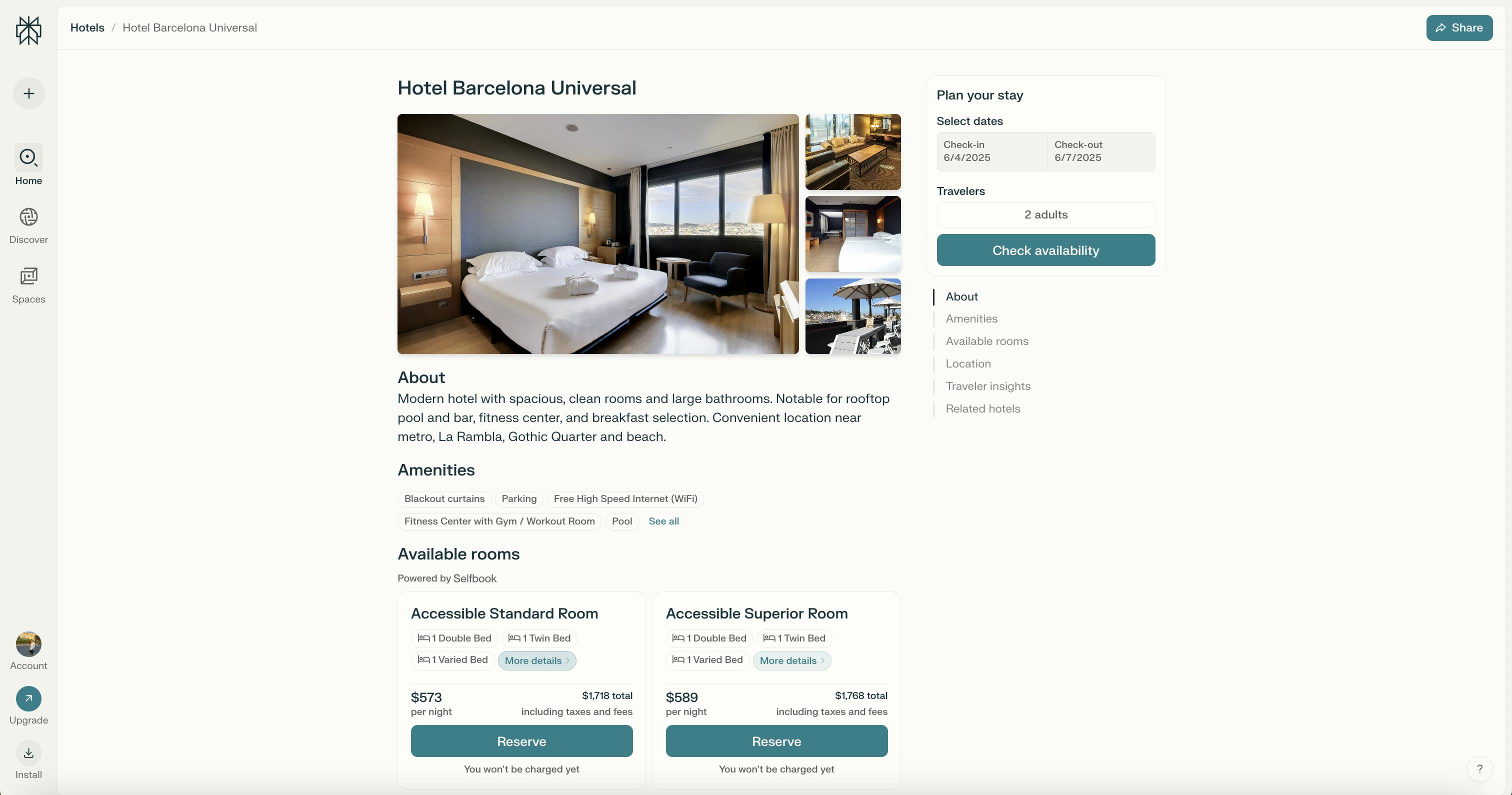
Source: Perplexity
Through its partnership with Tripadvisor, Perplexity now surfaces personalized travel recommendations backed by over 1 billion reviews, 11 million listings, and Viator’s inventory of over 300K experiences. Users can access AI-generated summaries of destinations, browse listings by rating and amenities, and reserve hotels using Selfbook’s secure checkout system—all within a single chat thread. The integration supports 22 languages and is live across 43 global markets.
Live Events
Perplexity is building out real-time coverage for live events, blending data feeds with its answer engine. The company has begun integrating structured information for sports, elections, and prediction markets, making it possible for users to stay informed and act on developments without leaving the platform.
In sports, Perplexity first partnered with Kalshi during the 2025 NCAA March Madness tournaments, displaying real-time prediction market odds for both men’s and women’s games. The goal is to expand Kalshi integrations beyond sports to other time-sensitive topics like economics and geopolitics. Users can now get summarized previews of matchups alongside probabilities, offering a deeper context than traditional sports apps or chatbots. Perplexity also launched live tracking for the Indian Premier League, NBA and other competitions, with dedicated pages for match scores, standings, and team updates.
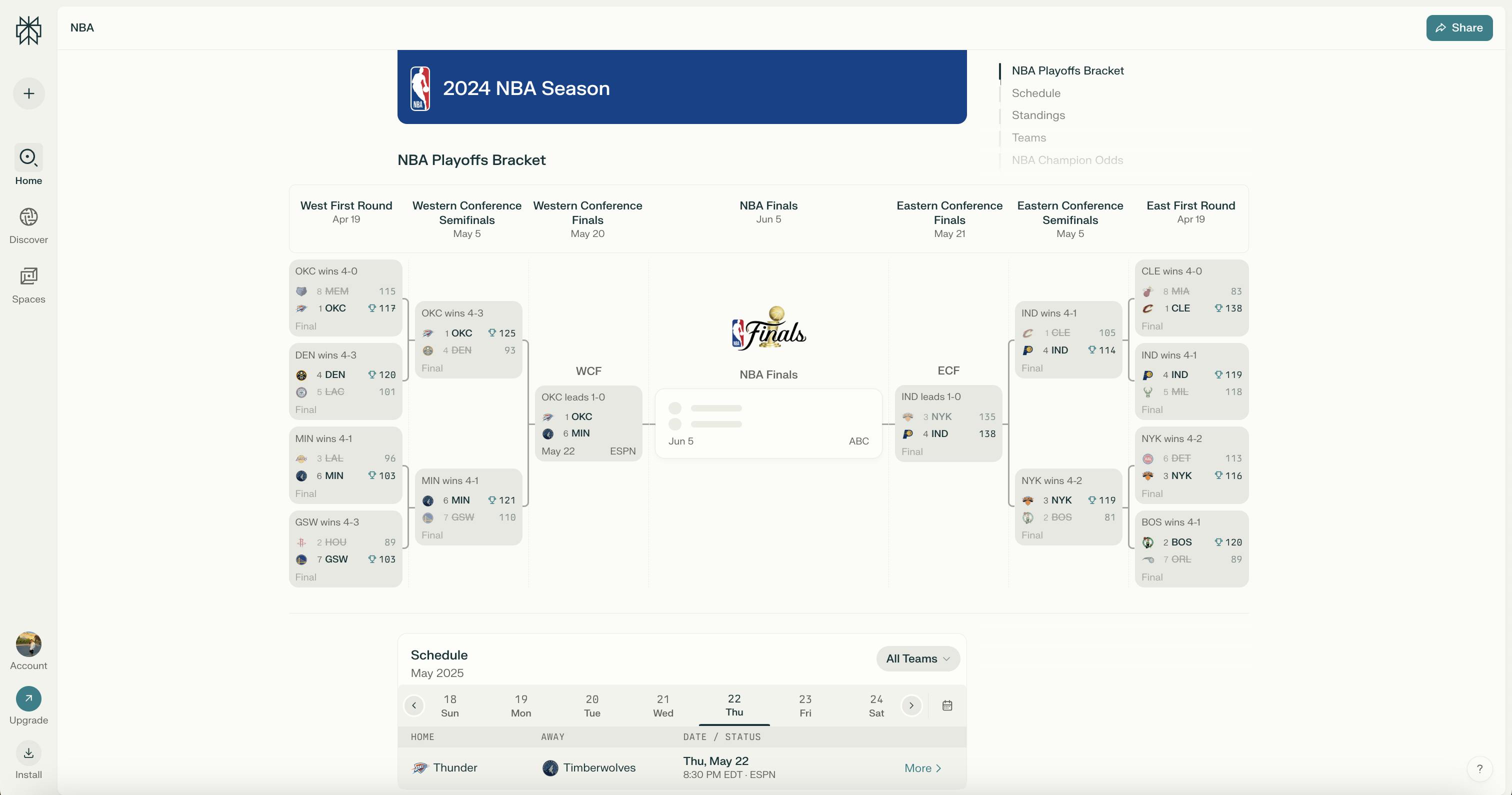
Source: Perplexity
Additionally, Perplexity has developed a dedicated Election Hub, first launched for the US presidential elections in November 2024. The hub offered live vote tallies as well as state-by-state breakdowns of results for presidential, congressional, and local races. Users could also ask election-related questions, including polling hours, candidate platforms, and ballot measure summaries, with answers grounded in verified sources.
Crypto
Perplexity established a partnership with Coinbase in July 2025 to integrate real-time crypto market data into its platform. The collaboration embeds Coinbase’s data directly into Perplexity’s large language model, beginning with the COIN50 index powering market analysis in the Comet browser. A second phase continuation of the partnership will extend this integration to Perplexity’s broader interface, allowing user queries to connect directly with live market data. Long-term, the partnership aims to enhance Perplexity AI assistants’ ability to move beyond analysis into tasks like executing trades, rebalancing portfolios, and managing staking.
Integrations
In December 2024, Perplexity announced its acquisition of Carbon, a startup focused on “connecting AI systems to external data sources.” With the capabilities of Carbon’s product, Perplexity is able to connect to “files and work messages in Notion, Google Docs, Slack, and other enterprise applications”. The new capability has been named File App Connectors and was launched in early 2025.
Market
Customer
Perplexity serves a wide range of customers, including individual users through its free and pro tiers, and organizations via its enterprise tier. In April 2025, Perplexity said it had over 30 million monthly active users, although some sources report monthly active users at 22 million in July 2025. In August 2025, Perplexity reported serving 780 million monthly queries, more than tripling from 250 million monthly queries from just over a year ago in July 2024.
Perplexity initially focused on refining its technology through a small user base on Discord. Over time, it began to offer a more comprehensive UI and product offering. In July 2024, Perplexity’s Chief Business Officer, Dmitry Shevelenk, estimated that Perplexity’s median query length was 10 words, compared to Google’s 2-3 words. According to the company’s August 2024 pitch deck, Perplexity’s user base predominantly consists of “high-income, white-collar professionals”.

Source: Perplexity
In April 2024, Perplexity launched its formal Enterprise Pro offering. This launch followed a period of early access testing with select companies across a number of industries, including Zoom, Stripe, Bridgewater, Snowflake, the Cleveland Cavaliers, Universal McCann, Thrive Global, Databricks, Paytm, ElevenLabs, HP, Vercel, and Replit. Those early adopters helped shape the enterprise solution. Through this phased approach, Perplexity has established a foundation in serving both individual and enterprise customers.
In addition to core knowledge worker users, the company’s October 2024 launch of Perplexity Finance exposed the company to a new specific user base of financial analysts, investors, equity researchers, and more. These customers typically use more specialized research tools, such as Bloomberg and FactSet, but Perplexity is attempting to bring the research process for these particular analysts into one platform.
Market Size
Perplexity is a player in the search market because it functions as an AI-powered search engine, allowing users to input queries and receive relevant search results. The global search engine market was valued at $167 billion in 2021 and is expected to grow to $529 billion by 2032, representing an 11% CAGR over the period. The rise in internet connectivity globally has significantly contributed to the growth of the search market. For instance, the share of adults using the internet in the US rose from 86% in 2015 to 95% in 2023. Likewise, digital advertising spend remains robust and continues to grow, and is expected to reach $350 billion by the end of 2023. Google is the dominant player in the search engine market, processing an estimated 14 billion queries per day in 2024, an equivalent of almost 90% of all processed queries. By contrast, ChatGPT and Perplexity processed an estimated 37 million and 14 million daily queries in the same period, respectively.
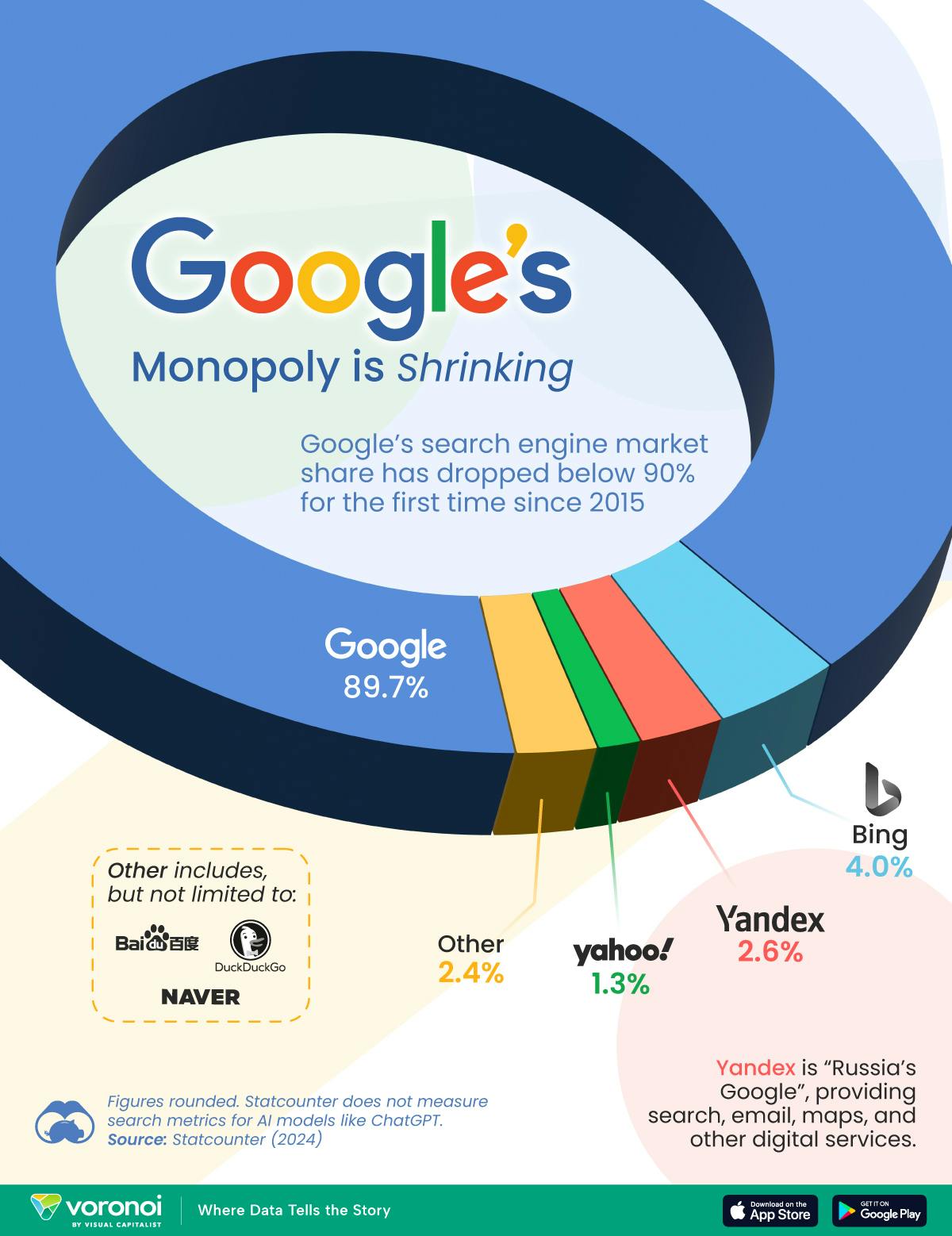
Source: Visual Capitalist
Additionally, with the development of its own models as well as its API offerings, Perplexity has also entered the generative AI market. The generative AI market was valued at $29 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 47.5% to reach $668 billion by 2030. Although much of the value of the market is being captured by leading foundation model players such as OpenAI, xAI and Anthropic, Perplexity may be able to carve out its own sizable position, especially with its focus on enterprise clients and future model offerings.
Competition
Perplexity operates in a highly competitive landscape that includes major incumbents like Google and Bing, as well as emerging AI-native platforms. Rather than relying on proprietary models alone, Perplexity’s strategy centers on product quality, speed, and trust. According to CTO Denis Yarats, its long-term edge will come from fine-tuning on user interactions, not model architecture. To overcome entrenched distribution barriers, the company is actively pursuing partnerships across hardware, telecom, and browser platforms to expand its surface area and reach users directly.
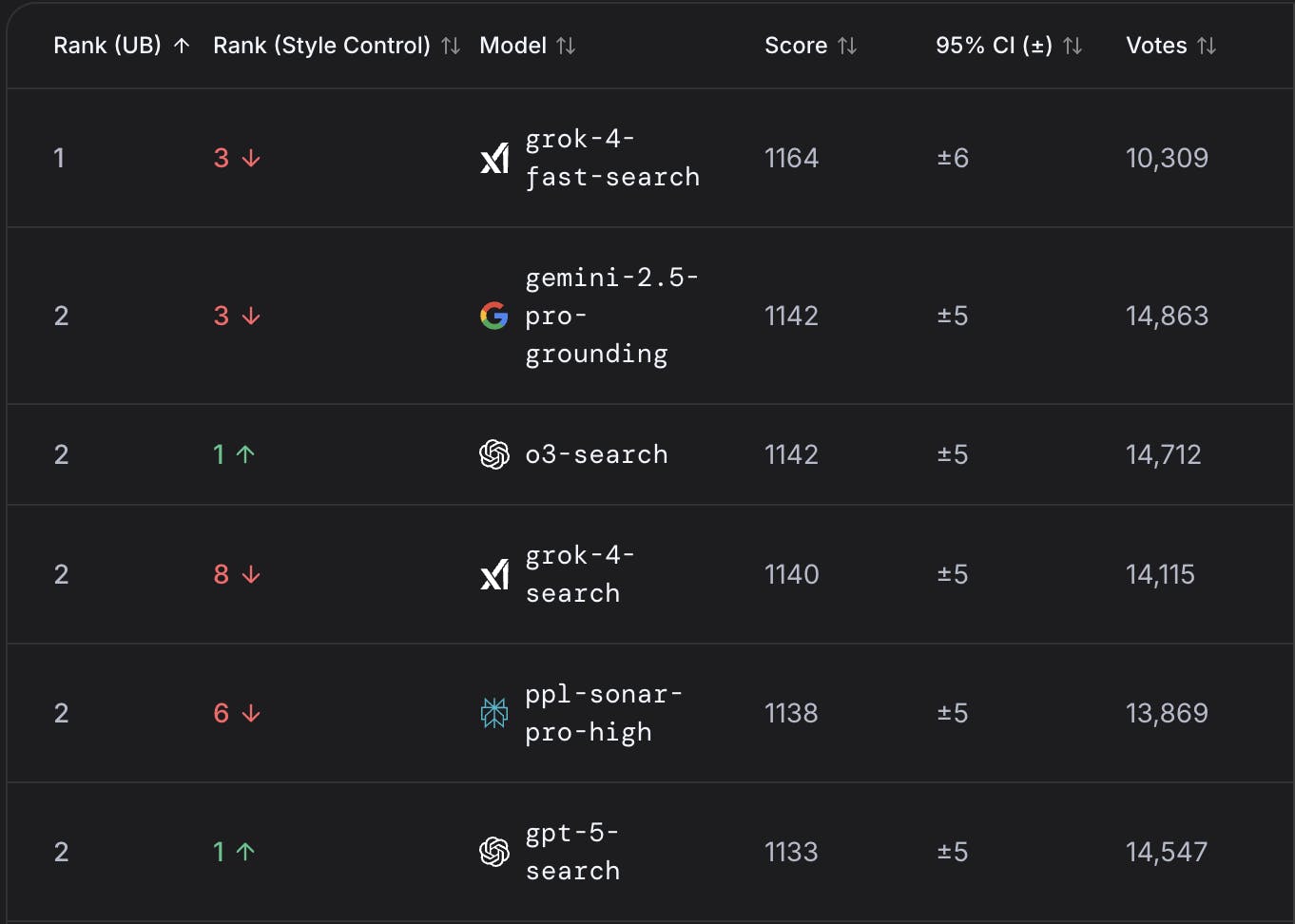
Source: LMArena
Google: As of October 2025, Google remained the dominant search engine globally, holding a market share of approximately 89.5%. It has been the leading search engine for well over a decade and answers approximately 2 trillion global searches per year. As of October 2025, Google’s market cap was $2.9 trillion. Founded in 1998 by Larry Page and Sergey Brin, Google owes much of its success to the groundbreaking PageRank algorithm, which revolutionized how search results are ranked and retrieved. Initially conceived as a research project at Stanford University, PageRank propelled Google to prominence by prioritizing web pages based on their relevance and authority rather than simply relying on keyword density. In November 2023, Google began experimenting with Generative AI in its own search product under an opt-in experience from its internal division, Search Labs.
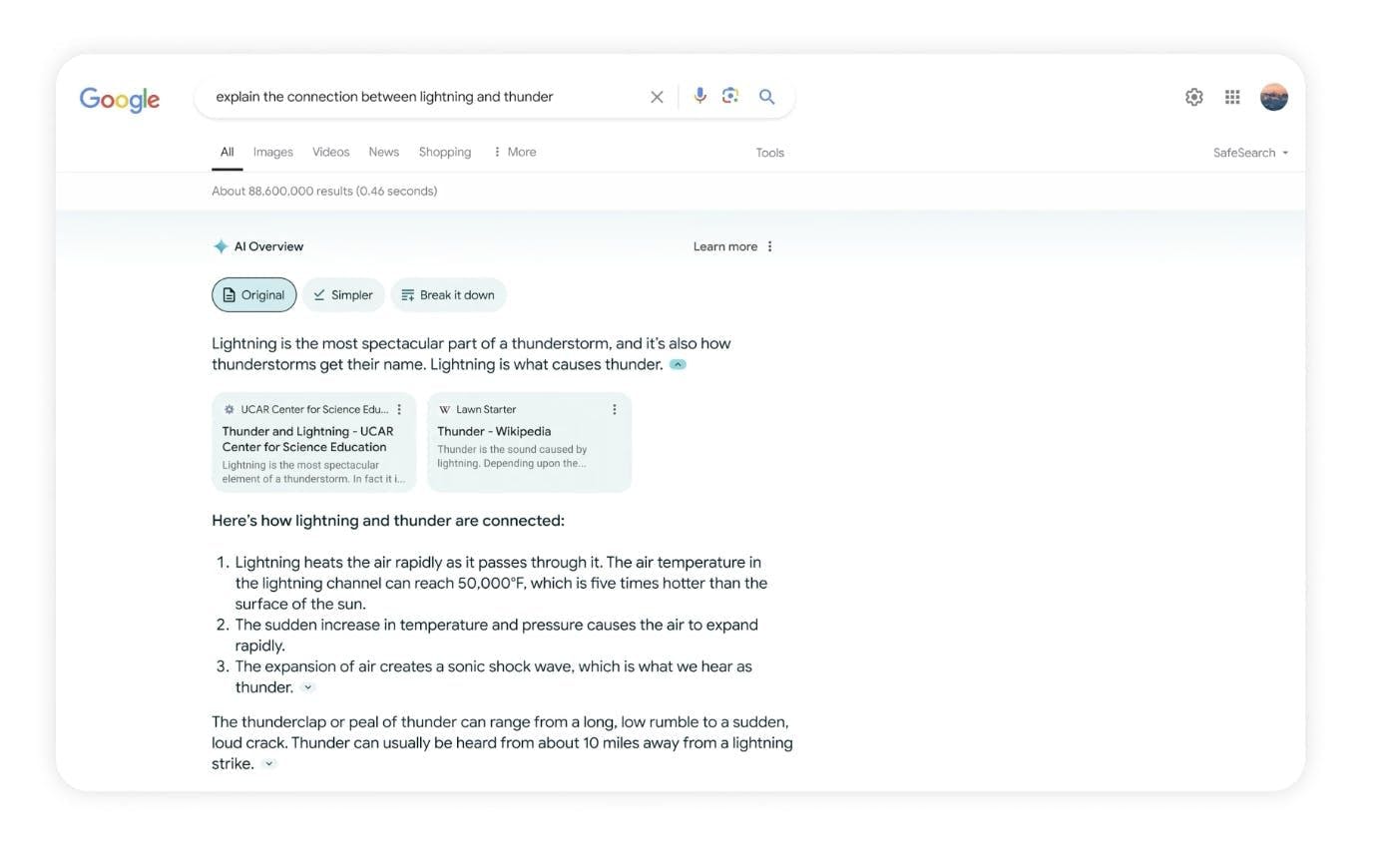
Source: Google
While Google’s AI overview feature is similar to Perplexity, including suggested questions and citations, it is worth noting that Google has received extensive criticism of the feature. The rollout has been mocked on social media, with users able to widely reproduce hallucinations on the overview feature that suggests users should eat rocks, put glue on pizza, or that dogs have played in the NBA. In each case, the answer was generated due to an over-reliance on user-generated content from blogs or Reddit, creating a larger question of what sources on the web should be treated as authoritative.
Although Perplexity and other AI-native search products also struggle with hallucinating answers, Google faces significant scrutiny and higher expectations relative to startup competitors, given the scale of its user base. Google has encountered substantial pushback with its AI releases, highlighting the innovator's dilemma that some see it currently facing. The launch of Gemini, Google's generative AI tool, was particularly criticized for its handling of racial demographics in image generation. Google admitted it had "missed the mark" after Gemini produced historically inaccurate images by overcompensating for diversity, such as depicting nonwhite individuals in contexts where they wouldn't historically appear.
In 2025, Google’s dominance in online search came under renewed regulatory scrutiny. Following a string of lawsuits filed by the DOJ and 38 state attorneys general, Judge Amit Mehta ruled that Google acted illegally to maintain its monopoly in search. Regulators argued that Google’s conduct entrenched its dominance by limiting distribution channels for rivals. “Google’s illegal conduct has created an economic goliath, one that wreaks havoc over the marketplace to ensure that—no matter what occurs—Google always wins,” the DOJ wrote in a filing in July 2025.
The DOJ’s remedy proposal called for Google to divest its Chrome browser, which regulators viewed as a critical distribution lever tying users to Google Search. At the same time, the DOJ softened earlier demands to force Google to sell off its AI investments, requiring only prior notification of future deals, and left the question of whether Android might also be spun off to future court decisions. Google has pushed back with alternative proposals, but regulators remain focused on unwinding Chrome’s role in cementing search dominance.
Against this backdrop, Perplexity submitted a $34.5 billion unsolicited all-cash bid to acquire Chrome in August 2025. Although the bid exceeded Perplexity’s own valuation, the company said that multiple funds have offered to finance the deal fully. Srinivas framed the acquisition as a way to merge Chrome’s billions of users with Perplexity’s AI-driven answer engine, creating a direct distribution channel. Perplexity’s bid also pledges to keep Chromium open source and invest $3 billion into the browser over two years.
OpenAI: Founded in 2015, OpenAI is an AI company that was originally a non-profit organization and became for-profit in 2019. The company is known for creating the Generative Pre-trained Transformers (GPT) series of AI models, which it first introduced in 2018. OpenAI has raised $78 billion in total funding as of October 2025. In March 2025, OpenAI raised $40 billion at a $300 billion valuation.
As of August 2024, both free and paid tiers of ChatGPT could browse the internet and, if prompted, provide sources for links it was pulling information from. As of August 2025, ChatGPT was estimated to have more than 700 million weekly active users, after having reached 100 million users within two months of its launch in November 2022. In April 2025, OpenAI launched a shopping feature, enabling users to make purchases directly in ChatGPT, similar to the Perplexity experience.
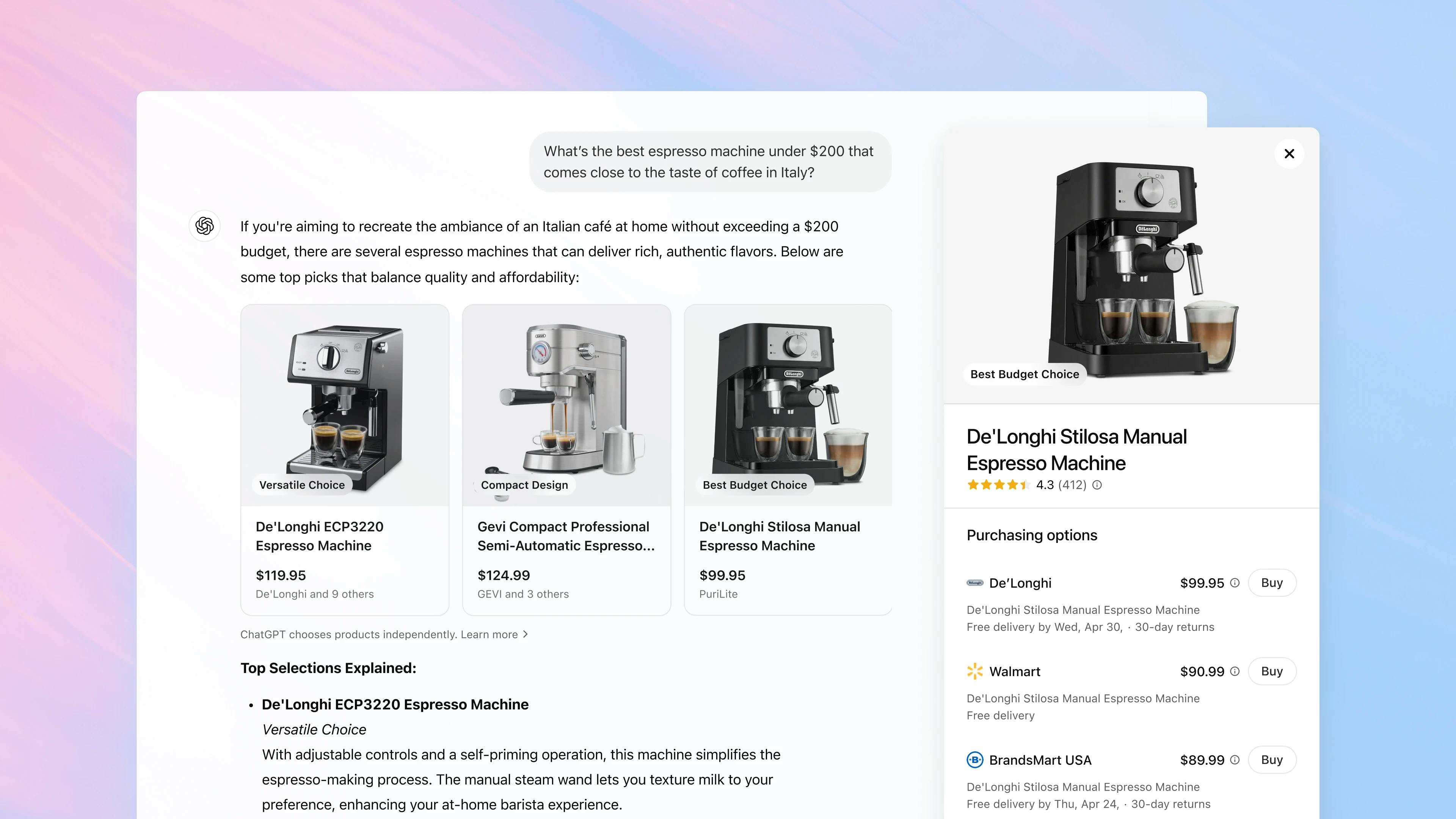
Source: OpenAI
Meta: Established in 2013, Meta AI develops the LLaMA series of open-source foundation AI models. In April 2024, Meta announced that its Meta AI assistant would be integrated into the existing product suite (Facebook, Instagram, WhatsApp) in order to bring information retrieval and LLM querying closer to the product experience for the 3.4 billion people who were daily active users on at least one Meta platform as of August 2024. As of October 2025, Meta’s market cap was $1.8 trillion.
Bing: Bing, owned by Microsoft, holds a smaller portion of the search market, with a share of about 4.0% globally as of September 2025. Despite significant investments in integrating AI into the search experience through features like Bing Copilot in 2025, Bing has struggled to significantly erode Google’s market share. Bing’s market position is bolstered by its integration into Microsoft’s products and services. As of October 2025, Microsoft’s market cap was $3.8 trillion.
You: You is a newer entrant in the search engine market that also positions itself as an AI-powered search engine. It was founded in 2020 by Richard Socher and Bryan McCann, both former employees at Salesforce, with the mission to create a more customizable and private search experience. Similar to Perplexity, You also has citation ability and uses other AI models to simplify the search feedback experience. You.com has raised a total of $100 million in funding as of September 2025.
Glean: Founded in 2019, Glean is a productivity startup that has developed a smart enterprise search assistant by indexing and understanding the context of documents from dozens of products through the use of over 100 APIs.
Perplexity’s December 2024 acquisition of Carbon made Glean a more direct competitor of Perplexity. Initially, Perplexity’s product was focused on search capabilities around information online. Carbon’s product is expected to expand Perplexity’s addressable search market to enterprise applications as well, such as “internal databases, cloud storage, or document repositories.” As of Glean’s $150 million Series F in June 2025, the company is valued at $7.2 billion and has reportedly surpassed $100 million in annual recurring revenue and grown to over 850 employees.
Business Model
Pricing & Revenue
Perplexity operates on a subscription-based freemium business model where basic functions are offered at no cost, and additional features may be added with a monthly fee. Perplexity had four pricing tiers as of October 2025.
Free: Unlimited Quick searches (searches using Perplexity’s own model that offer faster and less in-depth information on a query), personalized answers, and five Pro searches per day.
Pro: The pro tier, which costs $20 per month, offers everything in the free plan, plus 600 Pro searches per day. Pro searches use a variety of models to provide extensively researched answers with improved accuracy, like GPT-4o and Claude-3. It also allows for file uploads and a $5 monthly credit to use on Perplexity’s API.
Enterprise: In April 2024, Perplexity announced that it had developed a suite of B2B offerings designed to cater to business clients. Users of Enterprise Pro have access to team management, single sign-on integration, and increased data privacy. In addition, Perplexity noted that it has already seen enterprise adoption from Databricks, Nvidia, Zoom, and the Cleveland Cavaliers basketball team, among others. The Enterprise Pro plan has a self-serve plan for companies with fewer than 250 employees, with pricing at $40 per month or $400 per year per seat, and custom pricing for companies with over 250 employees.
Max: In July 2025, Perplexity launched its most advanced subscription tier for users who want unrestricted access to AI tools and have exclusive access to new features. In addition to features included in Pro, Perplexity Max users get unlimited use of Labs and early access to products like Comet. Additionally, Max provides access to top-tier AI models such as OpenAI’s o3‑pro and Anthropic’s Claude Opus 4, with future “frontier models” added over time, accompanied by priority support. Perplexity Max is priced at $200 per month.
In addition to its subscription services, Perplexity has expanded to generating revenue through advertising. In November 2024, Perplexity officially started experimenting with incorporating advertising into its platform. The ads will show up, as the company explains, as “sponsored follow-up questions” that appear next to generated answers and will be clearly labelled as “sponsored.” Unlike most advertising businesses that are built around user targeting and data sharing, Perplexity indicated that its ads business would still allow its AI to generate answers, as opposed to letting ad buyers customize the content. In addition, advertisers would not get any access to users’ personal data.
In April 2024, the company announced future plans to integrate ads into its platform. This move comes as a reversal of its previous stance on its website, where it had previously stated that search should be “free from the influence of advertising-driven models” (this line was removed from Perplexity’s site in March 2024). In this announcement, Perplexity’s Chief Business Officer, Dmitry Shevelenko, said, “Advertising was always part of how we’re going to build a great business.” Srinivas noted that “when ads are done right, it’s amazing, and generative AI is going to help us build even better targeting.” In October 2025, Perplexity announced that it was pausing signing new advertising clients to re-assess the business model.
Perplexity’s advertisement business has drawn cautious interest from marketers. Brands like Indeed, Whole Foods, Universal McCann, and PMG signed on as initial partners, and agencies have begun testing Perplexity’s Merchant Program, though progress has been slow and limited in scope. Media buyers cite low scale, unclear ROI, and CPM efficiency as reasons for hesitating to commit significant spend, noting that the platform is still more focused on product development than ad infrastructure. As one executive said, while Perplexity’s vision of an “agentic future” is compelling, its ad platform “still seemed very early and conceptual—not a fully formed ad business by any means.”
Expenses
As of December 2024, Perplexity had reportedly improved its gross margins from 30% in January 2024 to 75%. Some of the cost of goods sold inherent in Perplexity’s product include “cloud fees, customer service and payment processing.”
When Perplexity’s product leverages externally developed proprietary models, such as GPT-4o or Claude-3, it requires payment to AI development companies like OpenAI and Anthropic. For example, over the course of 2024, Perplexity reportedly spent between $15 million and $20 million on access to OpenAI’s models.
Another expense inherent in Perplexity’s business model is a reliance on search engine capabilities from Brave. Founded in May 2015, Brave is a search engine and web browser focused on privacy that is used by 70 million people. In addition to offering its own search engine product, Brave also provides a platform for other products offering search engine functionality. As one November 2024 overview of Brave explains:
“A true search engine, in Brave’s view, requires a web index—an organized database of webpages—and the ability to pull up-to-date results from that index. Brave says its 20-billion-page web index has screened out more spam and junk content than other indices.”
As a result, while companies like Perplexity may be claiming to offer an AI-powered search engine, its product is more accurately described as an “’answer engine’ for questions [that] relies on web data and search results” from companies like Brave. As a result, Perplexity is dependent on Brave for access to its web index and pays for that capability.
In addition to model costs and web index licensing, Perplexity is increasingly exposed to revenue share relationships with content owners. In response to concerns and even lawsuits from publishers, such as News Corp. and The New York Times Co., Perplexity agreed to establish revenue share agreements with publishers such as Time, Fortune, and the Los Angeles Times. As Perplexity scales, it may continue to bear a specific burden to share a percentage of its revenue with the original content owners of the sources being referenced in the answers generated by Perplexity’s AI platform.
Despite reporting a 60% gross margin in 2024, internal documents showed Perplexity spending at least $57 million on AI models and infrastructure in 2024, including $33 million supporting free and trial users. Instead of recognizing these as cost of revenue, Perplexity classified them as R&D expenses, boosting reported margins. Without this reclassification, its gross profit would have been negative.
Traction
Perplexity launched its flagship answer engine in December 2022. Four months later, in March 2023, the company reached 2 million monthly active users. Throughout 2023, Perplexity would grow to process half a billion queries. By January 2024, Perplexity reported that it had expanded its user base to 10 million monthly active users. As of August 2025, external reports estimate Perplexity’s active user base at 22 million and processes 780 million monthly queries. By The company has also made strides in global market penetration, particularly in India, which reached 1 million in February 2024.
As of April 2024, Perplexity was serving 169 million monthly queries and was reported to have $20 million in ARR. In terms of users, Perplexity reportedly ended 2024 with 240K subscribers to its premium service and predicted that it would double to 500K over the course of 2025. As of July 2025, Perplexity’s ARR was reportedly at $150 million, up from $35 million in August 2023, earned through premium subscriptions, sponsored follow-up questions, and APIs.
Perplexity has also attracted several major enterprise users for its Perplexity Enterprise Pro product. Notable companies include Databricks, Zoom, Hewlett-Packard, the Cleveland Cavaliers, Stripe, and Thrive Global.
In January 2025, Perplexity submitted a bid to acquire TikTok’s US operations. The proposal included a plan to merge Perplexity with TikTok US under a new company structure that would also involve additional investors and grant the US government up to 50% ownership following a future IPO. The move followed regulatory pressure on TikTok’s parent company, ByteDance, to divest TikTok’s US business or face a potential ban, and indicated Perplexity’s interest in expanding on its Discover feed and consumer offering.
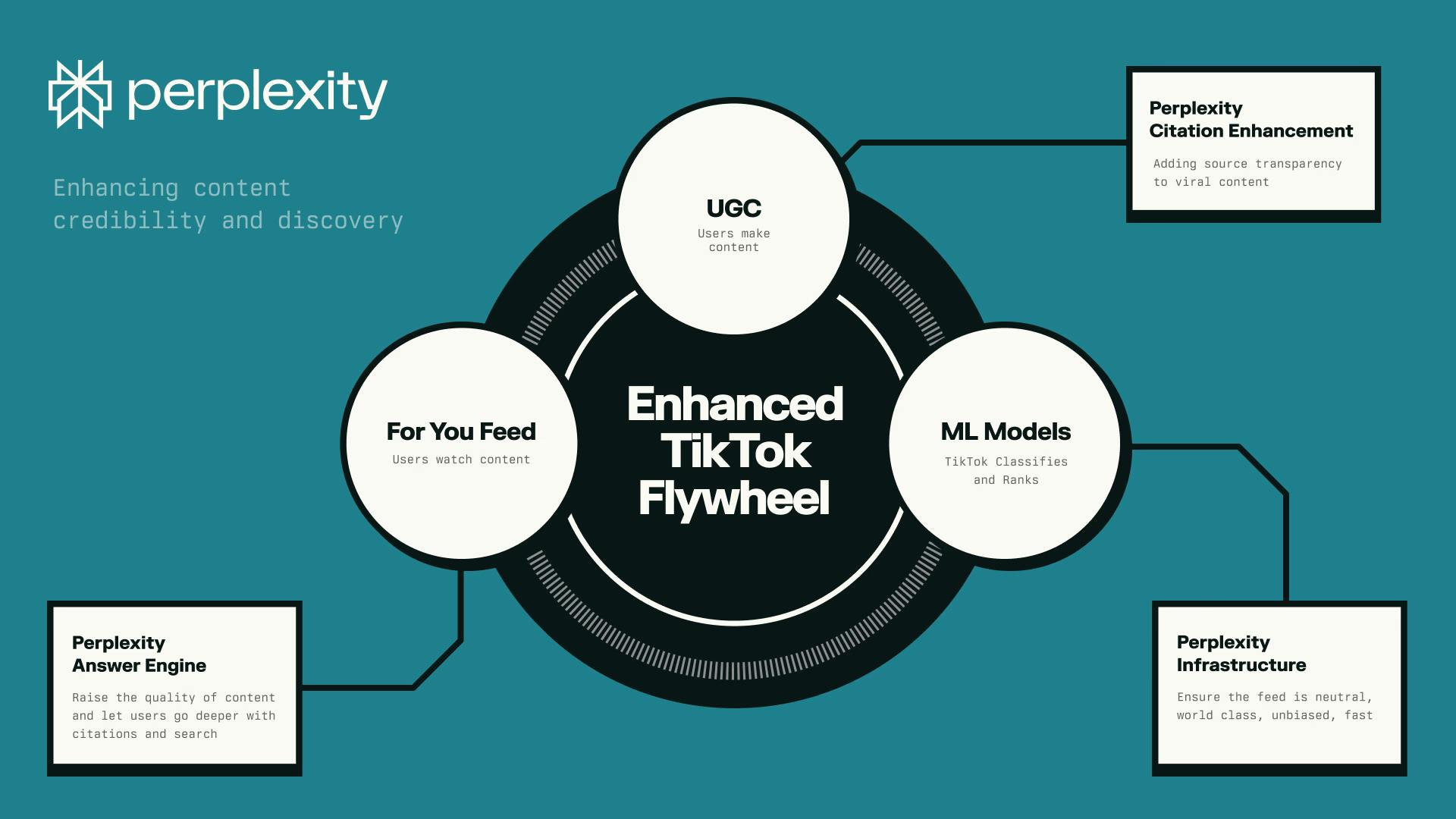
Source: Perplexity
In August 2025, Trump Media announced that it had begun beta testing Truth Search AI, a new search engine integrated into its Truth Social platform. The feature is powered through a partnership with Perplexity, which provides access to its Sonar API.
Valuation
In June 2024, Perplexity raised a $250 million round of funding, including between $10 million and $20 million from Softbank, which valued the company at $3 billion. Just six months later, Perplexity raised an additional $500 million at a valuation of $9 billion from existing investor IVP. Five months after that round, Perplexity raised another $500 million round at a $14 billion valuation led by Accel. It raised an additional $100 million in July 2025, just two months after its previous round, valuing the company at $18 billion. This round saw participation from Nvidia, SoftBank, NEA, and IVP.
As of October 2025, Perplexity had raised a total of $1.3 billion in funding, including four separate rounds in 2024 alone. Perplexity’s $18 billion valuation represents a 120x ARR multiple on its reported annualized revenue of $150 million in July 2025.
Several of Perplexity’s existing investors include Jeff Bezos, NVIDIA, Tobi Lutke, Elad Gil, Nat Friedman, Naval Ravikant, Andrej Karpathy, NEA, Nvidia, Balaji Srinivasan, and Austen Allred. In addition to funding rounds, Perplexity had reportedly received acquisition interest from several larger companies, including X, OpenAI, and Notion, in the first half of 2023.
Key Opportunities
Shifting Paradigms in Internet Search
The exponential growth of data on the internet has necessitated the evolution of information retrieval technologies. Approximately 149 zettabytes of data were created globally in 2024, with projections reaching up to 394 zettabytes by 2028. This massive influx of information comes as traditional search engines are increasingly returning low-quality, highly search engine-optimized content. The deterioration in the quality of search results, coupled with the physical displacement of top organic links to lower positions on the search pages, has led to consumer dissatisfaction and a shift towards alternative platforms like Reddit and TikTok for information retrieval.
In response to these challenges, advancements in AI have paved the way for more sophisticated AI-driven platforms that benefit from big data. Transformers, which utilize self-attention mechanisms, allow for the parallel processing of data sequences, significantly enhancing the speed and efficiency of training LLMs. These models, exemplified by the adoption and growth of ChatGPT, have shown remarkable capabilities in generating human-like text and processing vast amounts of information quickly. However, they suffer from drawbacks such as expensive training costs and the tendency to produce factually incorrect “hallucinations.” Perplexity represents a new approach in this landscape, combining real-time web searches with the processing power of LLMs, and can benefit by continuing to position itself as encompassing the best of both worlds.
Customer Expansion
Perplexity’s launch of Enterprise Pro, a service tailored for business clients, in April 2024 marked its entry into the B2B sector. This move into the enterprise market represents a significant opportunity for growth, diversifying the company's revenue streams beyond its consumer base and Pro subscriptions.
Additionally, the company announced plans for global expansion in April 2024, with partnerships with major telecom companies, SoftBank in Japan, and Deutsche Telekom in Germany. The collaboration with these telecom providers is expected to distribute and market Perplexity's services to over 365 million additional users, spanning both mobile and broadband sectors. Perplexity can continue to expand to encompass enterprise customers and partnerships like those with Softbank to differentiate itself against other AI answer engines and search engines in a competitive market.
In December 2024, Perplexity CEO Arvind Srinivas met with Indian Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi. India likely represents a massive market opportunity for Perplexity, especially given that some reports indicate that nearly 25% of Perplexity’s users may be based in India.
Partnership with Device Manufacturers
Major smartphone manufacturers are racing to embed AI in their devices. Google has already invested heavily in AI integrations with its launch of the Pixel 10 series. Powered by the Gemini AI model and the Tensor G5 chip, Pixels provide real-time contextual actions, voice translation, personalized health coaching, and camera guidance. Viewed as lagging in AI capabilities, Apple and Samsung are both actively integrating AI in their devices, and both have expressed interest in Perplexity.
Since April 2025, Samsung has begun discussions with Perplexity on AI collaboration. By June 2025, the discussions had advanced significantly, with Samsung reporting a wide-reaching deal to invest in Perplexity, preloading its Sonar LLM in upcoming Samsung devices, and integrating its search functionality into the Samsung browser. The Perplexity integration is expected to materialize through the upcoming Galaxy S26 launch in the first half of 2026. If the integration proves effective for users, Samsung could expand its partnership and integrate Perplexity across its suite of upcoming devices as a part of its effort to reduce dependency on Google.
Apple has reportedly been interested in a major acquisition of Perplexity. Bloomberg revealed that in June 2025, Apple’s M&A Chief, Adrian Perica, discussed acquiring Perplexity for an estimated $25 to $30 billion, roughly doubling Perplexity’s valuation then at $14 billion. Apple is also reportedly working with multiple LLM providers, including Anthropic and OpenAI, to power Siri to pursue an AI orchestration strategy of relying on each partner to play a differentiated role. Even if an acquisition does not happen, Perplexity could still become a major AI partner for Apple’s 2.2 billion active devices. Such a partnership could solidify Perplexity’s position as the frontier search model, invite a large investment, and generate continuous revenue.
Key Risks
Foundational Model Improvements
From 2024 to 2025, foundational LLMs have made notable strides in reducing hallucinations and improving accuracy. For example, OpenAI’s GPT-5 model is ~45% less likely to contain factual errors compared to GPT-4o and ~80% less than GPT o3 when thinking. Google’s Gemini 2.5 Pro also improved with Vertex AI Search by including response grounding against enterprise and web corpora, pushing down hallucination rates. LLMs are incorporating and improving techniques like retrieval-augmented generation and structured self-checking through Chain-of-Verification, which have successfully reduced factual errors by conditioning responses on retrieved evidence and verifying drafts before finalizing outputs. These techniques are increasingly being used in LLMs’ dedicated web query functionalities, like ChatGPT’s Search.
When compared with Perplexity’s Sonar model, the foundational model providers have improved slightly. LMArena’s Search ranking as of October 2025 places Perplexity’s models tied for second and tied for ninth, behind only grok-4-fast-search.
Copyright Issues
In October 2024, News Corp’s Dow Jones (publisher of the Wall Street Journal) and the New York Post filed a lawsuit against Perplexity. Accused of copyright infringement, Perplexity is alleged to have engaged in unauthorized copying of publishers' content to drive traffic to its platform while bypassing the sources, leading to potential revenue losses for publishers.
If the court rules in favor of News Corp, Perplexity could face statutory damages: up to $150K for each infringement, alongside actual damages and lost profits claims. This could not only strain its financial resources but also harm its reputation, complicating its efforts to raise new funding. Furthermore, this legal action and similar copyright concerns from other major publishers could lead to a broader industry backlash against its practices. In an October 2024 interview at the WSJ Tech Conference, Srinivas replied to the allegations by saying:
“I’m here to make it very clear that I would love to have a commercial contract. And regardless of Wall Street Journal alone, we have a select publisher program that we announced months ago where we clearly said we’re going to do advertising on Perplexity, and whenever we make advertising revenue, we’re going to share that revenue with the content publishers in a manner inspired by Spotify, where the creators are still getting paid as long as Spotify keeps growing.”
The copyright infringement claims have been an ongoing concern for Perplexity. This lawsuit comes after The New York Times sent Perplexity a cease and desist, Forbes accused the company of stealing its reporting, and Wired accused it of illicitly scraping its site. In August 2025, Japan’s Yomiuri Shimbun, one of the world’s largest news newspapers, is reported to be suing Perplexity for $15 million for “free-riding” on its content. The UK’s BBC is also seeking an injunction for citing its sources verbatim, demanding financial compensation.
The legal implications of AI tools summarizing articles are murky. Perplexity’s head of business, Dmitry Shevelenko, compared Perplexity’s summaries to journalists incorporating information from other sources to support their own reporting, and summaries, by themselves, aren’t necessarily illegal. According to US copyright law, “it is permissible to use limited portions of a work, including quotes, for purposes such as commentary, criticism, news reporting, and scholarly reports.” However, AI tools like Perplexity can generate these summaries much faster than reporters incorporating outside information in their stories.
Facing similar issues, OpenAI has signed licensing deals with at least seven prominent media companies, helping it navigate the complicated relationship between generative AI and publishers. Similarly, in July 2024, Perplexity followed suit, announcing several revenue-sharing agreements with media companies such as “Time, Fortune, [and] WordPress.com-owner Automattic.” Later, in December 2024, Perplexity added properties such as “the Los Angeles Times, Blavity, The Independent, Prisa Media (the leading Spanish-language media brand), Lee Enterprises (owners of local newspapers in 73 markets),” and others. The arrangement aligns incentives better by ensuring that when Perplexity earns revenue on specific results, the publishers who were referenced in that content will earn a share.
Jessica Chan, Head of Perplexity’s publishing partnerships, says Perplexity is committed to becoming a partner, not a threat, to the publishing industry. “Our success is tied to a thriving journalism and digital publishing ecosystem, because we know these journalists produce these high-quality, verified facts,” Chan says. “We need the continual production of that type of information. There is really no world in which Perplexity is successful but publishers are not.”
Despite the ongoing legal battles and budding content partnerships, one report found that Perplexity was still scraping and displaying non-partnership paywalled content as recently as late October 2024. In addition, Perplexity has opted not to let partners determine how their content appears in search results, unlike OpenAI’s more flexible approach. Overall, this is a situation where technology has outpaced current regulatory frameworks as of October 2025, and the outcome of News Corp’s lawsuit will likely play a large role in shaping the future relationship between media and generative AI companies.
Web Crawler Usage
In August 2025, Cloudflare accused Perplexity of using undeclared “stealth” crawlers that obscured their identity to bypass network blocks and ignore robots.txt restrictions. The company alleged that Perplexity repeatedly modified user agents, impersonated Chrome traffic when declared crawlers are blocked, and shifted ASNs to avoid detection, behaviour that led Cloudflare to de-list Perplexity as a verified bot.
Meanwhile, Perplexity and some defenders argue that AI agents differ fundamentally from traditional crawlers, which fetch only user-requested content in real time rather than stockpiling entire websites. “I WANT perplexity to visit any public content on my behalf when I give it a request/task!” wrote one person in response to Cloudflare calling out Perplexity. Perplexity argued that “user-driven fetching” is more similar to an agent gathering sources on behalf of a specific human inquiry, not an automated web scraper. It also punched back against Cloudflare by arguing that it is “fundamentally inadequate for distinguishing between legitimate AI assistants and actual threats” and that Cloudflare must not be the gatekeeper for the open web.
The episode also underscores a broader tension: with bots accounting for over 50% of all web traffic in 2025, AI crawlers contribute to 16% of all known-bot impressions in 2024, and Gartner projecting a 25% drop in search engine volume by 2026, websites face a dilemma between protecting content and enabling AI assistants that many users expect to act on their behalf.
It is difficult to predict how the internet business model will shake out, although a restructuring is likely. During this transitional phase, the optics of evading technical safeguards expose Perplexity to certain reputational risk and possible regulatory scrutiny. As Cloudflare pointed out, OpenAI’s crawlers have clearly outlined rules, respect robots.txt files, and stop crawling when disallowed with no additional follow-up crawls with undeclared agnates or third-party bots. If Perplexity is seen as unethical by infrastructure providers or the broader internet community, a decrease in user trust and regulatory pressure could become an emerging risk.
Scalability of Ads Business
Perplexity’s relationship with advertising has shifted significantly over its life. While the company had previously stated that search should be “free from the influence of advertising-driven models,” it later announced future plans to integrate ads into its platform. Perplexity’s Chief Business Officer, Dmitry Shevelenko, even went as far as to say, “advertising was always part of how we’re going to build a great business.” In November 2024, Perplexity began testing ads in its product.
While the format of Perplexity’s ads is similar to Google’s with “sponsored answers” appearing next to generated ones, Perplexity has significantly limited the customizability of these ads by limiting advertisers in terms of both editorial control over the sponsored content and advertisers’ access to user data in order to better target their ad efforts. As a result, many marketing analysts express concerns about the quality of the product.
First, Perplexity represents a significantly smaller user base. For reference, Perplexity reported 20 million queries per day as of December 2024. Each query would likely represent one ad placement. For comparison, Google sees 8.5 billion searches each day. Second, Perplexity’s audience is very specific, and skewed towards “educated, high-income professionals who may be in senior leadership at their companies.” This has led Perplexity to price its ad inventory at a premium to Google’s more generalized audience. Finally, Perplexity’s audience may be geographically quite skewed as well, with potentially 50% of its users being in India or Indonesia.
On top of all of this, Perplexity is reportedly not sharing user data with advertisers, which will make targeting specific ad campaigns much more difficult. All of this means that the risk for Perplexity will be whether it can scale an audience base quickly enough to attract advertisers before more traditional platforms, like Google or OpenAI, can build similar functionality that is more attractive to advertisers.
Summary
The rapid growth in online data has challenged traditional search engines. Studies reveal deteriorating search result quality, with users sometimes feeling misled. Meanwhile, advancements in natural language processing, particularly the transformer architecture, have led to advancements in AI with the advent of LLMs. Perplexity, founded in 2022, leverages real-time web searches combined with LLMs to provide sourced answers in a conversational format, intended to address issues like misinformation and inaccurate answers. This approach aims to transform the search experience by prioritizing transparency and reliability and represents a shift from traditional search engines towards AI-driven, interactive search solutions.